Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2009;21(2):197-203
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2009000200013
The acute respiratory distress syndrome is the clinical presentation of acute lung injury characterized by diffuse alveolar damage and development of non-cardiogenic pulmonary edema due to increased pulmonary alveolar-capillary membrane permeability. Alveolar recruitment maneuvers and prone position can be used in the treatment of acute respiratory distress syndrome. The objective of this review of literature was to identify possible benefits, indications, complications and care of the associated recruitment maneuvers and prone position for treatment of the acute respiratory distress syndrome. This national and international scientific literature review was developed according to the established criteria for searching the databases MedLine, LILACS, SciElo, PubMed, Cochrane, from 1994 to 2008 in Portuguese and English, with the key words: acute respiratory distress syndrome, alveolar recruitment maneuver and prone position. Despite advances in the understanding of acute respiratory distress syndrome pathophysiology, mortality is still expressive. Alveolar recruitment maneuvers and prone position significantly contribute to treatment of acute respiratory distress syndrome patient aiming to improve oxygenation and minimizing complications of refractory hypoxemia and reduction of pulmonary compliance. However,as there are few studies in literature associating alveolar recruitment maneuvers and prone position for treatment of acute respiratory distress syndrome, additional research and evidences of clinical application are required.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2009;21(1):80-88
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2009000100012
Pneumonia is the most common nosocominal infection in intensive care units and mechanical ventilation is a significant factor associated to its development. The objective of this study was to describe the impact of the open and closed tracheal suction systems on the incidence of ventilation-associated pneumonia. A search in the Pubmed database was performed to identify randomized controlled trials, published from 1990 to November 2008. Nine studies were included. Of the studies reviewed, seven did not disclose any significant advantages of using the closed system when compared to th e open, whereas two reported that use of the closed system increased colonization rates but not incidence of ventilation-associated pneumonia and one observed that use of the closed system did not increase colonization of the respiratory tract but reduced the spread of infection resulting in decreased sepsis rates. Only two studies found a reduction in the incidence of ventilation-associated pneumonia with use of the closed system, and one revealed a 3.5 times greater risk of developing this infection with the open system. Results suggest that the impact of the open and closed tracheal suction system is similar on development of ventilation-associated pneumonia, choice of the suction system should therefore be based on other parameters. While the closed system increases risk of colonization of the respiratory tract, but has the advantages of continuing mechanical ventilation and lessening hemodynamic impairment.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2008;20(4):325-330
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2008000400002
OBJECTIVES: Sedation scores are important tools for use in pediatric intensive care units. The Comfort-Behavior scale is a valid method for the assessment of children although it is considered an extensive scale. The motor activity assessment scale is validated for an adult population. We considered it simpler then the one above and suitable for application in children. None of these scores had been translated into Portuguese. Our objective was to apply both scales in Portuguese to a pediatric population under mechanical ventilation. Secondary objectives were to evaluate the sedation level of children on mechanical ventilation in tertiary pediatric intensive care units and to compare the Comfort- Behavior and motor activity assessment scales in this population. METHODS: After translating the scales into Portuguese, both were simultaneously applied to 26 patients by 2 pediatricians. Each scale was applied 116 times in total. RESULTS: The intraclass correlation coefficient was 0.90 (0.85 - 0.93 CI 95%) for the Comfort-Behavior and 0.94 (0.92 - 0.96 CI 95%) for the motor activity assessment scale. When applying the Comfort-Behavior scale, the Crombach's alpha was 0.81 for observer A and 0.92 for observer B. The Spearman coefficient was 0.86 for observer A and 0.91 for observer B. These patients were found to be deeply sedated, showing low values in both scales. CONCLUSIONS: The scales were successfully translated into Portuguese and both were adequate to assess pain and sedation in the pediatric population under mechanical ventilation. Sedation level was high in this sample of applications.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2008;20(4):344-348
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2008000400005
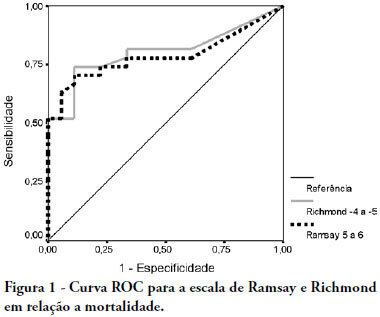
OBJECTIVE: The main purpose of this study was to compare performance of the Ramsay and Richmond sedation scores on mechanically ventilated critically ill patients, in a university-affiliated hospital. METHODS: This was a 4-month prospective study, which included a total of 45 patients mechanically ventilated, with at least 48 hours stay in the intensive care unit. Each patient was assessed daily for sedation mode, sedative and analgesic doses and sedation level using the Ramsay and Richmond scores. Statistical analysis was made using Student's t-test, Pearson's and Spearman's correlation, and constructing ROC-curves. RESULTS: A high general mortality of 60% was observed. The length of sedation and daily dose of medication did not correlate with mortality. Deep sedation (Ramsay > 4 or Richmond < -3) was positively correlated with probability of death with an AUC > 0.78. An adequate level of sedation (Ramsay 2 to 4 or Richmond 0 to -3) was sensitively correlated with probability of survival with an AUC > 0.80. A low level of sedation was observed in 63 days evaluated (8.64%), and no correlation was found between occurrence of agitation and unfavorable outcomes. Correlation between Ramsay and Richmond scores (Pearson's > 0.810 - p<0.0001) was good. CONCLUSION: In this study, Ramsay and Richmond sedation scores were similar for the assessment of deep, insufficient and adequate sedation. Both have good correlation with mortality in over sedated patients.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2008;20(3):313-317
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2008000300015
Anesthetic management of patients with severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease is extensively discussed, due to the high rates of complications in this subtype of patients submitted to medium and high complexity surgical procedures. The objective of this study is to report use of noninvasive positive pressure mechanical ventilation - bilevel positive airway pressure - and spinal anesthesia in a patient with severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease during total hip arthroplasty. An 81 year old, male patient with severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (GOLD 4) was submitted to total hip arthroplasty due to a femoral bone fracture under spinal anestesia and noninvasive positive pressure mechanical ventilation-bilevel positive airway pressure with expiratory pressure of 7 cmH2O, inspiratory pressure of 15 cmH2O and O2 flow of 3 L/min. During the procedure, the patient had one episode of bronchospasm that was promptly reverted pharmacologically with no complications in the postoperative period. The combination of less invasive anesthetic and ventilation techniques is easy to apply and may be useful in the perioperative management of patients with high anesthetic morbidity. Interaction between clinical, surgical and anesthetic teams for these cases is very important to reduce the mortality associated with extensive procedures in severe patients.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2008;20(3):254-260
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2008000300008
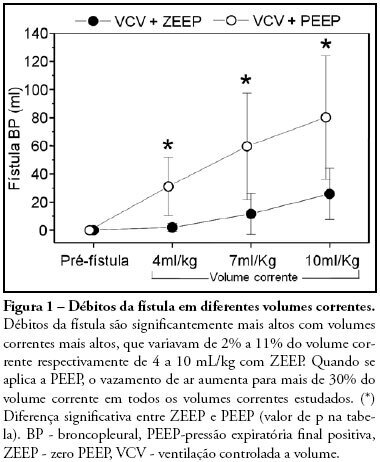
OBJECTIVES: The present study was designed to identify the effect of positive end expiratory pressure (PEEP) and the ideal pulmonary tidal volume to ventilate animals with a surgically produced bronchopleural fistula, aiming to reduce fistula output without affecting gas exchange. METHODS: Hemodynamic and respiratory assessment of gas exchange was obtained in five, healthy, young, mechanically ventilated Large White pigs under volume controlled ventilation with FiO2 of 0.4 and an inspiration:expiration ratio of 1:2, keeping respiratory rate at 22 cpm. A bronchopleural fistula was produced by resection of the lingula. Underwater seal drainage was installed and the thorax was hermetically closed. Gas exchange and fistula output were measured with the animals ventilated sequentially with tidal volumes of 4 ml/kg, 7 ml/kg and 10 ml/Kg alternating zero of positive end expiratory pressure (ZEEP) and PEEP of 10 cmH2O, always in the same order. RESULTS: These findings are attributed to reduced alveolar ventilation and ventilation/perfusion abnormalities and were attenuated with larger tidal volumes. PEEP increases air leak, even with low volume (of 2.0 ± 2.8mL to 31 ± 20.7mL; p= 0.006) and decreases alveolar ventilation in all tidal volumes. Alveolar ventilation improved with larger tidal volumes, but increased fistula output (10 mL/kg - 25.8 ± 18.3mL to 80.2 ± 43.9mL; p=0.0010). Low tidal volumes result in hypercapnia (ZEEP - Toneloto MGC, Terzi RGG, Silva WA, Moraes AC, Moreira MM 83.7± 6.9 mmHg and with PEEP 10 - 93 ± 10.1mmHg) and severely decreased arterial oxygen saturation, about of 84%. CONCLUSIONS: The tidal volume of 7 ml/Kg with ZEEP was considered the best tidal volume because, despite moderate hypercapnia, arterial oxygen saturation is sustained around 90%, alveolar ventilation improves and the fistula output is reduced when compared with a tidal volume of 10ml/Kg. A low tidal volume results in hypercapnia and severe desaturation. Finally, at any tidal volume, PEEP increases the fistula leak and decreases alveolar ventilation.