Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2009;21(2):155-161
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2009000200007
OBJECTIVES: Patients unable to perform breathing functions may be submitted to invasive mechanical ventilation. Chest physiotherapy acts directly on the treatment of these patients for the purpose of improving their lung function. The objective of this study was to evaluate the effects of manual rib-cage compression versus the positive end expiratory pressure-zero end expiratory pressure (PEEP-ZEEP) maneuver, on compliance of the respiratory system and oxygenation in patients under invasive mechanical ventilation. METHODS: A double centric, prospective, randomized and crossover study, with patients under invasive mechanical ventilation, in controlled mode for more than 48 hours was carried out. The protocols of chest physiothe-rapy were randomly applied at an interval of 24 hours. Data of respiratory system compliance and oxygenation were collected before application of the protocols and 30 minutes after. RESULTS: Twelve patients completed the study. Intragroup analysis, for both techniques showed a statistically significant difference in tidal volume (p=0.002), static compliance (p=0.002) and dynamic compliance (p=0.002). In relation to oxygenation, in the group of manual rib-cage compression, peripheral oxygen saturation increased with a significant difference (p=0.011). CONCLUSIONS: Manual rib-cage compression and PEEP-ZEEP maneuver have positive clinical effects. In relation to oxygenation we found a favorable behavior of peripheral oxygen saturation in the group of manual rib-cage compression.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2009;21(1):72-79
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2009000100011
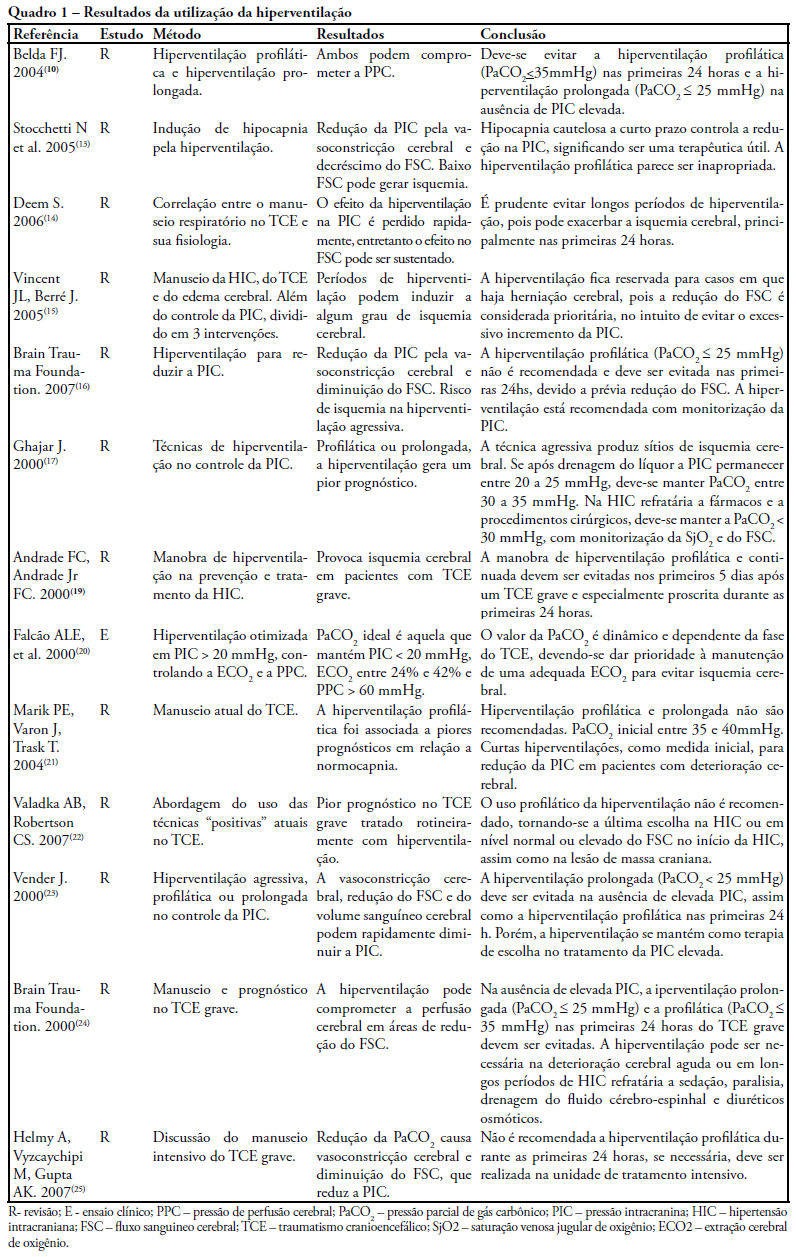
The study intended to make a critical review on use of pulmonary hyperventilation maneuvers and the different positive end-expiratory pressures applied to traumatic brain injury patients. As a reference were used publications in English, Spanish and Portuguese, contained in the following databases: MedLine, SciELO and LILACS, from 2000 to 2007, we included all studies about the use of pulmonary hyperventilation maneuvers and the different positive end-expiratory levels used for adult patients with brain injury at acute or chronic stage. Thirty one trials were selected, 13 about pulmonary hyperventilation, as prophylaxis, prolonged or optimized and 9 shows the levels of positive end-expiratory pressures used, ranging from 0 to 15 cmH2O. The prophylactic hyperventilation maneuver in the first 24 hours can lead to an increase of cerebral ischemia; the prolonged hyperventilation must be avoided if intracranial pressure did not increase; however optimized hyperventilation seems to be the most promising technique for control of the intracranial pressure and cerebral perfusion pressure; the rise of the positive end-expiratory pressure, up to 15cmH2O, can be applied in a conscientious form aiming to increase arterial oxygen saturation in lung injury.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2008;20(3):313-317
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2008000300015
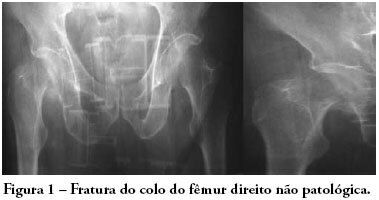
Anesthetic management of patients with severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease is extensively discussed, due to the high rates of complications in this subtype of patients submitted to medium and high complexity surgical procedures. The objective of this study is to report use of noninvasive positive pressure mechanical ventilation - bilevel positive airway pressure - and spinal anesthesia in a patient with severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease during total hip arthroplasty. An 81 year old, male patient with severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (GOLD 4) was submitted to total hip arthroplasty due to a femoral bone fracture under spinal anestesia and noninvasive positive pressure mechanical ventilation-bilevel positive airway pressure with expiratory pressure of 7 cmH2O, inspiratory pressure of 15 cmH2O and O2 flow of 3 L/min. During the procedure, the patient had one episode of bronchospasm that was promptly reverted pharmacologically with no complications in the postoperative period. The combination of less invasive anesthetic and ventilation techniques is easy to apply and may be useful in the perioperative management of patients with high anesthetic morbidity. Interaction between clinical, surgical and anesthetic teams for these cases is very important to reduce the mortality associated with extensive procedures in severe patients.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2008;20(3):254-260
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2008000300008
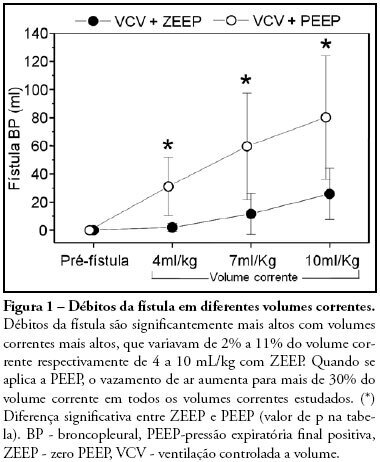
OBJECTIVES: The present study was designed to identify the effect of positive end expiratory pressure (PEEP) and the ideal pulmonary tidal volume to ventilate animals with a surgically produced bronchopleural fistula, aiming to reduce fistula output without affecting gas exchange. METHODS: Hemodynamic and respiratory assessment of gas exchange was obtained in five, healthy, young, mechanically ventilated Large White pigs under volume controlled ventilation with FiO2 of 0.4 and an inspiration:expiration ratio of 1:2, keeping respiratory rate at 22 cpm. A bronchopleural fistula was produced by resection of the lingula. Underwater seal drainage was installed and the thorax was hermetically closed. Gas exchange and fistula output were measured with the animals ventilated sequentially with tidal volumes of 4 ml/kg, 7 ml/kg and 10 ml/Kg alternating zero of positive end expiratory pressure (ZEEP) and PEEP of 10 cmH2O, always in the same order. RESULTS: These findings are attributed to reduced alveolar ventilation and ventilation/perfusion abnormalities and were attenuated with larger tidal volumes. PEEP increases air leak, even with low volume (of 2.0 ± 2.8mL to 31 ± 20.7mL; p= 0.006) and decreases alveolar ventilation in all tidal volumes. Alveolar ventilation improved with larger tidal volumes, but increased fistula output (10 mL/kg - 25.8 ± 18.3mL to 80.2 ± 43.9mL; p=0.0010). Low tidal volumes result in hypercapnia (ZEEP - Toneloto MGC, Terzi RGG, Silva WA, Moraes AC, Moreira MM 83.7± 6.9 mmHg and with PEEP 10 - 93 ± 10.1mmHg) and severely decreased arterial oxygen saturation, about of 84%. CONCLUSIONS: The tidal volume of 7 ml/Kg with ZEEP was considered the best tidal volume because, despite moderate hypercapnia, arterial oxygen saturation is sustained around 90%, alveolar ventilation improves and the fistula output is reduced when compared with a tidal volume of 10ml/Kg. A low tidal volume results in hypercapnia and severe desaturation. Finally, at any tidal volume, PEEP increases the fistula leak and decreases alveolar ventilation.