Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2013;25(3):225-232
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20130039
This study sought to compare patients at public and private intensive care units according to the nursing workload and interventions provided.
This retrospective, comparative cohort study included 600 patients admitted to 4 intensive care units in São Paulo. The nursing workload and interventions were assessed using the Nursing Activities Score during the first and last 24 hours of the patient's stay at the intensive care unit. Pearson's chi-square test, Fisher's exact test, the Mann-Whitney test, and Student's t test were used to compare the patient groups.
The average Nursing Activities Score upon admission to the intensive care unit was 61.9, with a score of 52.8 upon discharge. Significant differences were found among the patients at public and private intensive care units relative to the average Nursing Activities Score upon admission, as well as for 12 out of 23 nursing interventions performed during the first 24 hours of stay at the intensive care units. The patients at the public intensive care units exhibited a higher average score and overall more frequent nursing interventions, with the exception of those involved in the "care of drains", "mobilization and positioning", and "intravenous hyperalimentation". The groups also differed with regard to the evolution of the Nursing Activities Score among the total case series as well as the groups of survivors from the time of admission to discharge from the intensive care unit.
Patients admitted to public and private intensive care units exhibit differences in their nursing care demands, which may help managers with nursing manpower planning.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2013;25(3):233-238
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20130040
The objective of this study was to assess the correlation between the European System for Cardiac Operative Risk Evaluation (EuroSCORE) score and the risk of developing acute kidney injury in cardiac surgery patients.
This retrospective study was conducted at a tertiary hospital on consecutive cardiac surgery patients (e.g., valvular, ischemic and congenital heart diseases) between October 2010 and July 2011.
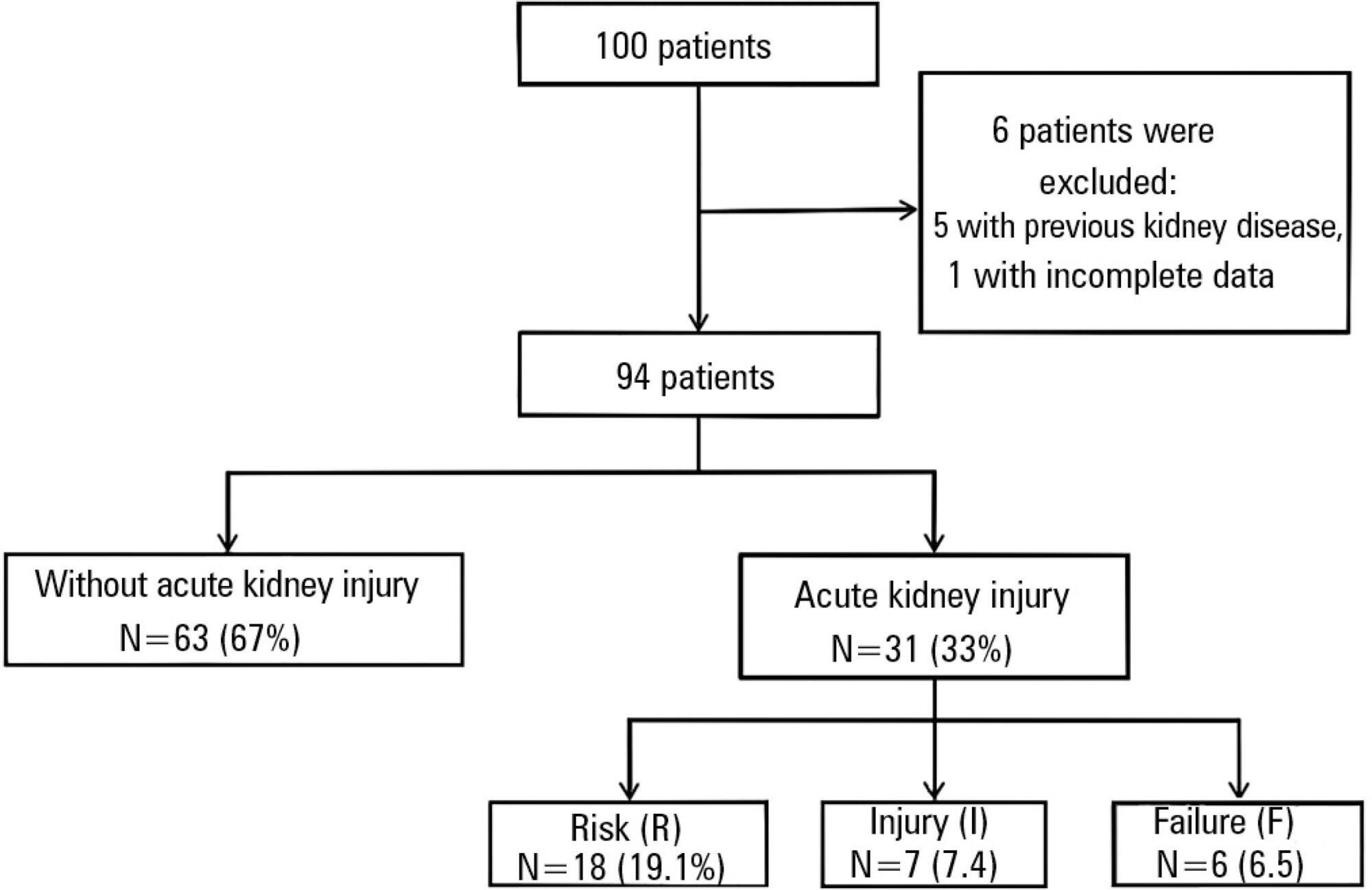
One hundred patients were assessed. Among the 100 patients, six were excluded, including five because of prior kidney disease or dialysis therapy and one because of incomplete medical records. The primary surgical indications were myocardial revascularization in 55 patients (58.5% of cases) and valve replacement in 28 patients (29.8%). According to the EuroSCORE, 55 patients were classified as high risk (58.5%), 27 patients as medium risk (28.7%) and 12 patients as low risk (12.8%). In the postoperative period, patients were classified with the Risk, Injury, Failure, Loss and End-stage kidney disease (RIFLE) score. Among the 31 patients (33%) who displayed an increase in serum creatinine, 18 patients (19.1%) were classified as RIFLE "R" (risk), seven patients (7.4%) were classified as RIFLE "I" (injury) and six patients (6.5%) were classified as RIFLE "F" (failure). Among the patients who were considered to be high risk according to the EuroSCORE criteria, 24 patients (43.6%) showed acute kidney injury. Among the patients who were classified as medium or low risk, acute kidney injury occurred in 18.5 and 16.6% of the cases, respectively. The correlations between risk stratification (low, medium and high) and the EuroSCORE and postoperative RIFLE scores were statistically significant (p=0.03).
In the studied population, there was a statistically significant correlation between the EuroSCORE and the risk of developing acute kidney injury in the postoperative period after cardiac surgery.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2013;25(3):239-244
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20130041
This study sought to evaluate infections related to health care caused by coagulase-negative Staphylococci in a neonatal intensive care unit by assessing antimicrobial susceptibility profiles and potentially effective antibiotic regimens.
This was a retrospective descriptive study performed on a case series of healthcare-associated infections, and the antimicrobial susceptibility profiles were evaluated. Newborns from other hospitals who were admitted to a neonatal intensive care unit in Rio de Janeiro between January 1, 2010, and June 30, 2012, were studied.
In total, 765 patients were admitted, totaling 3,051 patient-days, and the incidence density of general infection was 18.9 per 1,000 patient-days. The rate of central venous catheter use was 71.6%, and the positive culture rate for all sites and all infections related to health care were 68.4%. Coagulase-negative Staphylococci were identified in 11 (19.2%) of 57 health care-related infections, and infections with extended-spectrum beta-lactamase producing Klebsiella pneumoniae and Candida sp. constituted 5 cases each. Of the 11 cases of coagulase-negative Staphylococci, 10 (90.9%) were primary bloodstream infections. The sensitivity of the coagulase-negative Staphylococci isolates to vancomycin, clindamycin, ciprofloxacin, oxacillin and gentamycin was 100%, 81.8%, 72.7%, 27.2% and 22.2%, respectively. There were no deaths directly attributed to coagulase-negative Staphylococci infection.
Coagulase-negative Staphylococci was the main agent identified in healthcare-associated infections, with low rates of infections related to central venous catheter. In hospitals with a high oxacillin resistance profile, similar to those included in this study, vancomycin may be used as an initial therapy, although clindamycin represents a viable alternative.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2013;25(3):245-250
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20130042
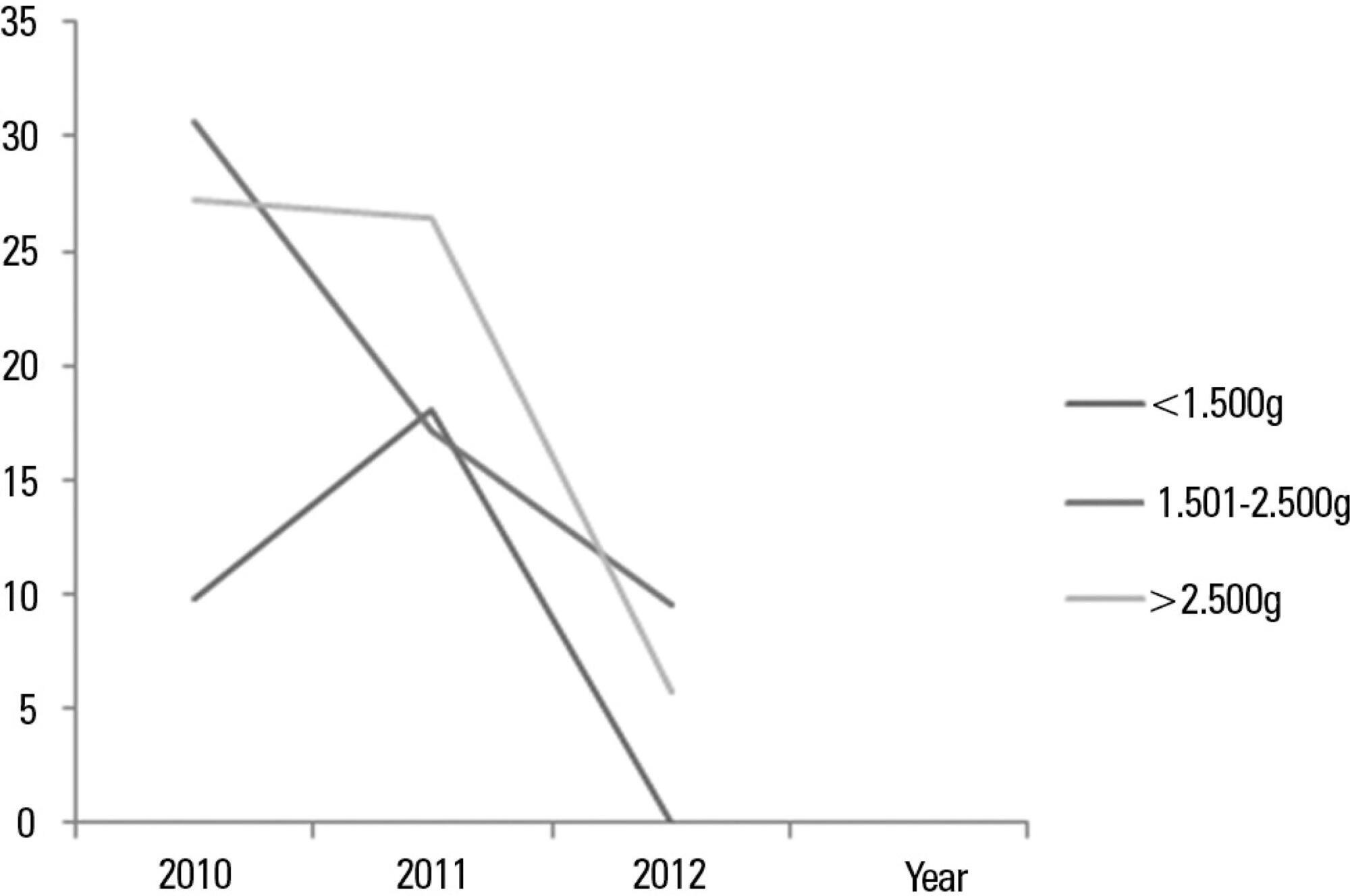
To analyze the incidence of early-onset nasal injury in infants with very low birth weight and indication for noninvasive ventilation via nasal prongs.
A prospective case series of infants with gestational age <37 weeks, weight <1.500 g and postnatal age <29 days. The patients were evaluated three times daily from the installation of nasal prongs to the 3rd day of use. The patients' clinical conditions and the device's characteristics and its application were analyzed. The initial analysis was descriptive, indicating the prevalence of nasal injury and factors associated with it. Categorical data were analyzed using the chi-squared test or Fisher's exact test, and numerical data were analyzed using the t-test or the Mann-Whitney test.
Eighteen infants were included; 12 (with a gestational age of 29.8±3.1 weeks, birth weight of 1.070±194 g and a Score for Neonatal Acute Physiology - Perinatal Extension (SNAPPE) of 15.4±17.5) developed nasal injuries (injury group), and 6 (with a gestational age of 28.0±1.9 weeks, weight of 1.003±317 g and SNAPPE of 26.2±7.5) showed no nasal injury (uninjured group). The injury group subjects were more often male (75% versus 17%), and their injuries appeared after an average of 18 hours, predominantly during the night (75%).
The incidence of nasal injury in preterm infants who experienced noninvasive ventilation via nasal prongs was high, and a study of associated factors may be planned based on this pilot.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2013;25(3):251-257
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20130044
To assess the oxygenation behavior and ventilatory mechanics after hemodialysis in patients under ventilatory support.
The present study was performed in the general intensive care unit of a tertiary public hospital. Patients over 18 years of age under mechanical ventilation and in need of dialysis support were included. Each patient was submitted to 2 evaluations (pre- and post-dialysis) regarding the cardiovascular and ventilatory parameters, the ventilatory mechanics and a laboratory evaluation.
Eighty patients with acute or chronic renal failure were included. The analysis of the ventilatory mechanics revealed a reduction in the plateau pressure and an increased static compliance after dialysis that was independent of a reduction in blood volume. The patients with acute renal failure also exhibited a reduction in peak pressure (p=0.024) and an increase in the dynamic compliance (p=0.026), whereas the patients with chronic renal failure exhibited an increase in the resistive pressure (p=0.046) and in the resistance of the respiratory system (p=0.044). The group of patients with no loss of blood volume after dialysis exhibited an increase in the resistive pressure (p=0.010) and in the resistance of the respiratory system (p=0.020), whereas the group with a loss of blood volume >2,000mL exhibited a reduction in the peak pressure (p=0.027). No changes in the partial pressure of oxygen in arterial blood (PaO2) or in the PaO2/the fraction of inspired oxygen (PaO2/FiO2) ratio were observed.
Hemodialysis was able to alter the mechanics of the respiratory system and specifically reduced the plateau pressure and increased the static compliance independent of a reduction in blood volume.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2013;25(3):258-262
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20130043
To perform an assessment of the available literature on manual hyperinflation as a respiratory physical therapy technique used in pediatric patients, with the main outcome of achieving airway clearance.
We reviewed articles included in the Lilacs (Latin American and Caribbean Literature on Health Sciences/Literatura Latino Americana e do Caribe em Ciências da Saúde), Cochrane Library, Medline (via Virtual Health Library and PubMed), SciELO (Scientific Electronic Library), and PEDro (Physiotherapy Evidence Database) databases from 2002 to 2013 using the following search terms: "physiotherapy (techniques)", "respiratory therapy", "intensive care", and "airway clearance". The selected studies were classified according to the level of evidence and grades of recommendation (method of the Oxford Centre for Evidence-Based Medicine) by two examiners, while a third examiner repeated the search and analysis and checked the classification of the articles.
Three articles were included for analysis, comprising 250 children (aged 0 to 16 years). The main diagnoses were acute respiratory failure, recovery following heart congenital disease and upper abdominal surgery, bone marrow transplantation, asthma, tracheal reconstruction, brain injury, airway injury, and heterogeneous lung diseases. The studies were classified as having a level of evidence 2C and grade of recommendation C.
Manual hyperinflation appeared useful for airway clearance in the investigated population, although the evidence available in the literature remains insufficient. Therefore, controlled randomized studies are needed to establish the safety and efficacy of manual hyperinflation in pediatric patients. However, manual hyperinflation must be performed by trained physical therapists only.