Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2009;21(3):292-298
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2009000300009
BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: An inspired oxygen fraction (FiO2) of 40% is often used for weaning patients, but lower FiO2 values are also recommended, if arterial oxygen pressure (PaO2)/ FiO2 >150-200 mmHg. This study aimed to compare respiratory variables and vital data values recorded during use of sufficient FiO2 (ideal) to maintain peripheral oxygen saturation at 92% with values recorded during use of FiO2 established at 40% (baseline) in weaning patients. METHODS: Prospective cross-over study. Respiratory variables (respiratory frequency, tidal volume, occlusion pressure, inspiratory time/total time ratio) and vital data (blood pressure and heart rate) were collected sequentially at 30 and 60 minutes with baseline FiO2, followed by ideal FiO2. These were compared to a generalized linear model for repeated measurements. Comparisons between baseline and ideal FiO2 values, and arterial blood gases were evaluated by the Student's t or Wilcoxon tests. RESULTS: In 30 adult patients the median of ideal FiO2 was 25% (IQ25%-75% 23-28). This was significantly lower than baseline FiO2 (40%) (p< 0.001). No significant difference was found in the PaO2/ FiO2 ratio between baseline FiO2 (269±53) and ideal FiO2 (268±47). Tidal volume was significantly lower during use of ideal FiO2 (p=0.003) and blood pressure was significantly higher during use of baseline FiO2 (p=0.041), but there was no clinical significance. The remaining variables were not affected by reduction in FiO2. The ideal FiO2 did not influence remaining variables. CONCLUSIONS: These results suggest that FiO2 levels sufficient to ensure a SpO2>92% did not alter breathing patterns or trigger clinical changes in weaning patients.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2008;20(2):149-153
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2008000200006
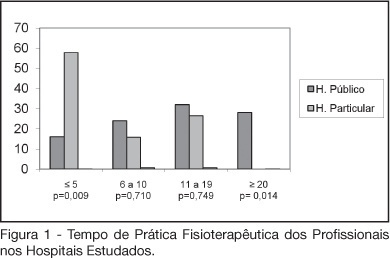
BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: The number of patients requiring prolonged time on mechanical ventilation is increasing considerably in the intensive care unit (ICU). The objective of this study was to characterize the variability of methods and criteria used by physiotherapists to obtain weaning parameters in hospitals of Fortaleza. METHODS: After approval by the UNIFOR Ethics Committee, survey questionnaires were distributed among physiotherapists working in the ICU of three public and three private hospitals. Forty-four physiotherapists answered thirty-two multiple choice questions anonymously. RESULTS: The main results concerned parameters commonly evaluated by physiotherapists. A significant difference between hospitals was found regarding the rapid shallow breathing index and maximum inspiratory pressure, which are more often used in private hospitals, with a percentage of 100% and 89.5%, respectively. Concerning the ventilatory mode for obtaining the weaning parameters for mechanical ventilation; the T-tube was the most used, not only in the public (56%) but also in the private hospitals (57.9%). CONCLUSIONS: Variability in the methods and criteria used to obtain weaning parameters by the physiotherapists was found in public and private hospitals in Fortaleza. Results from this survey stress the need to develop new scientific studies to standardize the techniques used for weaning.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2006;18(4):351-359
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2006000400006
BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: The weaning of patients under mechanical ventilation (MV) is one of the critical stages of respiratory assistance in intensive care. There are several criteria for taking patients out of respiratory prothesis. The aim of this work was to assess if there is a group of parameter which can predict the patients who will succeed in weaning from mechanical ventilation. METHODS: Sixty patients were studied in a prospective way within 24 months. All of them had been in MV for, time > 48 hours. The specific mechanical parameters were monitored for the weaning, clinical data, gasometrical values and laboratory results. The patients were divided into both succeeding and unsucceeding groups for comparable analysis. By the ROC curve, it was observed the best cut point for the numerical variables evaluated for the success of the weaning. RESULTS: In analysis of logistic regression performed to evaluate the simultaneous influence of all the factors: MV < 8 days, APACHE II (Acute Physiologic and Chronic Health Evaluation II) < 16 and Pimax (maximum respiratory pression) > (-) 20 cmH2O were statistically significant to predict the success to weaning, in this order of explainable capacity. CONCLUSIONS: We could conclude that the indexes evaluated were suitable for the determination of the success in the weaning of those patients in mechanical ventilation. APACHE II because of admition constitutes severity indicator and allows awareness from the patient. MV timing, optimizing the treatment in order to accelerate the process of weaning is conducts that aim not only for the weaning success but also interfere both in the evolution and period of hospital admition.
Search
Search in:
Case reports (56) Child (53) Coronavirus infections (34) COVID-19 (46) Critical care (116) Critical illness (54) Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (26) Infant, newborn (27) Intensive care (72) Intensive care units (256) Intensive care units, pediatric (31) mechanical ventilation (38) Mortality (76) Physical therapy modalities (28) Prognosis (61) Respiration, artificial (119) Respiratory insufficiency (26) risk factors (34) SARS-CoV-2 (28) Sepsis (98)