You searched for:"Patrícia Rieken Macedo Rocco"
We found (5) results for your search.-
Review Article
Rationale and limitations of the SpO2/FiO2 as a possible substitute for PaO2/FiO2 in different preclinical and clinical scenarios
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2022;34(1):185-196
Abstract
Review ArticleRationale and limitations of the SpO2/FiO2 as a possible substitute for PaO2/FiO2 in different preclinical and clinical scenarios
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2022;34(1):185-196
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20220013-en
Views3ABSTRACT
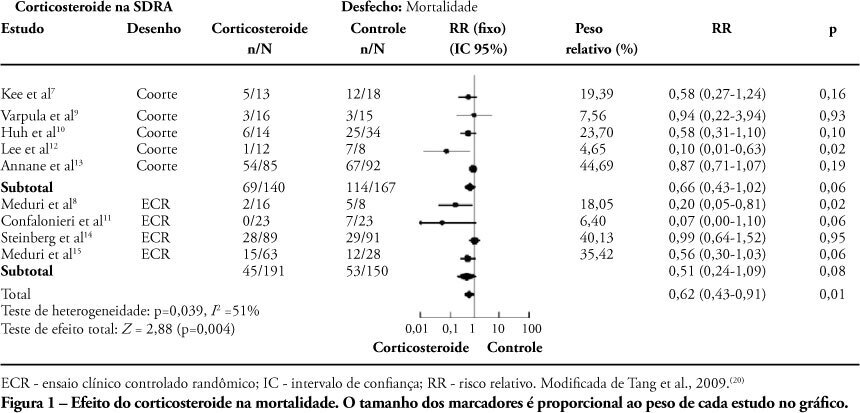
Although the PaO 2/FiO 2 derived from arterial blood gas analysis remains the gold standard for the diagnosis of acute respiratory failure, the SpO2/FiO2 has been investigated as a potential substitute. The current narrative review presents the state of the preclinical and clinical literature on the SpO2/FiO2 as a possible substitute for PaO2/FiO2 and for use as a diagnostic and prognostic marker; provides an overview of pulse oximetry and its limitations, and assesses the utility of SpO2/ FiO2 as a surrogate for PaO2/FiO2 in COVID-19 patients. Overall, 49 studies comparing SpO2/FiO2 and PaO2/FiO2 were found according to a minimal search strategy. Most were conducted on neonates, some were conducted on adults with acute respiratory distress syndrome, and a few were conducted in other clinical scenarios (including a very few on COVID-19 patients). There is some evidence that the SpO2/ FiO2 criteria can be a surrogate for PaO2/FiO2 in different clinical scenarios. This is reinforced by the fact that unnecessary invasive procedures should be avoided in patients with acute respiratory failure. It is undeniable that pulse oximeters are becoming increasingly widespread and can provide costless monitoring. Hence, replacing PaO2/FiO2 with SpO2/FiO2may allow resourcelimited facilities to objectively diagnose acute respiratory failure.
Keywords:Adultblood gas analysisCOVID-19InfantInfant, newbornOximetryOxygenOxygen saturationPrognosisRespiratory distress syndromeRespiratory insufficiencySARS-CoV-2See more
-
Commentary
Recruitment maneuvers for acute respiratory distress syndrome: the panorama in 2016
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2016;28(2):104-106
Abstract
CommentaryRecruitment maneuvers for acute respiratory distress syndrome: the panorama in 2016
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2016;28(2):104-106
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20160023
Views0CONCLUSIONEven though experimental studies, systematic reviews, and meta-analyses have suggested that RMs are associated with beneficial effects for lung function and morphology in ARDS, their impact on clinical outcomes is still being debated. Different methods with different benefit and risk profiles have been used to recruit the lungs, and further studies are required to identify […]See more -
Review Articles
Controversies involving hypercapnic acidosis in acute respiratory distress syndrome
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2009;21(4):404-415
Abstract
Review ArticlesControversies involving hypercapnic acidosis in acute respiratory distress syndrome
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2009;21(4):404-415
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2009000400011
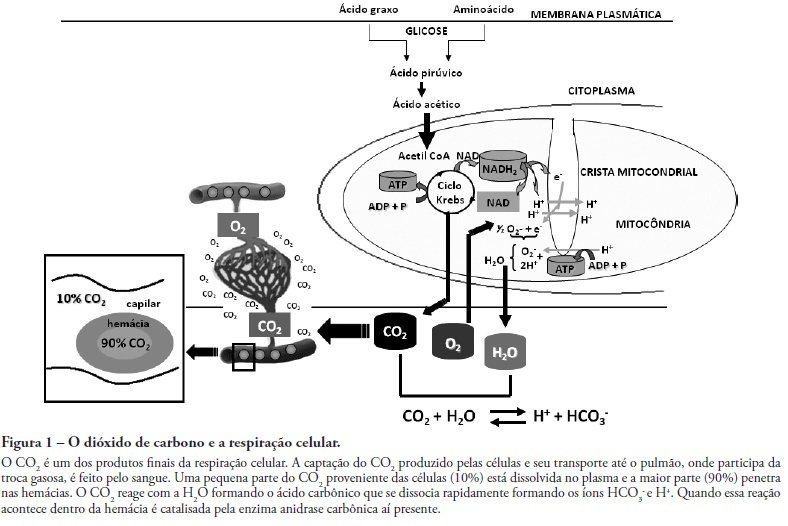
Views0See moreAcute respiratory distress syndrome is characterized by a diffuse inflammatory reaction of lung parenchyma induced by a direct insult to the alveolar epithelium (pulmonary acute respiratory distress syndrome) or an indirect lesion through the vascular endothelium (extrapulmonary acute respiratory distress syndrome). The main therapeutic strategy for acute respiratory distress syndrome is the ventilatory support. However, mechanical ventilation can worsen lung injury. In this context, a protective ventilatory strategy with low tidal volume has been proposed. The use of low tidal volume reduced the mortality rate of acute respiratory distress syndrome patients, but result in hypercapnic acidosis. The current article presents a review of literature on the effects of permissive hypercapnia in acute respiratory distress syndrome. To that end, we carried out a systematic review of scientific literature based on established criteria for documental analysis including clinical and experimental articles, using as data bases MedLine, LILACS, SciELO, PubMed, Cochrane. Hypercapnic acidosis has been considered by some authors as a modulator of the inflammatory process of acute respiratory distress syndrome. However, clinical and experimental studies on the effects of hypercapnic acidosis have shown controversial results. Therefore it is important to better elucidate the role of hypercapnic acidosis in acute respiratory distress syndrome.
-
Review Articles
Stem cell therapy in acute respiratory distress syndrome
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2009;21(1):51-57
Abstract
Review ArticlesStem cell therapy in acute respiratory distress syndrome
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2009;21(1):51-57
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2009000100008
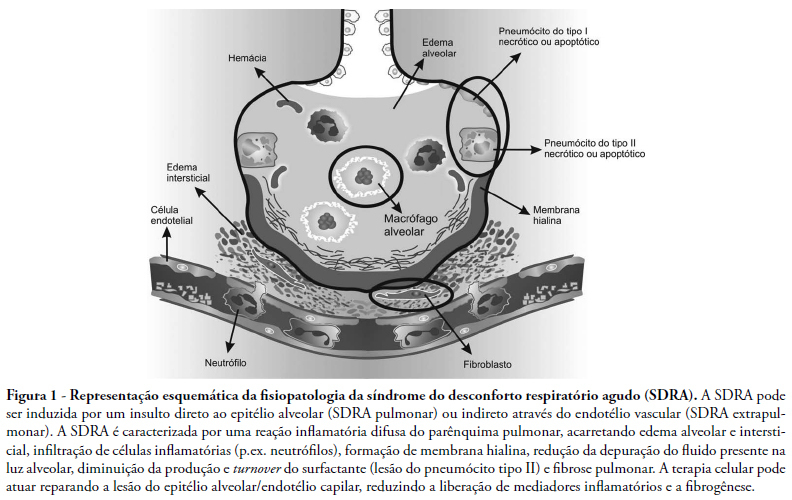
Views0See moreAcute respiratory distress syndrome is characterized by an acute pulmonary inflammatory process induced by the presence of a direct (pulmonary) insult that affects lung parenchyma, or an indirect (extrapulmonary) insult that results from an acute systemic inflammatory response. It is believed that an efficient therapy for the acute respiratory distress syndrome should attenuate inflammatory response and promote adequate repair of the lung injury. This article presents a brief review on the use of stem cells and their potential therapeutic effect on the acute respiratory distress syndrome. This systematic review was based upon clinical and experimental acute respiratory distress syndrome studies included in the MedLine and SciElO database during the last 10 years. Stem cell transplant lead to an improvement in lung injury and fibrotic process by inducing adequate tissue repair. This includes alveolar epithelial cell differentiation,and also reduces pulmonary and systemic inflammatory mediators and secretion of growth factors. Stem cells could be a potential therapy for acute respiratory distress syndrome promoting lung repair and attenuating the inflammatory response. However, mechanisms involving their anti-inflammatory and antifibrinogenic effects require better elucidation, limiting their immediate clinical use in acute respiratory distress syndrome.
Search
Search in:
KEY WORDS
Case reports Child Coronavirus infections COVID-19 Critical care Critical illness Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation Infant, newborn Intensive care Intensive care units Intensive care units, pediatric mechanical ventilation Mortality Physical therapy modalities Prognosis Respiration, artificial Respiratory insufficiency risk factors SARS-CoV-2 Sepsis