Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2016;28(4):413-419
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20160074
To evaluate the incidence of agitation in the first 7 days after intensive care unit admission, its risk factors and its associations with clinical outcomes.
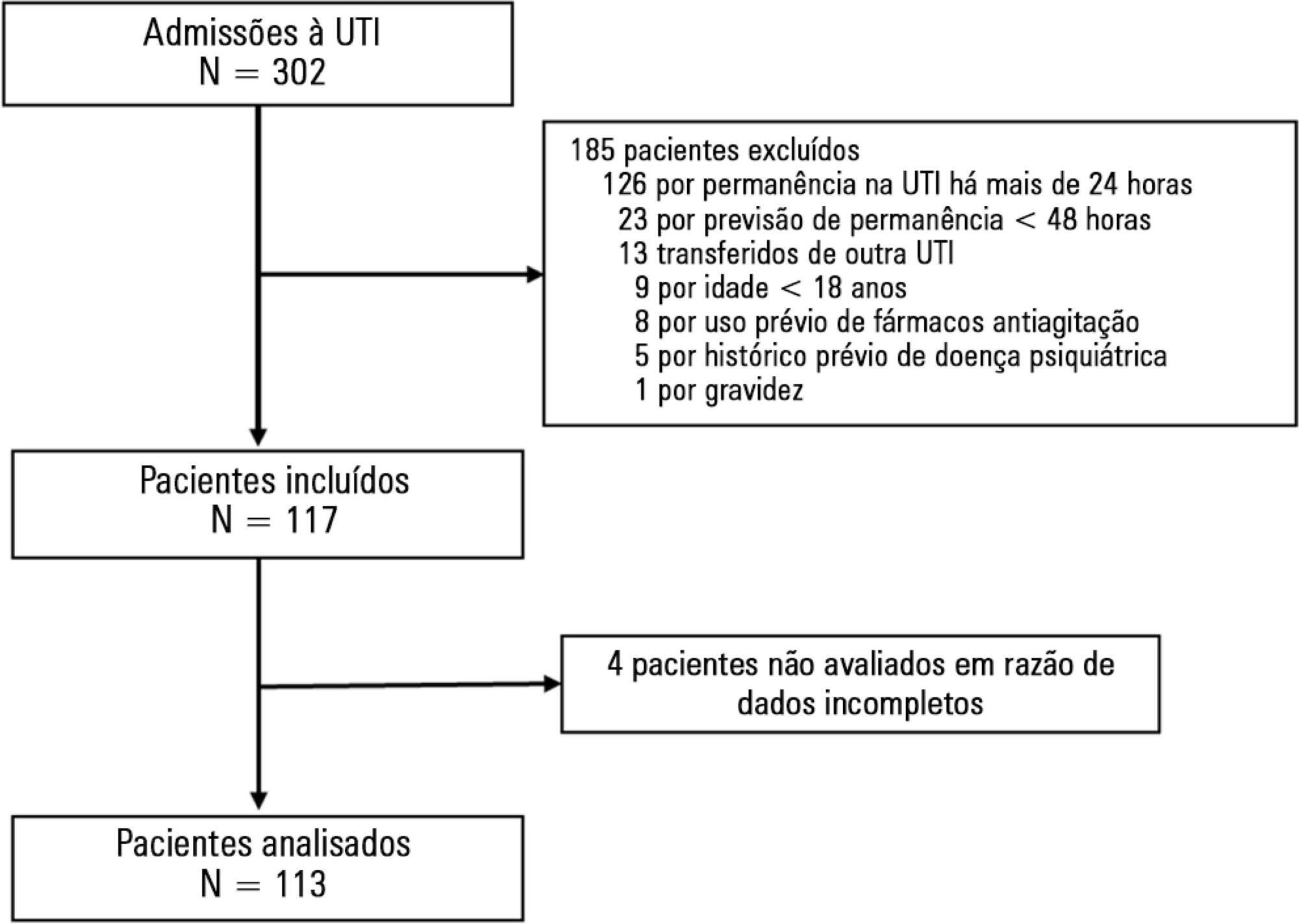
This single-center prospective cohort study included all patients older than 18 years with a predicted stay > 48 hours within the first 24 hours of intensive care unit admission. Agitation was defined as a Richmond Agitation Sedation Scale score ≥ +2, an episode of agitation or the use of a specific medication recorded in patient charts.
Agitation occurred in 31.8% of the 113 patients. Multivariate analysis showed that delirium [OR = 24.14; CI95% 5.15 - 113.14; p < 0.001], moderate or severe pain [OR = 5.74; CI95% 1.73 - 19.10; p = 0.004], mechanical ventilation [OR = 10.14; CI95% 2.93 - 35.10; p < 0.001], and smoking habits [OR = 4.49; CI95% 1.33 - 15.17; p = 0.015] were independent factors for agitation, while hyperlactatemia was associated with a lower risk [OR = 0.169; CI95% 0.04 - 0.77; p = 0.021]. Agitated patients had fewer mechanical ventilation-free days at day 7 (p = 0.003).
The incidence of agitation in the first 7 days after admission to the intensive care unit was high. Delirium, moderate/severe pain, mechanical ventilation, and smoking habits were independent risk factors. Agitated patients had fewer ventilator-free days in the first 7 days.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2016;28(4):420-426
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20160075
To determine the incidence of afferent limb failure of the in-hospital Medical Emergency Team, characterizing it and comparing the mortality between the population experiencing afferent limb failure and the population not experiencing afferent limb failure.
A total of 478 activations of the Medical Emergency Team of Hospital Pedro Hispano occurred from January 2013 to July 2015. A sample of 285 activations was obtained after excluding incomplete records and activations for patients with less than 6 hours of hospitalization. The sample was divided into two groups: the group experiencing afferent limb failure and the group not experiencing afferent limb failure of the Medical Emergency Team. Both populations were characterized and compared. Statistical significance was set at p ≤ 0.05.
Afferent limb failure was observed in 22.1% of activations. The causal analysis revealed significant differences in Medical Emergency Team activation criteria (p = 0.003) in the group experiencing afferent limb failure, with higher rates of Medical Emergency Team activation for cardiac arrest and cardiovascular dysfunction. Regarding patient outcomes, the group experiencing afferent limb failure had higher immediate mortality rates and higher mortality rates at hospital discharge, with no significant differences. No significant differences were found for the other parameters.
The incidence of cardiac arrest and the mortality rate were higher in patients experiencing failure of the afferent limb of the Medical Emergency Team. This study highlights the need for health units to invest in the training of all healthcare professionals regarding the Medical Emergency Team activation criteria and emergency medical response system operations.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2016;28(4):427-435
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20160076
The objective of this study was to analyze the clinical profile of patients with in-hospital cardiac arrest using the Utstein style.
This study is an observational, prospective, longitudinal study of patients with cardiac arrest treated in intensive care units over a period of 1 year.
The study included 89 patients who underwent cardiopulmonary resuscitation maneuvers. The cohort was 51.6% male with a mean age 59.0 years. The episodes occurred during the daytime in 64.6% of cases. Asystole/bradyarrhythmia was the most frequent initial rhythm (42.7%). Most patients who exhibited a spontaneous return of circulation experienced recurrent cardiac arrest, especially within the first 24 hours (61.4%). The mean time elapsed between hospital admission and the occurrence of cardiac arrest was 10.3 days, the mean time between cardiac arrest and cardiopulmonary resuscitation was 0.68 min, the mean time between cardiac arrest and defibrillation was 7.1 min, and the mean duration of cardiopulmonary resuscitation was 16.3 min. Associations between gender and the duration of cardiopulmonary resuscitation (19.2 min in women versus 13.5 min in men, p = 0.02), the duration of cardiopulmonary resuscitation and the return of spontaneous circulation (10.8 min versus 30.7 min, p < 0.001) and heart disease and age (60.6 years versus 53.6, p < 0.001) were identified. The immediate survival rates after cardiac arrest, until hospital discharge and 6 months after discharge were 71%, 9% and 6%, respectively.
The main initial rhythm detected was asystole/bradyarrhythmia; the interval between cardiac arrest and cardiopulmonary resuscitation was short, but defibrillation was delayed. Women received cardiopulmonary resuscitation for longer periods than men. The in-hospital survival rate was low.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2016;28(4):436-443
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20160077
To evaluate the clinical course and respiratory parameters of mechanically ventilated children with cancer suffering from sepsis-related acute respiratory distress syndrome.
This 2-year prospective, longitudinal, observational cohort study enrolled 29 children and adolescents. Clinical data, measurements of blood gases and ventilation parameters were collected at four different time points. Fluctuations between measurements as well as differences in estimated means were analyzed by linear mixed models in which death within 28 days from the onset of acute respiratory distress syndrome was the primary endpoint.
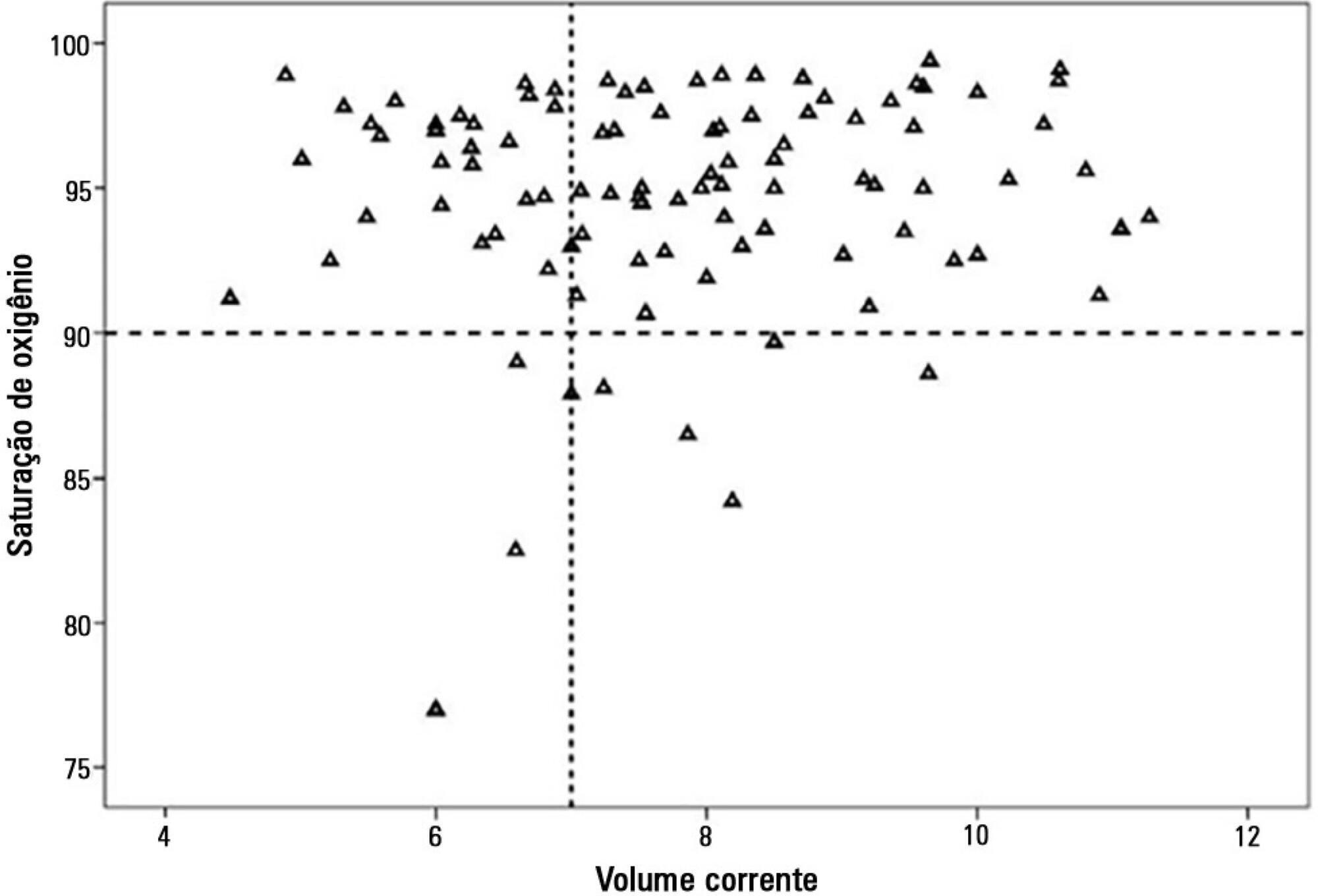
There were 17 deaths within 28 days of acute respiratory distress syndrome onset and another 7 between 29 - 60 days. Only 5 patients survived for more than 60 days. Nine (31%) patients died as a direct consequence of refractory hypoxemia, and the others died of multiple organ failure and catecholamine-refractory shock. In 66% of the measurements, the tidal volume required to obtain oxygen saturation equal to or above 90% was greater than 7mL/kg. The estimated means of dynamic compliance were low and were similar for survivors and non-survivors but with a negative slope between the first and final measurements, accompanied by a negative slope of the tidal volume for non-survivors. Non-survivors were significantly more hypoxemic, with PaO2/FiO2 ratios showing lower estimated means and a negative slope along the four measurements. Peak, expiratory and mean airway pressures showed positive slopes in the non-survivors, who also had more metabolic acidosis.
In most of our children with cancer, sepsis and acute respiratory distress syndrome progressed with deteriorating ventilation indexes and escalating organic dysfunction, making this triad nearly fatal in children.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2016;28(4):444-451
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20160078
The aim of this study was to systematically review studies that compared a mild target sedation protocol with daily sedation interruption and to perform a meta-analysis with the data presented in these studies.
We searched Medline, Scopus and Web of Science databases to identify randomized clinical trials comparing sedation protocols with daily sedation interruption in critically ill patients requiring mechanical ventilation. The primary outcome was mortality in the intensive care unit.
Seven studies were included, with a total of 892 patients. Mortality in the intensive care unit did not differ between the sedation protocol and daily sedation interruption groups (odds ratio [OR] = 0.81; 95% confidence interval [CI] 0.60 - 1.10; I2 = 0%). Hospital mortality, duration of mechanical ventilation, intensive care unit and hospital length of stay did not differ between the groups either. Sedation protocols were associated with an increase in the number of days free of mechanical ventilation (mean difference = 6.70 days; 95%CI 1.09 - 12.31 days; I2 = 87.2%) and a shorter duration of hospital length of stay (mean difference = -5.05 days, 95%CI -9.98 - -0.11 days; I2 = 69%). There were no differences in regard to accidental extubation, extubation failure and the occurrence of delirium.
Sedation protocols and daily sedation interruption do not appear to differ in regard to the majority of analyzed outcomes. The only differences found were small and had a high degree of heterogeneity.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2016;28(4):452-462
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20160066
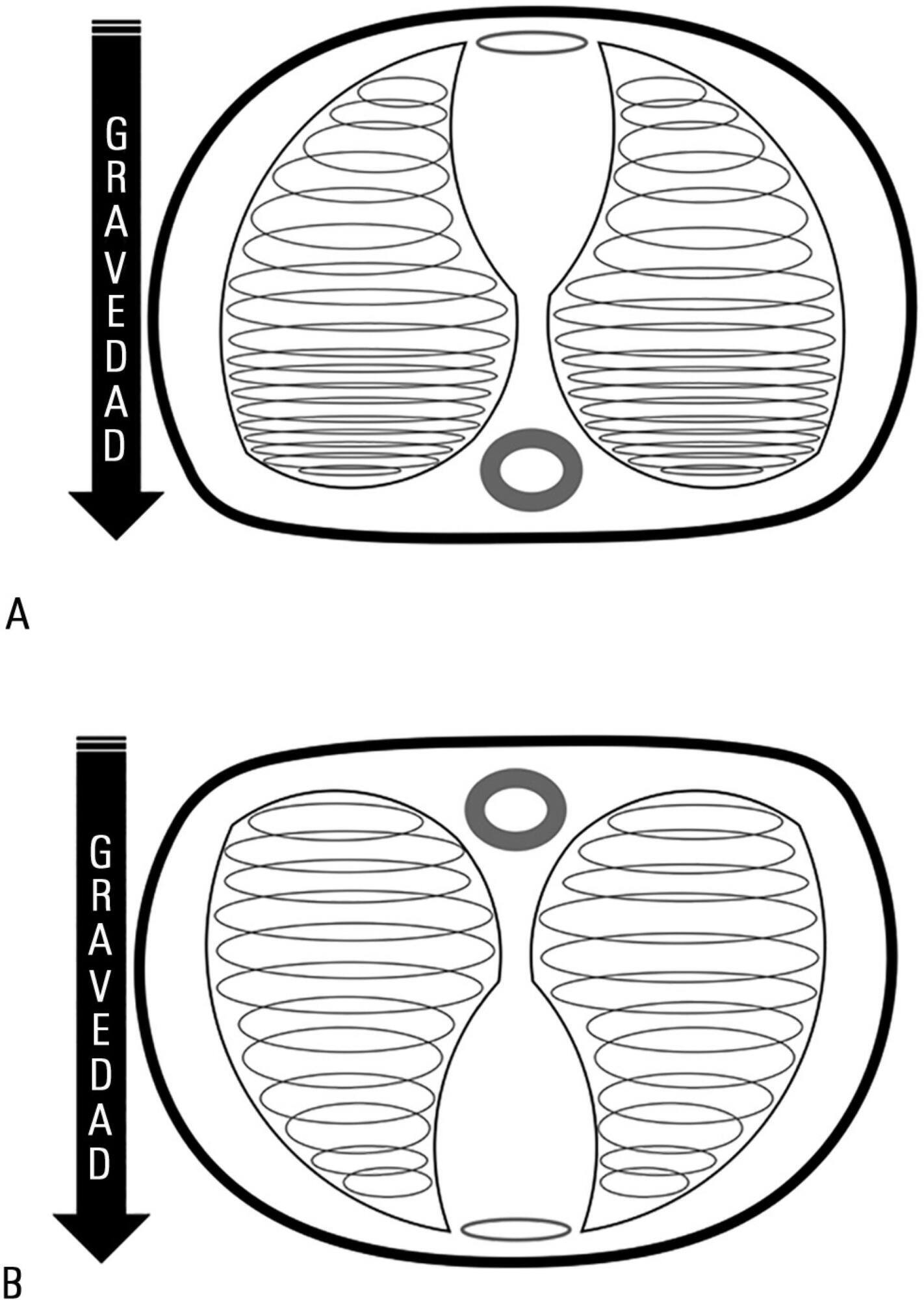
Acute respiratory distress syndrome occupies a great deal of attention in intensive care units. Despite ample knowledge of the physiopathology of this syndrome, the focus in intensive care units consists mostly of life-supporting treatment and avoidance of the side effects of invasive treatments. Although great advances in mechanical ventilation have occurred in the past 20 years, with a significant impact on mortality, the incidence continues to be high. Patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome, especially the most severe cases, often present with refractory hypoxemia due to shunt, which can require additional treatments beyond mechanical ventilation, among which is mechanical ventilation in the prone position. This method, first recommended to improve oxygenation in 1974, can be easily implemented in any intensive care unit with trained personnel.
Prone position has extremely robust bibliographic support. Various randomized clinical studies have demonstrated the effect of prone decubitus on the oxygenation of patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome measured in terms of the PaO2/FiO2 ratio, including its effects on increasing patient survival.
The members of the Respiratory Therapists Committee of the Sociedad Argentina de Terapia Intensiva performed a narrative review with the objective of discovering the available evidence related to the implementation of prone position, changes produced in the respiratory system due to the application of this maneuver, and its impact on mortality. Finally, guidelines are suggested for decision-making.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2016;28(4):463-471
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20160079
Timely fluid administration is crucial to maintain tissue perfusion in septic shock patients. However, the question concerning which fluid should be used for septic shock resuscitation remains a matter of debate. A growing body of evidence suggests that the type, amount and timing of fluid administration during the course of sepsis may affect patient outcomes. Crystalloids have been recommended as the first-line fluids for septic shock resuscitation. Nevertheless, given the inconclusive nature of the available literature, no definitive recommendations about the most appropriate crystalloid solution can be made. Resuscitation of septic and non-septic critically ill patients with unbalanced crystalloids, mainly 0.9% saline, has been associated with a higher incidence of acid-base balance and electrolyte disorders and might be associated with a higher incidence of acute kidney injury. This can result in greater demand for renal replacement therapy and increased mortality. Balanced crystalloids have been proposed as an alternative to unbalanced solutions in order to mitigate their detrimental effects. Nevertheless, the safety and effectiveness of balanced crystalloids for septic shock resuscitation need to be further addressed in a well-designed, multicenter, pragmatic, randomized controlled trial.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2016;28(4):472-482
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20160080
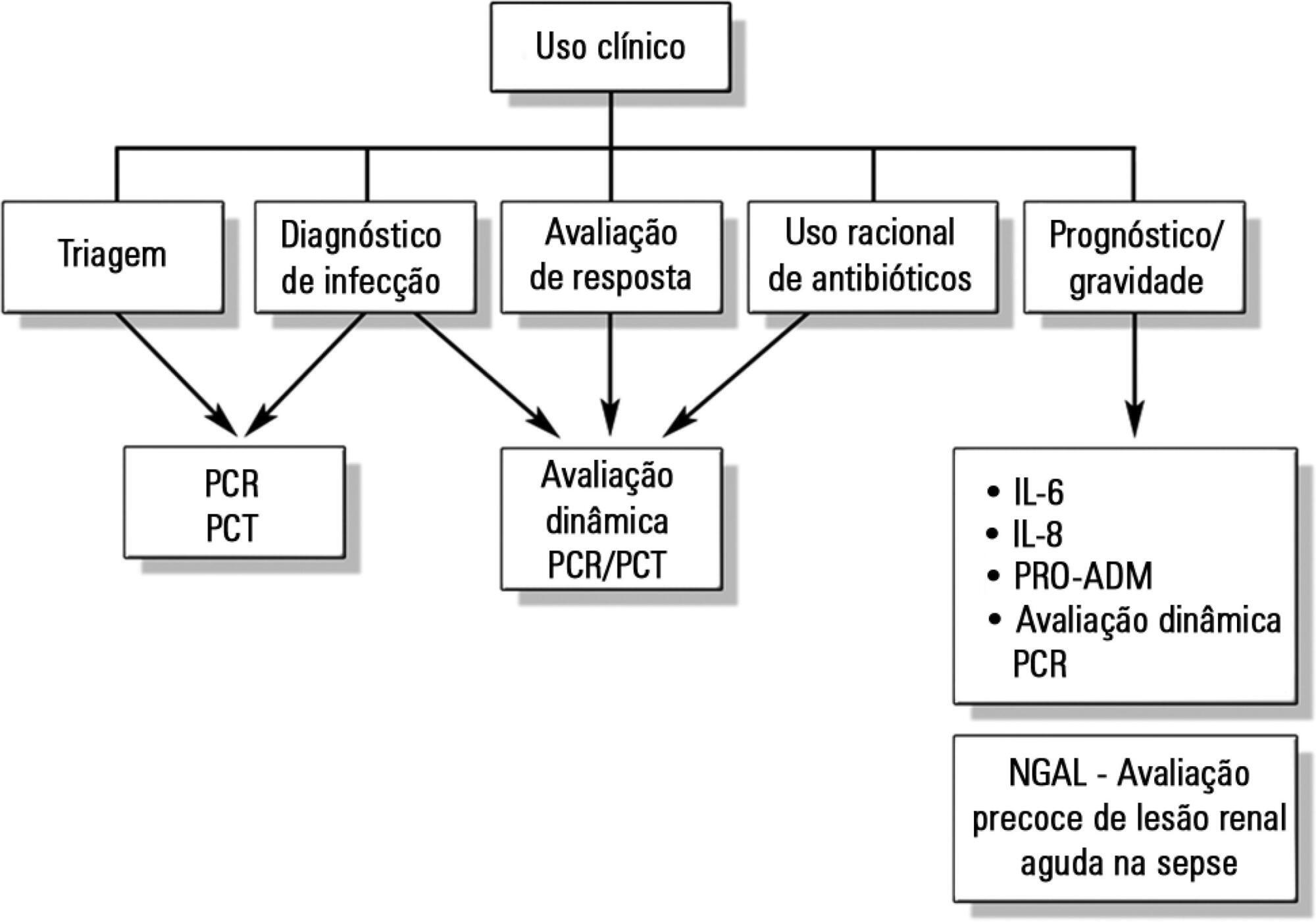
Despite advances in recent years, sepsis is still a leading cause of hospitalization and mortality in infants and children. The presence of biomarkers during the response to an infectious insult makes it possible to use such biomarkers in screening, diagnosis, prognosis (risk stratification), monitoring of therapeutic response, and rational use of antibiotics (for example, the determination of adequate treatment length). Studies of biomarkers in sepsis in children are still relatively scarce. This review addresses the use of biomarkers in sepsis in pediatric patients with emphasis on C-reactive protein, procalcitonin, interleukins 6, 8, and 18, human neutrophil gelatinase, and proadrenomedullin. Assessment of these biomarkers may be useful in the management of pediatric sepsis.