Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2021;33(3):362-373
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20210059
To determine the effectiveness of noninvasive ventilation versus conventional oxygen therapy in patients with acute respiratory failure after extubation failure.
A pragmatic clinical trial was conducted in an intensive care unit from March 2009 to September 2016. Patients on mechanical ventilation > 24 hours who developed acute respiratory failure after scheduled extubation were included and were assigned to noninvasive ventilation or conventional oxygen therapy. The primary objective was to reduce the reintubation rate. The secondary objectives were to improve respiratory parameters and reduce complications, the duration of mechanical ventilation, the intensive care unit stay, the hospital stay, and mortality in the intensive care unit, in the hospital, and 90 days after discharge. Factors correlated with reintubation were also analyzed.
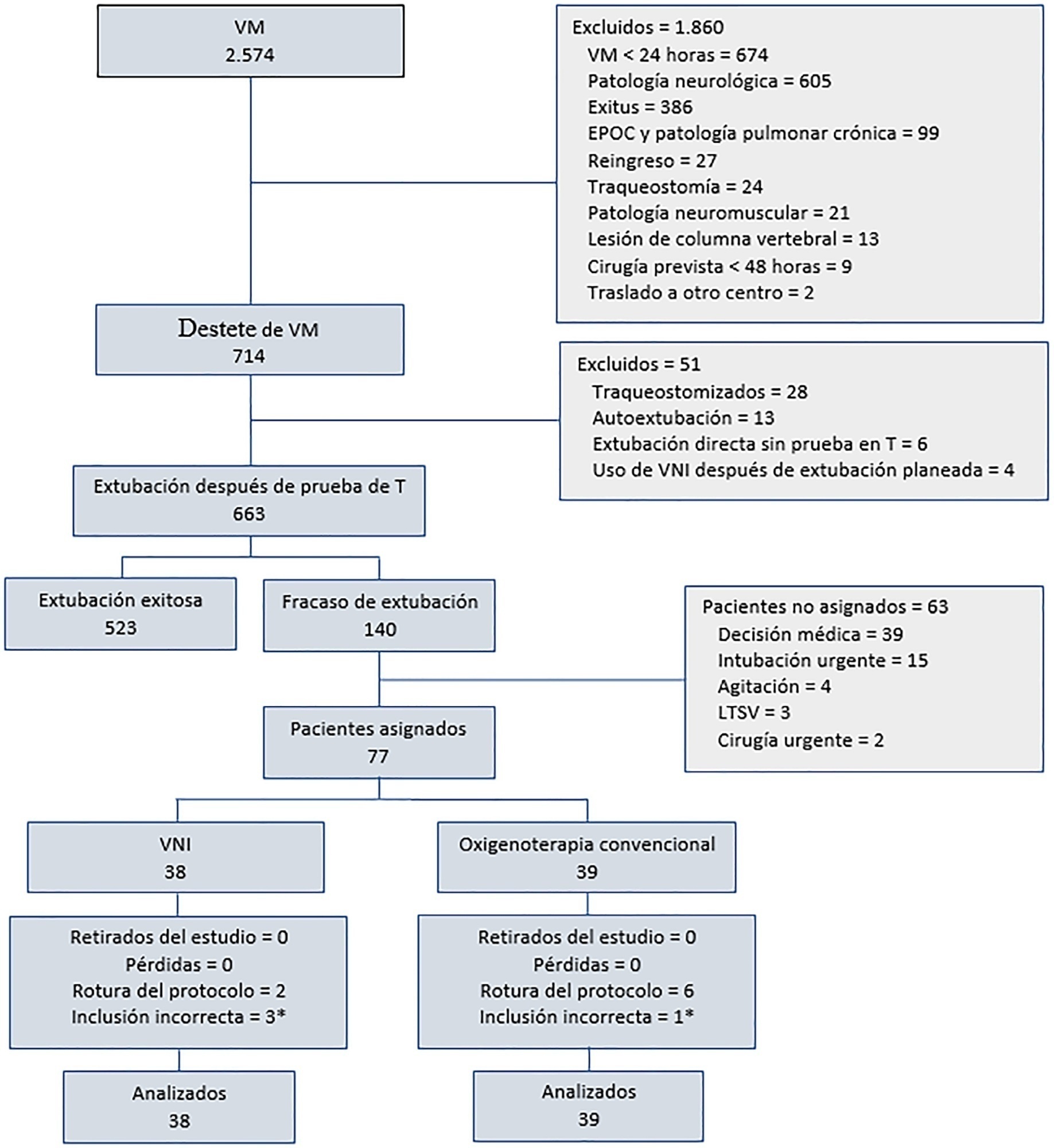
Of a total of 2,574 patients, 77 were analyzed (38 in the noninvasive ventilation group and 39 in the conventional oxygen therapy group). Noninvasive ventilation reduced the respiratory and cardiac rates more rapidly than conventional oxygen therapy. Reintubation was less common in the noninvasive ventilation group [12 (32%) versus 22 (56%) in the conventional oxygen therapy group, relative risk 0.58 (95%CI 0.34 - 0.97), p = 0.039]. The rest of the parameters did not show significant differences. In the multivariate analysis, noninvasive ventilation protected against reintubation [OR 0.17 (95%CI 0.05 - 0.56), p = 0.004], while liver failure before extubation and the inability to maintain airway patency predisposed patients to reintubation.
The use of noninvasive ventilation in patients who failed extubation could be beneficial compared to conventional oxygen therapy.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2008;20(1):57-62
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2008000100009
BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: It is important to know the risk factors for extubation failure (EF) in children submitted to cardiac surgery in order to avoid inherent events due to reintubation (airways injury, usage of medications, cardiovascular changes) and because of prolonged ventilatory support (pneumonias, reduction of the ventilatory muscles strength). The objective of this study is to evaluate mechanical ventilation (MV) parameters, ventilatory mechanics [rapid shallow breathing index (RSBI), ventilatory muscles force [the maximum inspiratory pressure (MIP), the maximum expiratory pressure (MEP) and the load/force balance (LFB)] and blood gases before and after extubation in pediatric patients undergoing cardiac surgery. METHODS: Prospective (March 2004 to March 2006) observational cross sectional study, enrolling children submitted to cardiac surgery admitted to an university PICU hospital and considered able to be extubated. With the tracheal tube in situ and maintaining the children spontaneously breathing we evaluate: expiratory minute volume (V E), MIP and MEP. We calculated the RSBI [(RR/VT)/Weight)], LFB [15x [(3xMAP)/MIP] + 0.03 x RSBI-5], the mean airway pressure (MAP) [MAP={(PIP-PEEP)x[Ti/(Te+Ti)]}+PEEP] and the oxygenation index (OI) [OI=(FiO2 x MAP/PaO2)x100]. Arterial blood gas was collected one hour before extubation. If after 48 hours there was no need to reintubate the patient the extubation was considered successful (SE). RESULTS: 59 children were included. EF was observed in 19% (11/59). Median (QI25%-75%) for age, weight, MAP, OI, duration of MV after cardiac surgery (DMV) were respectively, 36 (12-82) months, 12 (8-20) kg, 8 (6-9), 2 (2-5), 1 (1-3) days. Median (QI25-75%) of EF in relation to SE for OI, LFB and DMV were respectively 5(3-8) versus 2(2-4), p = 0.005; [8(6-11) versus 5(4-6), p =0.002 and 3(2-5) versus 1(1-2) days, p = 0.026. Mean ± SD of EF in relation to SE for V E, PaO2 and MIP were respectively 1.7 ± 0.82 versus 3 ± 2.7 mL/kg/min, p = 0.003); 64 ± 34 versus 111 ± 50 mmHg, p = 0.002 and 53 ± 18 versus 78 ± 28 cmH2O; p=0.002. Concerning the risk factors for EF: OI > 2 (area under the ROC 0.74, p = 0.017) and LFB > 4 (area under the ROC 0.80, p = 0.002), achieved a sensibility of 100% and specificity of 80%; MIP < -35 cmH2O (area under the ROC 0.23; p= 0.004) achieved a sensibility of 80% and specificity of 60%. CONCLUSIONS: EF in children submitted to cardiac surgery is related to OI > 2, LFB > 4, DMV > 3 days; V E < 1.7 mL/kg/min, PaO2 < 64 mmHg and MIP < - 53 cmH2O. The kind of cardiac defect, MAP, RSBI and arterial blood gas were not related to EF.
Search
Search in:
Case reports (56) Child (53) Coronavirus infections (34) COVID-19 (46) Critical care (115) Critical illness (54) Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (26) Infant, newborn (27) Intensive care (72) Intensive care units (256) Intensive care units, pediatric (31) mechanical ventilation (38) Mortality (76) Physical therapy modalities (28) Prognosis (61) Respiration, artificial (119) Respiratory insufficiency (26) risk factors (34) SARS-CoV-2 (28) Sepsis (98)