Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2015;27(2):155-160
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20150027
To evaluate the changes in ventilatory mechanics and hemodynamics that occur in patients dependent on mechanical ventilation who are subjected to a standard respiratory therapy protocol.
This experimental and prospective study was performed in two intensive care units, in which patients dependent on mechanical ventilation for more than 48 hours were consecutively enrolled and subjected to an established respiratory physiotherapy protocol. Ventilatory variables (dynamic lung compliance, respiratory system resistance, tidal volume, peak inspiratory pressure, respiratory rate, and oxygen saturation) and hemodynamic variables (heart rate) were measured one hour before (T-1), immediately after (T0) and one hour after (T+1) applying the respiratory physiotherapy protocol.
During the period of data collection, 104 patients were included in the study. Regarding the ventilatory variables, an increase in dynamic lung compliance (T-1 = 52.3 ± 16.1mL/cmH2O versus T0 = 65.1 ± 19.1mL/cmH2O; p < 0.001), tidal volume (T-1 = 550 ± 134mL versus T0 = 698 ± 155mL; p < 0.001), and peripheral oxygen saturation (T-1 = 96.5 ± 2.29% versus T0 = 98.2 ± 1.62%; p < 0.001) were observed, in addition to a reduction of respiratory system resistance (T-1 = 14.2 ± 4.63cmH2O/L/s versus T0 = 11.0 ± 3.43cmH2O/L/s; p < 0.001), after applying the respiratory physiotherapy protocol. All changes were present in the assessment performed one hour (T+1) after the application of the respiratory physiotherapy protocol. Regarding the hemodynamic variables, an immediate increase in the heart rate after application of the protocol was observed, but that increase was not maintained (T-1 = 88.9 ± 18.7 bpm versus T0 = 93.7 ± 19.2bpm versus T+1 = 88.5 ± 17.1bpm; p < 0.001).
Respiratory therapy leads to immediate changes in the lung mechanics and hemodynamics of mechanical ventilation-dependent patients, and ventilatory changes are likely to remain for at least one hour.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2015;27(2):161-169
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20150028
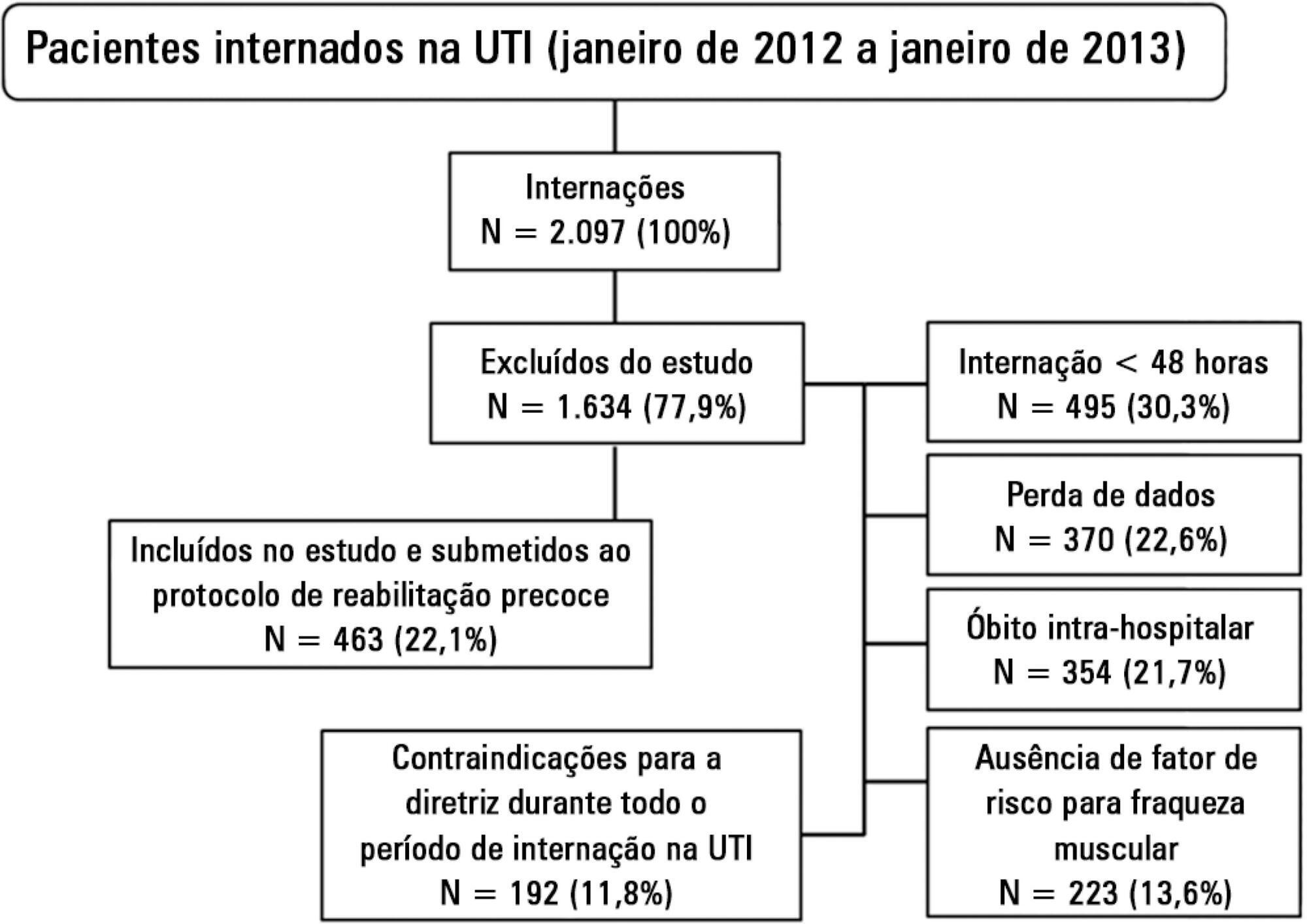
Evaluation of the functional outcomes of patients undergoing an early rehabilitation protocol for critically ill patients from admission to discharge from the intensive care unit.
A retrospective cross-sectional study was conducted that included 463 adult patients with clinical and/or surgical diagnosis undergoing an early rehabilitation protocol. The overall muscle strength was evaluated at admission to the intensive care unit using the Medical Research Council scale. Patients were allocated to one of four intervention plans according to the Medical Research Council score, the suitability of the plan’s parameters, and the increasing scale of the plan expressing improved functional status. Uncooperative patients were allocated to intervention plans based on their functional status. The overall muscle strength and/or functional status were reevaluated upon discharge from the intensive care unit by comparison between the Intervention Plans upon admission (Planinitial) and discharge (Planfinal). Patients were classified into three groups according to the improvement of their functional status or not: responsive 1 (Planfinal > Planinitial), responsive 2 (Planfinal = Planinitial) and unresponsive (Planfinal < Planinitial).
In total, 432 (93.3%) of 463 patients undergoing the protocol responded positively to the intervention strategy, showing maintenance and/or improvement of the initial functional status. Clinical patients classified as unresponsive were older (74.3 ± 15.1 years of age; p = 0.03) and had longer lengths of intensive care unit (11.6 ± 14.2 days; p = 0.047) and hospital (34.5 ± 34.1 days; p = 0.002) stays.
The maintenance and/or improvement of the admission functional status were associated with shorter lengths of intensive care unit and hospital stays. The results suggest that the type of diagnosis, clinical or surgical, fails to define the positive response to an early rehabilitation protocol.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2015;27(2):170-177
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20150029
The aim of this study was to investigate whether plasma serotonin levels or acetylcholinesterase activities determined upon intensive care unit admission could predict the occurrence of acute brain dysfunction in intensive care unit patients.
A prospective cohort study was conducted with a sample of 77 non-consecutive patients observed between May 2009 and September 2010. Delirium was determined using the Confusion Assessment Method for the Intensive Care Unit tool, and the acetylcholinesterase and serotonin measurements were determined from blood samples collected up to a maximum of 24 h after the admission of the patient to the intensive care unit.
In the present study, 38 (49.6%) patients developed delirium during their intensive care unit stays. Neither serum acetylcholinesterase activity nor serotonin level was independently associated with delirium. No significant correlations of acetylcholinesterase activity or serotonin level with delirium/coma-free days were observed, but in the patients who developed delirium, there was a strong negative correlation between the acetylcholinesterase level and the number of delirium/coma-free days, indicating that higher acetylcholinesterase levels are associated with fewer days alive without delirium or coma. No associations were found between the biomarkers and mortality.
Neither serum acetylcholinesterase activity nor serotonin level was associated with delirium or acute brain dysfunction in critically ill patients. Sepsis did not modify these relationships.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2015;27(2):178-184
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20150030
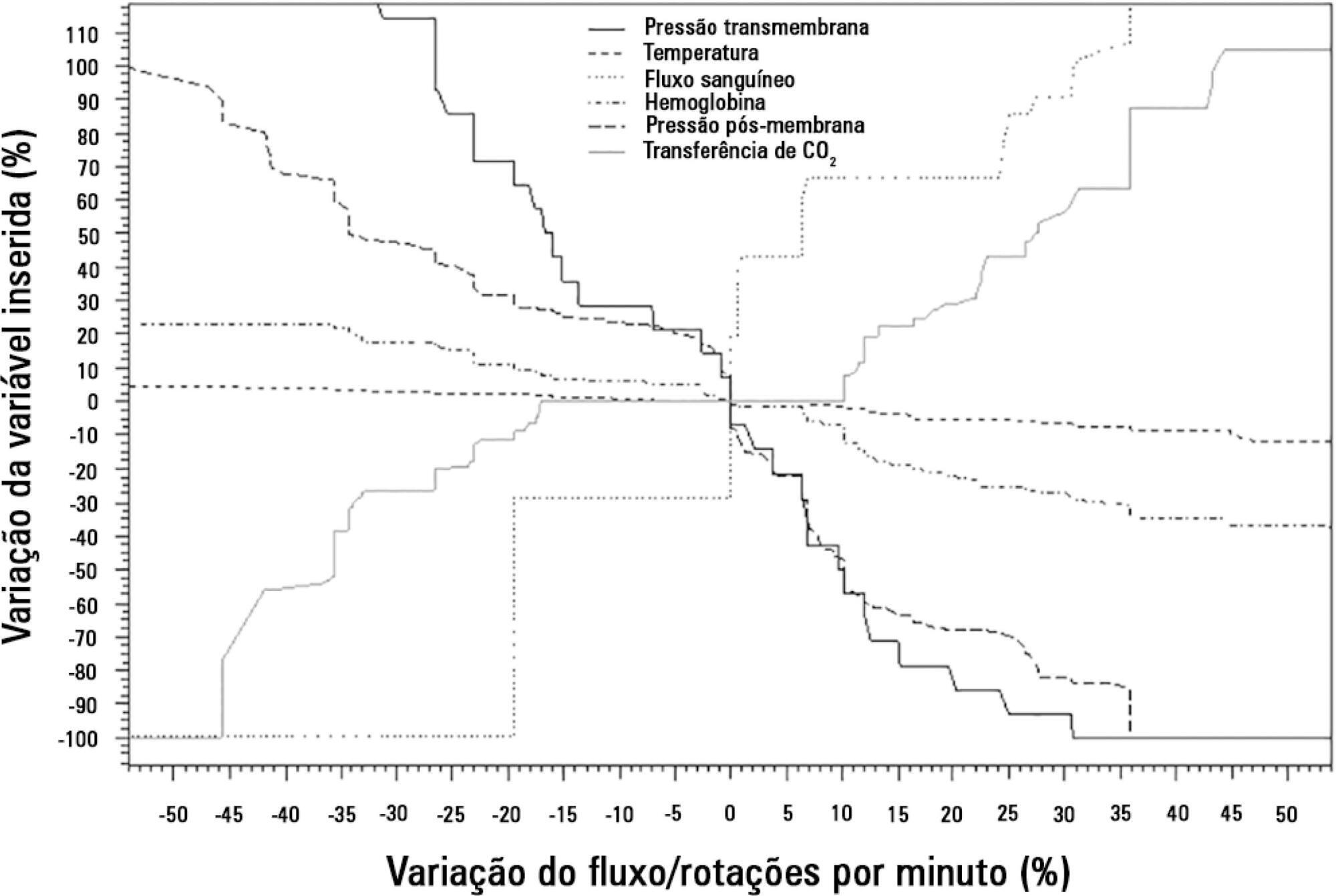
To analyze the correlations of the blood flow/pump rotation ratio and the transmembrane pressure, CO2 and O2 transfer during the extracorporeal respiratory support.
Five animals were instrumented and submitted to extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in a five-step protocol, including abdominal sepsis and lung injury.
This study showed that blood flow/pump rotations ratio variations are dependent on extracorporeal membrane oxygenation blood flow in a positive logarithmic fashion. Blood flow/pump rotation ratio variations are negatively associated with transmembrane pressure (R2 = 0.5 for blood flow = 1500mL/minute and R2 = 0.4 for blood flow = 3500mL/minute, both with p < 0.001) and positively associated with CO2 transfer variations (R2 = 0.2 for sweep gas flow ≤ 6L/minute, p < 0.001, and R2 = 0.1 for sweep gas flow > 6L/minute, p = 0.006), and the blood flow/pump rotation ratio is not associated with O2 transfer variations (R2 = 0.01 for blood flow = 1500mL/minute, p = 0.19, and R2 = - 0.01 for blood flow = 3500 mL/minute, p = 0.46).
Blood flow/pump rotation ratio variation is negatively associated with transmembrane pressure and positively associated with CO2 transfer in this animal model. According to the clinical situation, a decrease in the blood flow/pump rotation ratio can indicate artificial lung dysfunction without the occurrence of hypoxemia.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2015;27(2):185-189
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20150031
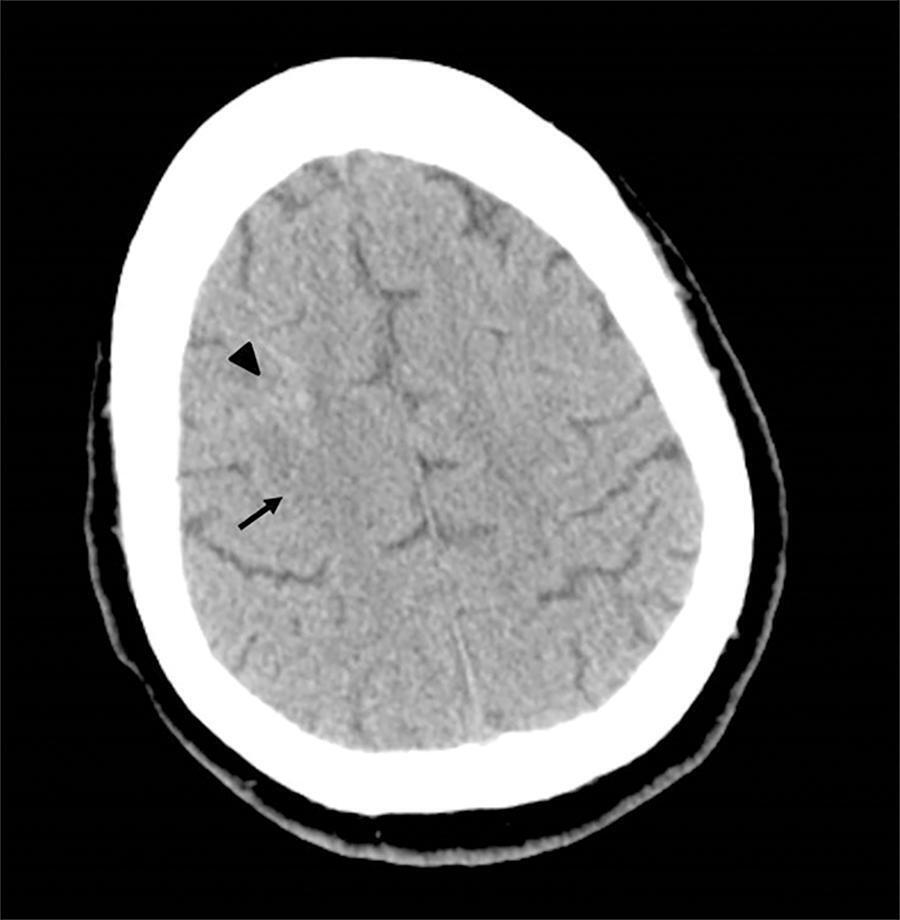
This is a case report of a 43-year-old Caucasian male with end-stage renal disease being treated with hemodialysis and infective endocarditis in the aortic and tricuspid valves. The clinical presentation was dominated by neurologic impairment with cerebral embolism and hemorrhagic components. A thoracoabdominal computerized tomography scan revealed septic pulmonary embolus. The patient underwent empirical antibiotherapy with ceftriaxone, gentamicin and vancomycin, and the therapy was changed to flucloxacilin and gentamicin after the isolation of S. aureus in blood cultures. The multidisciplinary team determined that the patient should undergo valve replacement after the stabilization of the intracranial hemorrhage; however, on the 8th day of hospitalization, the patient entered cardiac arrest due to a massive septic pulmonary embolism and died. Despite the risk of aggravation of the hemorrhagic cerebral lesion, early surgical intervention should be considered in high-risk patients.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2015;27(2):89-91
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20150016
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2015;27(2):92-95
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20150017
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2015;27(2):96-101
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20150018