Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2020;32(3):405-411
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20200069
We investigated the frequency of apnea tests, and the use of ancillary tests in the diagnosis of brain death in our hospital, as well as the reasons for not being able to perform apnea testing and the reasons for using ancillary tests.
In this retrospective study, the files of patients diagnosed with brain death between 2012 - 2018 were examined. The preferred test was determined if an ancillary test was performed in the diagnosis of brain death. The rate and frequency of use of these tests were analyzed.
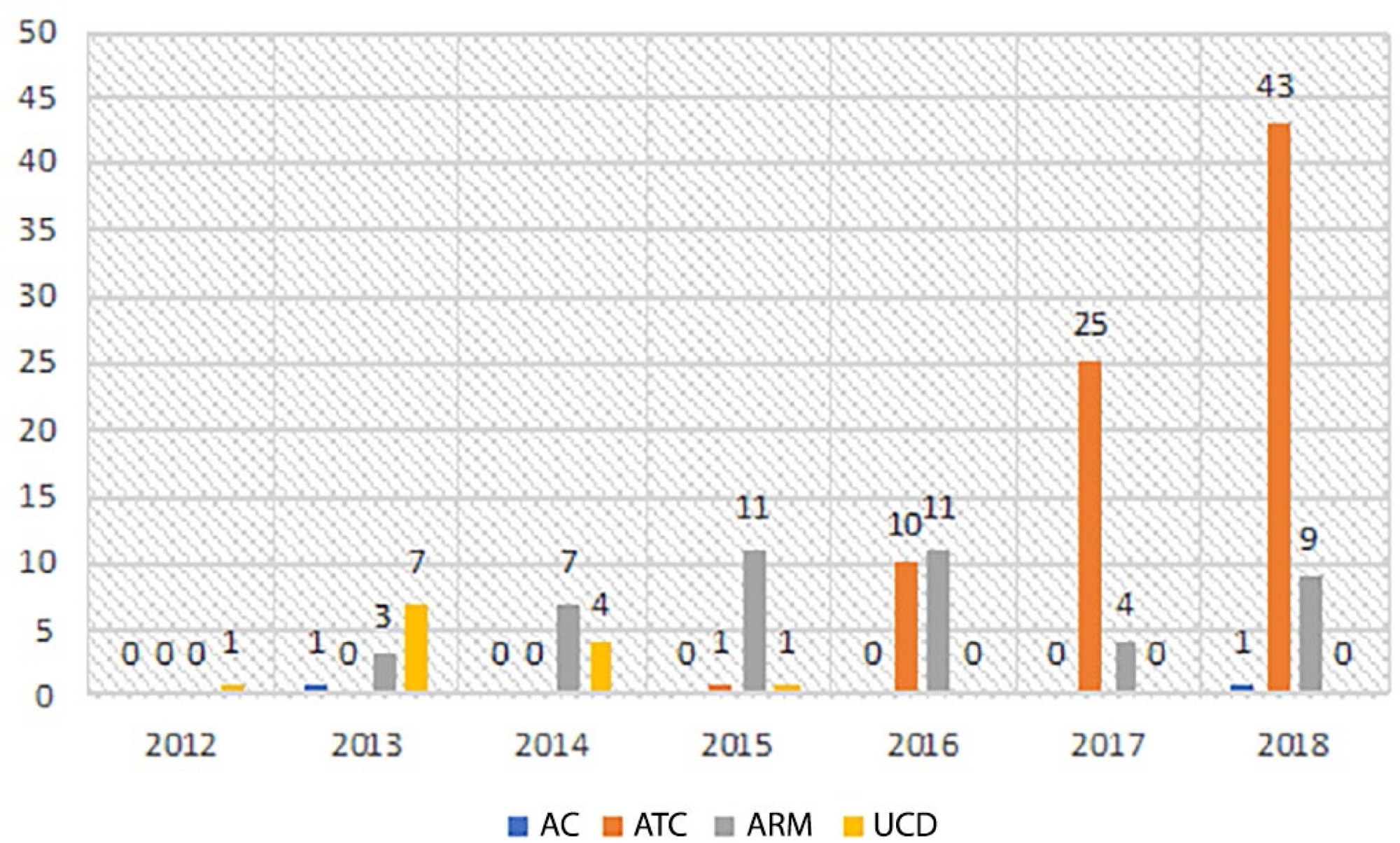
During the diagnosis of brain death, an apnea test was performed on 104 (61.5%) patients and was not or could not be performed on 65 (38.5%) patients. Ancillary tests were performed on 139 (82.8%) of the patients. The most common ancillary test was computed tomography angiography (79 patients, 46.7%). Approval for organ donation was received in the meetings with the family following the diagnosis of brain death for 55 (32.5%) of the 169 patients.
We found an increase in the rate of incomplete apnea tests and concordantly, an increase in the use of ancillary tests in recent years. Ancillary tests should be performed on patients when there is difficulty in reaching a decision of brain death, but it should not be forgotten that there is no worldwide consensus on the use of ancillary tests.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2020;32(2):312-318
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20200048
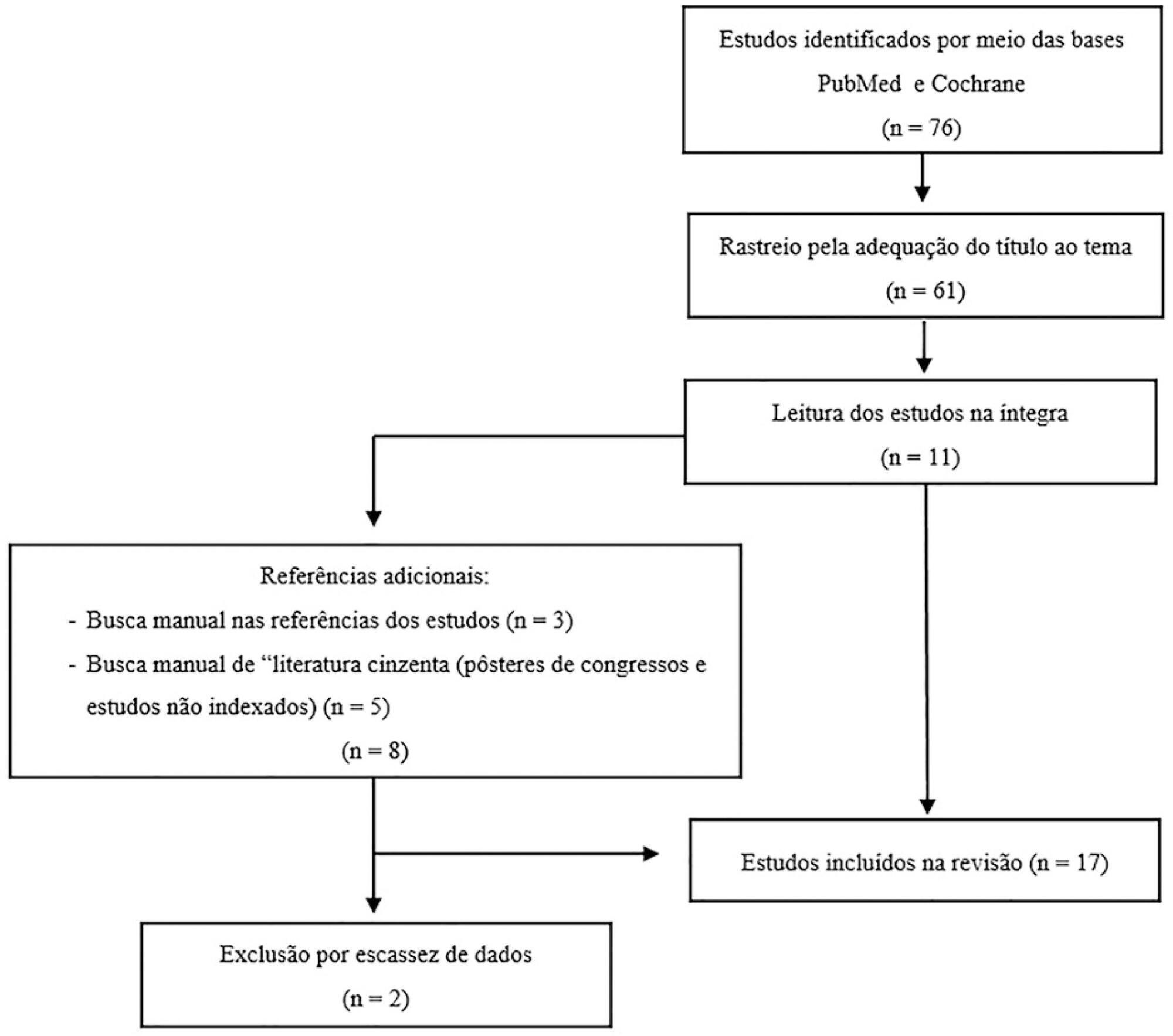
Among the potential complications of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, neurological dysfunctions, including brain death, are not negligible. In Brazil, the diagnostic process of brain death is regulated by Federal Council of Medicine resolution 2,173 of 2017. Diagnostic tests for brain death include the apnea test, which assesses the presence of a ventilatory response to hypercapnic stimulus. However, gas exchange, including carbon dioxide removal, is maintained under extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, making the test challenging. In addition to the fact that the aforementioned resolution does not consider the specificities of the diagnostic process under extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, studies on the subject are scarce. This review aims to identify case studies (and/or case series) published in the PubMed® and Cochrane databases describing the process of brain death diagnosis. A total of 17 publications (2011 - 2019) were identified. The practical strategies described were to provide pretest supplemental oxygenation via mechanical ventilation and extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (fraction of inspired oxygen = 1.0) and, at the beginning of the test, titrate the sweep flow (0.5 - 1.0L/minute) to minimize carbon dioxide removal. It is also recommended to increase blood flow and/or sweep flow in the presence of hypoxemia and/or hypotension, which may be combined with fluid infusion and/or the escalation of inotropic/vasoactive drugs. If the partial pressure of carbon dioxide threshold is not reached, repeating the test under supplementation of carbon dioxide exogenous to the circuit is an alternative. Last, in cases of venoarterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, to measure gas variation and exclude differential hypoxia, blood samples of the native and extracorporeal (post-oxygenator) circulations are recommended.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2019;31(3):303-311
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20190055
To evaluate the medical knowledge regarding the application of the diagnostic criteria for brain death and to correlate it with training parameters for this diagnosis according to Federal Council of Medicine resolution 2,173 of 2017.
We interviewed 174 physicians with experience with comatose patients. A structured questionnaire adapted from previous studies was used. The associations of the variables were tested using the chi-square test for independence. A multivariate logistic model was fitted for associations with p values ≤ 0.20.
Among the interviewees, 40% had been working for more than 1 year in intensive care, and 23% had initiated ten or more brain death protocols complying with the new resolution. Forty-five percent of the interviewees reported having difficulty following the criteria, 94% acknowledged the need for complementary tests for diagnosis, and 8% of them reported the existence of incorrect tests. The difficulty with these criteria decreased with an increase in the number of years of medical training (OR = 0.487; p = 0.045; 95%CI 0.241 - 0.983) and with a higher number of initiated brain death protocols (OR = 0.223; p = 0.0001; 95%CI 0.117 - 0.424).
Difficulties in the application of brain death criteria were identified by a significant portion of the sample. However, among other factors, more years of training and a greater number of initiated brain death protocols were associated with greater ease in the application of brain death criteria according to the guidelines provided in Resolution 2,173 of the Federal Council of Medicine.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2019;31(3):403-409
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20190050
Brain death, defined as the complete and irreversible loss of brain functions, has a history that is linked to the emergence of intensive care units and the advancement of artificial ventilatory support. In Brazil, by federal law, the criteria for the diagnosis of brain death have been defined by the Federal Council of Medicine since 1997 and apply to the entire Brazilian territory. Resolution 2,173/2017 of the Federal Council of Medicine updated the criteria for diagnosing brain death. These changes include the following: the requirement for the patient to meet specific physiological prerequisites and for the physician to provide optimized care to the patient before starting the procedures for diagnosing brain death and to perform complementary tests, as well as the need for specific training for physicians who make this diagnosis. Other changes include the reduction of the time interval between the two clinical examinations, the possibility of continuing procedures in the presence of unilateral ear or eye injury, the performance of a single apnea test and the creation of a statement of brain death determination that includes the recording of all procedures in a single document. This document, despite the controversy surrounding it, increases the safety necessary when establishing a diagnosis of such importance and has positive implications that extend beyond the patient and the physician to reach the entire health system.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2014;26(3):240-252
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20140035
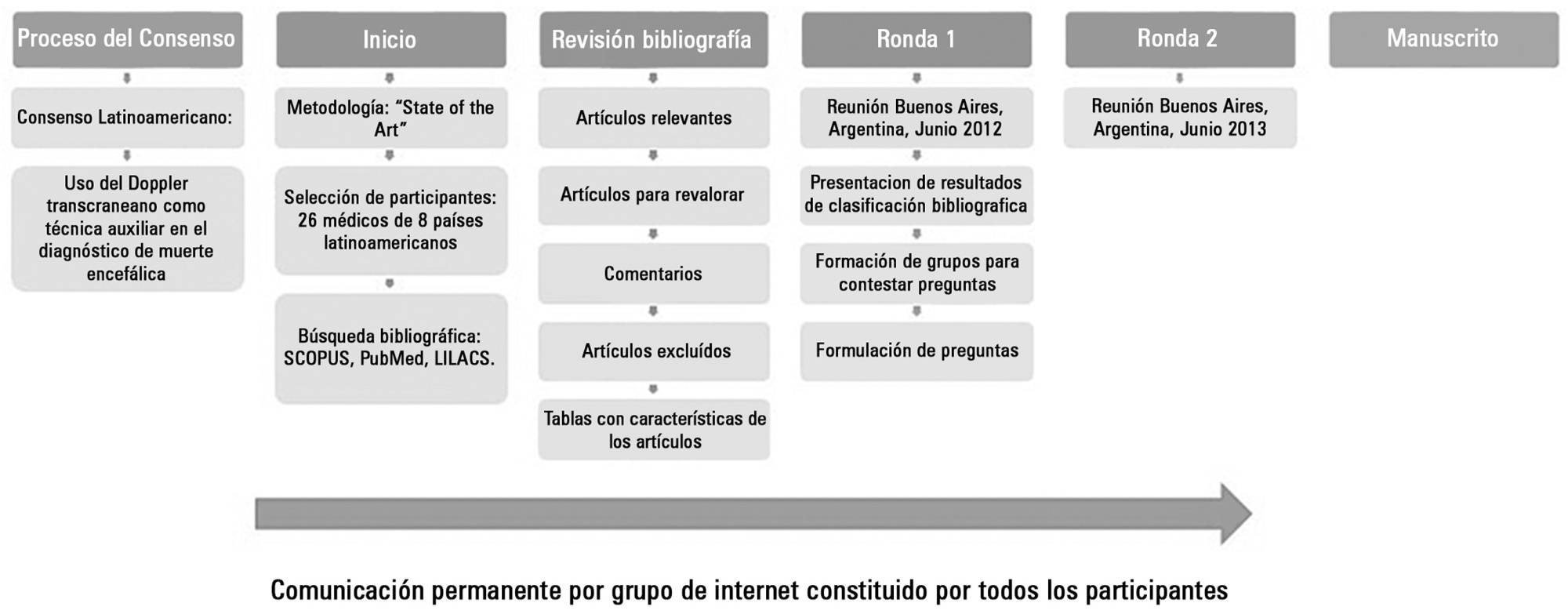
Transcranial Doppler evaluates cerebral hemodynamics in patients with brain injury and is a useful technical tool in diagnosing cerebral circulatory arrest, usually present in the brain-dead patient. This Latin American Consensus was formed by a group of 26 physicians experienced in the use of transcranial Doppler in the context of brain death. The purpose of this agreement was to make recommendations regarding the indications, technique, and interpretation of the study of transcranial ultrasonography in patients with a clinical diagnosis of brain death or in the patient whose clinical diagnosis presents difficulties; a working group was formed to enable further knowledge and to strengthen ties between Latin American physicians working on the same topic.
A review of the literature, concepts, and experiences were exchanged in two meetings and via the Internet. Questions about pathophysiology, equipment, techniques, findings, common problems, and the interpretation of transcranial Doppler in the context of brain death were answered. The basic consensus statements are the following: cerebral circulatory arrest is the final stage in the evolution of progressive intracranial hypertension, which is visualized with transcranial Doppler as a "pattern of cerebral circulatory arrest". The following are accepted as the standard of cerebral circulatory arrest: reverberant pattern, systolic spikes, and absence of previously demonstrated flow. Ultrasonography should be used - in acceptable hemodynamic conditions - in the anterior circulation bilaterally (middle cerebral artery) and in the posterior (basilar artery) territory. If no ultrasonographic images are found in any or all of these vessels, their proximal arteries are acceptable to be studied to look for a a pattern of cerebral circulatory arrest.
Search
Search in:
Case reports (56) Child (53) Coronavirus infections (34) COVID-19 (46) Critical care (116) Critical illness (54) Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (26) Infant, newborn (27) Intensive care (72) Intensive care units (256) Intensive care units, pediatric (31) mechanical ventilation (38) Mortality (76) Physical therapy modalities (28) Prognosis (61) Respiration, artificial (119) Respiratory insufficiency (26) risk factors (34) SARS-CoV-2 (28) Sepsis (98)