Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2019;31(2):122-128
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20190037
To evaluate the impact of the presence of sepsis on in-hospital mortality after intensive care unit discharge.
Retrospective, observational, single-center study. All consecutive patients discharged alive from the intensive care unit of Hospital Vila Franca de Xira (Portugal) from January 1 to December 31, 2015 (N = 473) were included and followed until death or hospital discharge. In-hospital mortality after intensive care unit discharge was calculated for septic and non-septic patients.
A total of 61 patients (12.9%) died in the hospital after being discharged alive from the intensive care unit. This rate was higher among the patients with sepsis on admission, 21.4%, whereas the in-hospital, post-intensive care unit mortality rate for the remaining patients was nearly half that, 9.3% (p < 0.001). Other patient characteristics associated with mortality were advanced age (p = 0.02), male sex (p < 0.001), lower body mass index (p = 0.02), end-stage renal disease (p = 0.04) and high Simplified Acute Physiology Score II (SAPS II) at intensive care unit admission (p < 0.001), the presence of shock (p < 0.001) and medical admission (p < 0.001). We developed a logistic regression model and identified the independent predictors of in-hospital mortality after intensive care unit discharge.
Admission to the intensive care unit with a sepsis diagnosis is associated with an increased risk of dying in the hospital, not only in the intensive care unit but also after resolution of the acute process and discharge from the intensive care unit.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2019;31(2):138-146
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20190031
To assess the quality of adult intensive care units.
This population-based, cross-sectional, observational, analytical study evaluated management type in Maranhão, Brazil. An assessment instrument was applied that assigned scores to each service (maximum 124 points). The units were categorized as insufficient (< 50% of the maximum score), typical (≥ 50% and <80% of the maximum score), or sufficient (≥ 80% of the maximum score).
Of the 26 intensive care units in Maranhão, 23 were evaluated; 15 (65.2%) were located in the state capital, and 14 (60.9%) were public. The mean final score was 67.2 (54.2% of the maximum). The worst performance was observed with regard to processes (50.9%) in the units located outside the capital (p = 0.037) and for hospitals with 68 beds or fewer (p = 0.027). The result of the assessment categorized services as a function of the overall total points earned. Specifically, 8 (34.8%) services were assessed as insufficient, 13 (56.5%) were assessed as typical, and 2 (8.7%) were assessed as sufficient.
The majority of the intensive care units in this study were assessed as typical. These services must be better qualified. The priorities are the processes of the units located outside the capital and in small hospitals.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2019;31(2):193-201
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20190033
To characterize resource availability from a nationally representative random sample of intensive care units in Brazil.
A structured online survey of participating units in the Sepsis PREvalence Assessment Database (SPREAD) study, a nationwide 1-day point prevalence survey to assess the burden of sepsis in Brazil, was sent to the medical director of each unit.
A representative sample of 277 of the 317 invited units responded to the resources survey. Most of the hospitals had fewer than 500 beds (94.6%) with a median of 14 beds in the intensive care unit. Providing care for public-insured patients was the main source of income in two-thirds of the surveyed units. Own microbiology laboratory was not available for 26.8% of the surveyed intensive care units, and 10.5% did not always have access to blood cultures. Broad spectrum antibiotics were not always available in 10.5% of surveyed units, and 21.3% could not always measure lactate within three hours. Those institutions with a high resource availability (158 units, 57%) were usually larger and preferentially served patients from the private health system compared to institutions without high resource availability. Otherwise, those without high resource availability did not always have broad-spectrum antibiotics (24.4%), vasopressors (4.2%) or crystalloids (7.6%).
Our study indicates that a relevant number of units cannot perform basic monitoring and therapeutic interventions in septic patients. Our results highlight major opportunities for improvement to adhere to simple but effective interventions in Brazil.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2019;31(2):156-163
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20190026
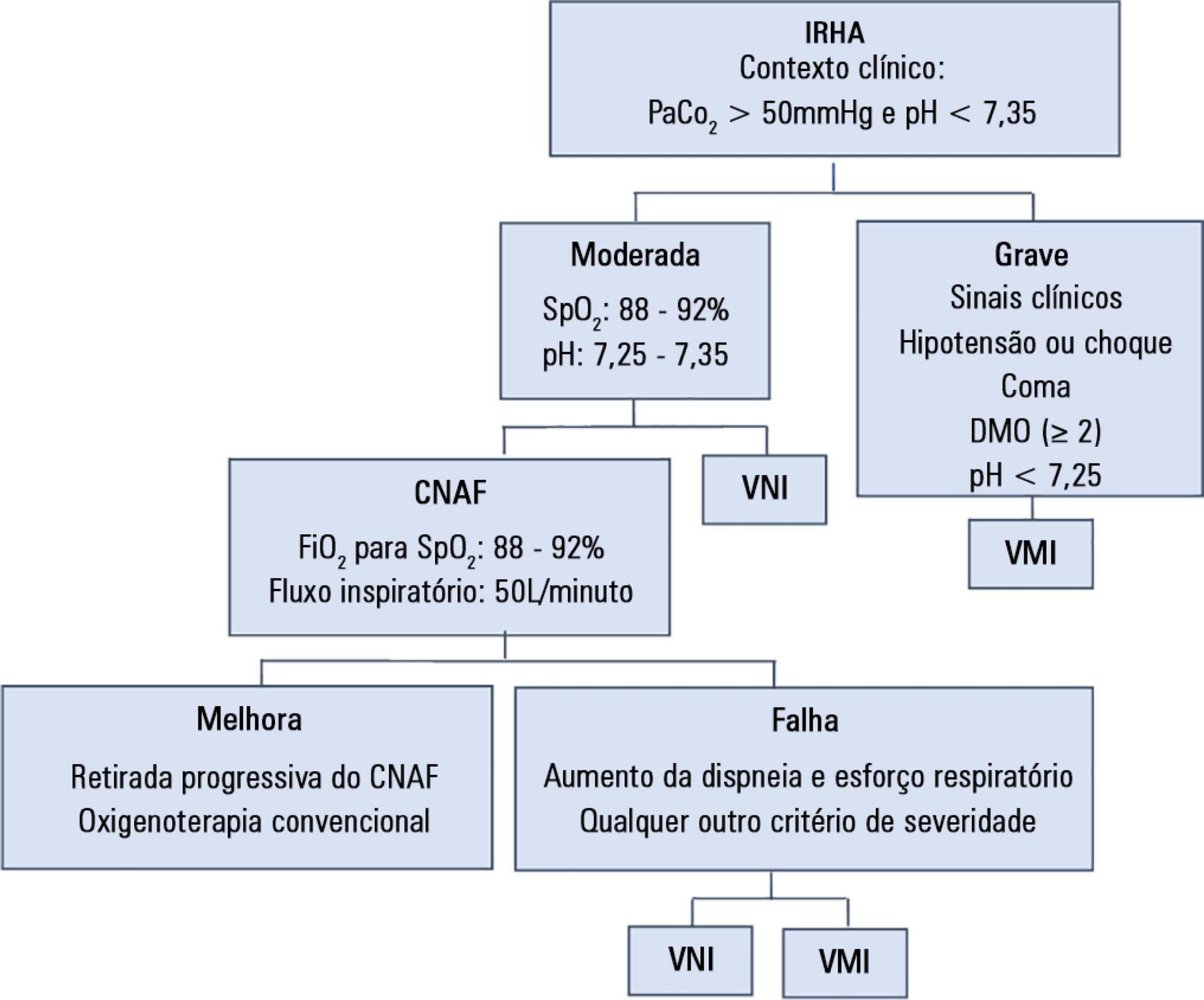
To assess the efficacy and safety of high-flow nasal cannula oxygen therapy in treating moderate hypercapnic respiratory failure in patients who cannot tolerate or have contraindications to noninvasive mechanical ventilation.
A prospective observational 13-month study involving subjects admitted to an intensive care unit with or developing moderate hypercapnic respiratory failure. Clinical and gas exchange parameters were recorded at regular intervals during the first 24 hours. The endpoints were a oxygen saturation between 88 and 92% along with a reduction in breathing effort (respiratory rate) and pH normalization (≥ 7.35). Subjects were considered nonresponders if they required ventilatory support.
Thirty subjects were treated with high-flow nasal cannula oxygen therapy. They consisted of a mixed population with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease exacerbation, acute cardiogenic pulmonary edema, and postoperative and postextubation respiratory failure. A nonsignificant improvement was observed in respiratory rate (28.0 ± 0.9 versus 24.3 ± 1.5, p = 0.22), which was apparent in the first four hours of treatment. The pH improved, although normal levels were only reached after 24 hours on high-flow nasal cannula therapy (7.28 ± 0.02 versus 7.37 ± 0.01, p = 0.02). The rate of nonresponders was 13.3% (4 subjects), of whom one needed and accepted noninvasive mechanical ventilation and three required intubation. Intensive care unit mortality was 3.3% (1 subject), and a patient died after discharge to the ward (hospital mortality of 6.6%).
High-flow nasal cannula oxygen therapy is effective for moderate hypercapnic respiratory failure as it helps normalize clinical and gas exchange levels with an acceptable rate of nonresponders who require ventilatory support.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2019;31(1):64-70
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20190010
To evaluate the neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio as a predictor of sepsis and mortality in patients admitted to an intensive care unit.
Case-control study of adult patients admitted to an intensive care unit. Patients who had sepsis as the reason for admission and who had a previous complete blood count examination were included as case patients. The following statistical analyses were performed: ROC curves, binary logistic regression, and Mann-Whitney and Pearson's chi-square tests. p < 0.05 was considered significant.
The ROC curve values were 0.62 for neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio, 0.98 for band neutrophils and 0.51 for total leukocytes. The presence of a neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio greater than 5.0, leukocyte count above 12,000mm3/mL and band neutrophil percentage above 10% were risk factors for sepsis; however, only the SAPS 3 and SOFA score were related to patient mortality.
The neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio and band neutrophils in combination with other parameters may be markers for the early detection of sepsis in intensive care units.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2019;31(1):27-33
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20190006
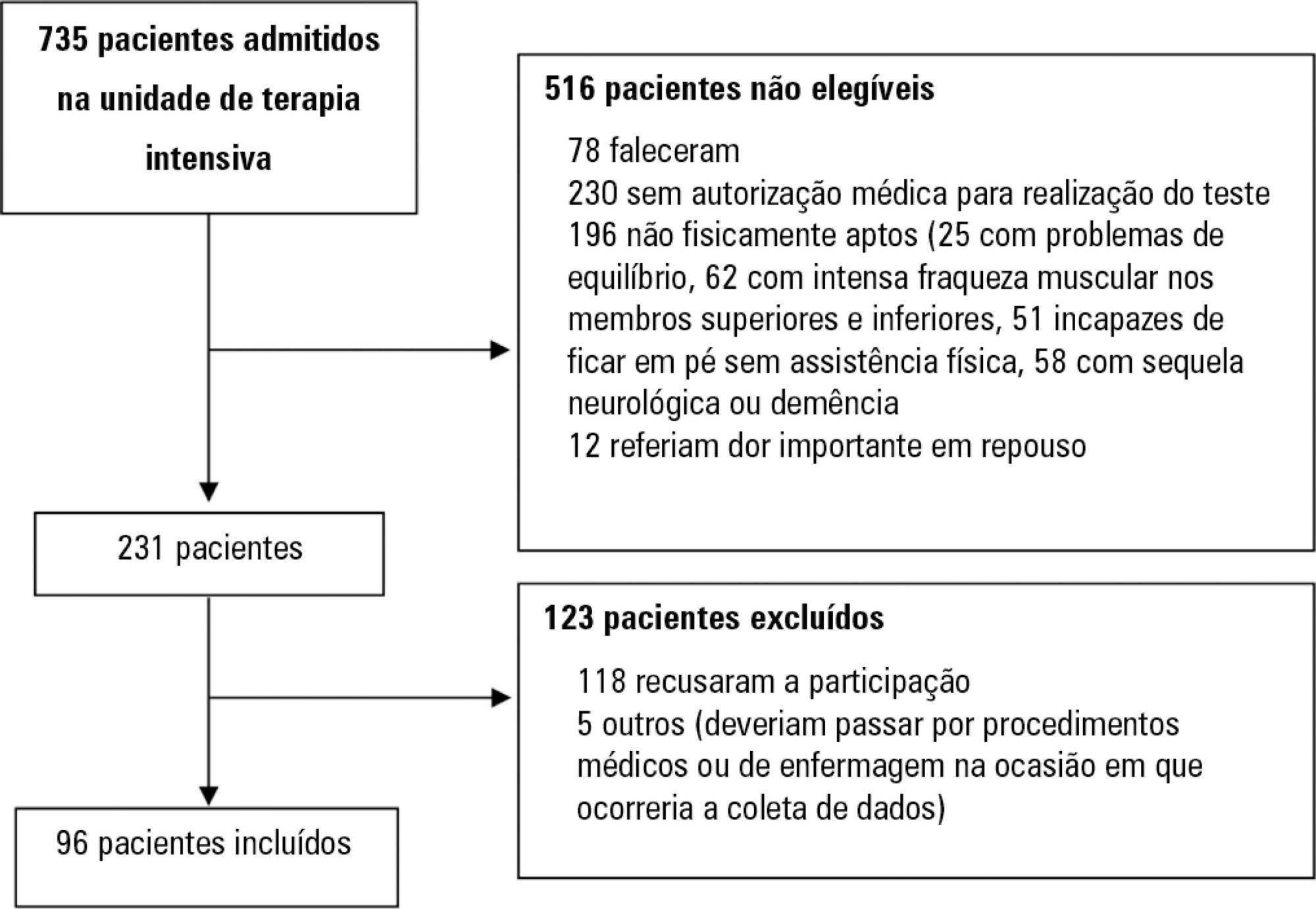
Assess the Five Times Sit-to-Stand Test safety and clinimetric properties in older patients hospitalized in an intensive care unit.
Test safety was assessed according to the incidence of adverse events and through hemodynamic and respiratory data. Additionally, reliability properties were investigated using the intraclass correlation coefficients, standard error of measurement, standard error percentage change, Altman-Bland plot and a survival agreement plot.
The overall suitability of the Five Times Sit-to-Stand Test was found to be low, with 29.8% meeting the inclusion criteria. Only 44% of the hospitalized patients who met the inclusion criteria performed the test, with no need for discontinuation in any patient. Heart rate (79.7 ± 10.2bpm/86.6 ± 9.7bpm; p = 0.001) and systolic blood pressure (118 ± 21.4mmHg/129 ± 21.5mmHg; p = 0.031) were the only variables that presented a significant statistical increase, with no evidence of exacerbated response to the test. Additionally, no adverse events were reported from participating and both test-retest and interrater reliability were high (intraclass correlation coefficient ≥ 0.99).
The Five Times Sit-to-Stand Test was proven to be safe and to have excellent reliability. Its clinical use, however, may be restricted to high-functioning older adults in hospital settings.
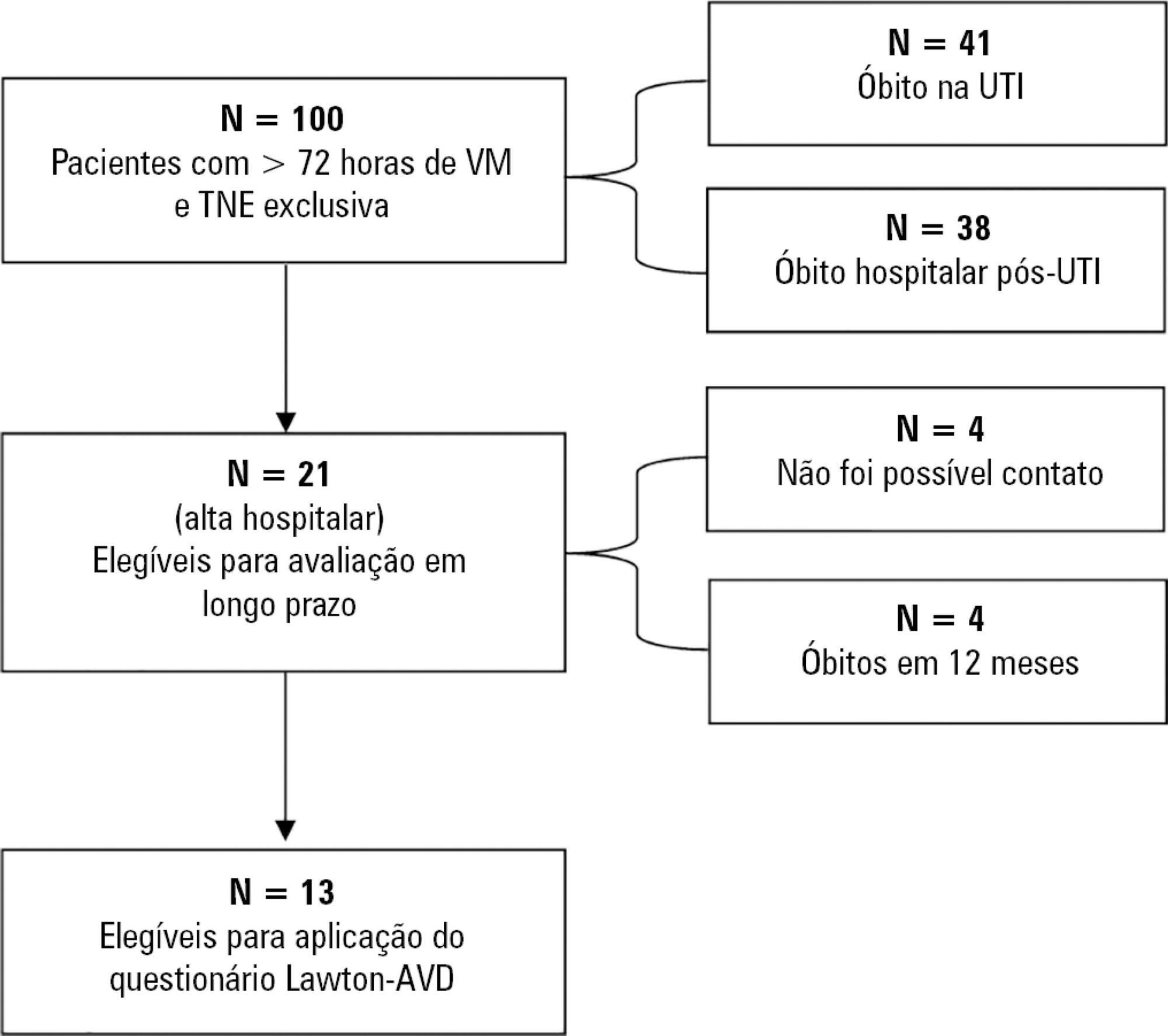
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2019;31(1):34-38
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20190004
To correlate short-term (duration of mechanical ventilation and length of intensive care unit stay) and long-term (functional capacity) clinical outcomes of patients who reached nutritional adequacy ≥ 70% of predicted in the first 72 hours of hospitalization in the intensive care unit.
This was a prospective observational pilot study conducted in an 18-bed intensive care unit. A total of 100 mechanically ventilated patients receiving exclusive enteral nutritional support and receiving intensive care for more than 72 hours were included. Patients who never received enteral nutrition, those with spinal cord trauma, pregnant women, organ donors and cases of family refusal were excluded. The variables studied were nutritional adequacy ≥ 70% of predicted in the first 72 hours of hospitalization, length of intensive care unit stay, duration of mechanical ventilation and the ability to perform activities of daily living after 12 months, assessed via telephone contact using the Lawton Activities of Daily Living Scale.
The mean duration of mechanical ventilation was 18 ± 9 days, and the mean intensive care unit length of stay was 19 ± 8 days. Only 45% of the patients received more than 70% of the target nutrition in 72 hours. There was no association between nutritional adequacy and short-term (duration of mechanical ventilation, length of stay in the intensive care unit and mortality) or long-term (functional capacity and mortality) clinical outcomes.
Critically ill patients receiving caloric intake ≥ 70% in the first 72 hours of hospitalization did not present better outcomes in the short term or after 1 year.