Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2007;19(3):322-326
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2007000300009
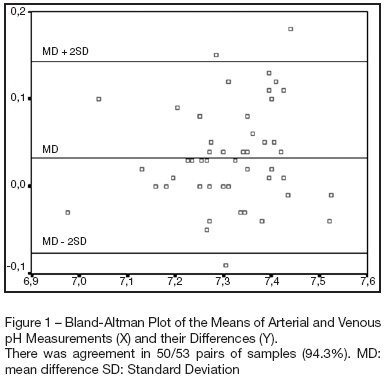
BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: Determine the extent of agreement and correlation between arterial samples and venous (obtained from a venous umbilical catheter), with respect to measurements of pH, bicarbonate, base excess and lactate, in critically ill term and premature newborns. METHODS: Arterial blood samples (0.5-1 mL) were obtained for gas analysis by radial artery puncture, and, within the limit of 5 minutes, samples were obtained from venous umbilical catheters. Bland-Altman plots were used to depict agreement between arterial and venous measurements. Limits of agreement were defined as the mean difference ± 2SD (Standard Deviation). Correlation was assessed by Pearson's method. RESULTS: A hundred and six samples (53 pairs) were taken from 53 patients for analysis of bicarbonate, pH and base excess. Lactate was analyzed in 49 pairs of samples. Differences were within the limits of agreement in 94.3% of pairs of samples for pH, and the same percentage was observed for bicarbonate. There was agreement in 96.2% of pairs for base excess, and in 91.8% for lactate. Mean differences were 0.03 units for pH, -1.2 mmol/L for bicarbonate, -0.24 mmol/L for base excess and 0.33 mmol/L for lactate. Pearson's correlation coefficients (r) were 0.87 for pH, 0.76 for bicarbonate, 0.86 for base excess and 0.95 for lactate. CONCLUSIONS: Although single venous values cannot be used as equivalent to arterial for assessing acid base status in newborns, venous blood samples can be used serially for monitoring trends over time.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2007;19(3):327-330
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2007000300010
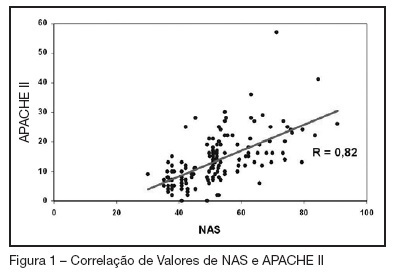
BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: Searching the literature, we found no studies which correlate the NAS (Nursing Activities Score), who determines the real time of nursing evaluation and patient care, with mortality for prognostic index. The objectives this study were to know the values of the NAS score at ours service, try to find correlations between this values and the APACHE II index and to analyze the mortality rates with NAS scores. METHODS: This is a prospective ICU inpatient study from July to November/2005. Our data's of the APACHE II score were recorded from the QuaTI system study. Qui-square test or equivalent was done to compare the proportions. For the analyses we utilized the EPI-INFO-6 software. RESULTS: The sample was 148 patients, mean age of 55.5 years with 59.4% males. The mean hospitalization time were 9.1 days, mortality rate of 29.7%, mean NAS score of 51.5% and mean APACHE II score of 13.4. There were a positive correlation ship between NAS and APACHE II index (R = 0.82). Selecting only the patients with NAS more than 51 we found that 41 in 83 died and 42 in 83 survived. Those whose NAS were under 51, only 3 in 65 died and 62 in 65 survived (p < 0.005), identifying an statistically significant group. CONCLUSIONS: In this study the mean value of NAS were 51.5%. There were good correlation with the APACHE II index and we shown that the mortality rate was high in the higher NAS values.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2007;19(3):331-336
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2007000300011
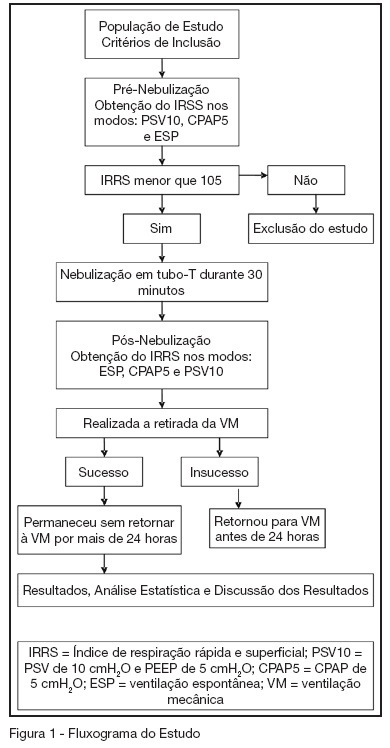
BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: To compare the attainment of the rapid shallow breathing index (IRRS) in modalities PSV 10 cmH2O and PEEP 5 cmH2O (PSV10), CPAP 5 cmH2O (CPAP5) and spontaneous breathing (SB), correlating them with success on failure in the withdrawal of mechanical ventilation (MV). METHODS: Prospective study including 54 patients in MV > 48 hours, submitted to the IRRS in three ventilatory modalities: PSV10, CPAP5 and SB at the moments before and after T-tube spontaneous breathing. The patients were removed from MV when IRRS was < 105. RESULTS: There wasn't statistically significant difference between IRRS values at the moments before and after T-tube SB. There was statistically significant difference IRRS value between the modalities CPAP5 and PSV10 (p = 0.008), and between the modalities SB and PSV10 (p = 0.01) at the moment before T-Tube SB and of IRRS value, gotten between CPAP5 and PSV10 (p = 0.01) at the moment after T-tube SB. CONCLUSIONS: From this sample, it can be observed that IRRS values are overestimated when gotten in modality PSV10. It was also evidenced that there is no need of a 30 min T-tube SB before extubation, when the weaning is performed with the technique of gradual reduction of PSV. This study suggested that IRRS is able to predict weaning success; however it is not able to determine failure when it was < 105. It is recommended that IRRS must be analyzed in association with other predictive weaning parameters.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2007;19(3):337-341
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2007000300012
BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: Pressure ulcers (PU) constitute an important health problem in particular in the intensive care unit (ICU). The objective of the study was to identify the number, degree and total score of PU on admission, ICU stay and discharge as well as to recognize factors influencing the appearance or development of PU and to identify the number of healed PU, thus so the incidence and prevalence. METHODS: All patients admitted > 24 hrs were prospectively included during one year. Seventy patients were excluded for insufficient data. The prevention protocol (Norton scale; positioning according the risk grade) and therapeutic protocol (hydrocolloid dressings; hydrogel dressings if tissue necrosis and/or devitalized and alginate dressings if ulcer bleeds) was applied to all patients. RESULTS: One hundred and fifty five patients were studied. Eighteen patients were admitted already with PU. During ICU stay, 40 patients developed a total of 125 PU. The prevalence of PU was 37.41% and incidence was 25.8%. The development of new PU occurred on average by the 7th day. Patients with PU presented 2.6 PU on the average. Seventy nine percent of the patients admitted in the ICU remained stable or improved. Patients admitted with PU had a SAPS 2 significantly higher than those without, 54 ± 8.7 and 44 ± 17, respectively (p = 0.015). At the day of discharge, patients classified as high risk had significantly more PU (p = 0.039). Non-survivors had significantly more PU than survivors (p < 0.001). Patients with longer ICU stay had more PU (p < 0.001) CONCLUSIONS: In our patient population we found 37.41% prevalence and 25.8% incidence of PU. The present prevention protocol of PU was effective in 79% of the patients; severely ill patients developed PU more frequently.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2007;19(3):342-347
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2007000300013
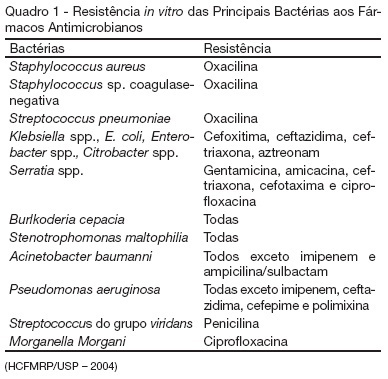
BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: Care in the intensive care unit (ICU) is constantly challenged by infections related to invasive procedures, which result in increased morbidity and mortality, hospitalization term and costs. This study aimed to prospectively evaluate critical patients according to age, clinical conditions, hospitalization term, occurrence of hospital infection, topography of hospital infection, occurrence of microbial multi-resistance or not, use of invasive procedures and antimicrobial agents. METHODS: This is a prospective, observational, clinical research, carried out at an ICU between February and July 2006. The research subjects were critical patients hospitalized for more than 24 hours at the ICU, followed from admission until discharge, transference or death. RESULTS: The study group consisted of 71 patients with a mean age of 53.5 ± 18.75 years. Forty-seven of these patients (66.2%) acquired hospital infection. Twenty-nine infections (37.6%) occurred in the blood stream, 20 (26%) respiratory and 13 (16.9%) urinary. The most frequent multi-resistant strains were: 14 (10.85%) Pseudomonas aeruginosa, 4 (3.1%) coagulase-negative Staphylococcus sp and 4 (3.1%) Staphylococcus aureus. The most used antimicrobial agents were carbapenem (22.4%), glycopeptides (21.6%) and cephalosporin (21.6%). Twenty-nine (40.8%) of these patients died. CONCLUSIONS: Hospital infection is aggravated if associated to the increased resistance of the microorganisms to the antibiotics.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2007;19(3):348-353
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2007000300014
BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: Each intensive care units result has to be observed in the context of medical care, as well as the institution witch it belongs. There are many types of prognostic index in intensive care. The APACHE II was introduced by Knaus et al. in 1985, being a widely used system to evaluate the illness severity in intensive care patients. This objective was evaluated the prognostic index (APACHE II) in patients submitted to elective or emergency gastrointestinal surgery admitted to the ICU. METHODS: Medical school intensive care unit. It was collected the following data: age, sex, length of stay, intensive care indication, type of surgery (elective or emergency), body mass index (BMI) APACHE II and predicted mortality. RESULTS: A total of 38 patients data were collected during the period of April 2005 to April 2006. Eighteen patients died and twenty survived. The age of the non-survivors varied from 44 to 92 (mean age 66.6); while the age of the survivors varied from 28 to 78 (mean age 59. 1). The BMI of the non-survivors varied from 22 to 29 (mean body mass index 26) while in the other group the mean body mass index was 25. 6. No significant difference was noted in the age and body mass index of both groups. The length of stay varied from 2 to 52 days in the non-survivors group (mean 11.3 days), while in the survivors group varied from 1 to 30 days (mean 4.9). The APACHE II varied from 5 to 32 in the non-survivors group (mean 19.14). While in the survivors group varied from 1 to 18 (mean 8.6). The length of stay and APACHE II demonstrated a significant difference in both groups, being higher in the non-survivors group. The non-survivors predicted mortality varied from 3.1 to 84.9 (mean 38.8); while the survivors mean was 7.5. The Standardized Mortality Rate in this study was 1.22. CONCLUSIONS: Non-survivors patients APACHE II was higher than the survivors; the SMR was similar to others studies; the length of stay was longer in the non-survivors group; no statistic difference was noted in the body mass index.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2007;19(3):354-356
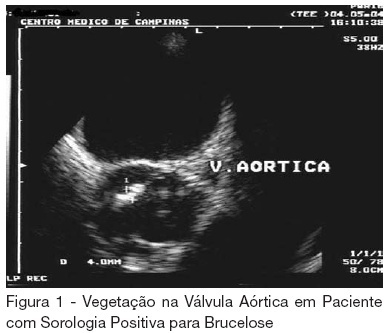
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2007000300015
BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: Endocarditis is a rare and serious complication of human brucellosis. The diagnosis is suspected in cases of endocarditis without response to conservative antibiotic treatment and it is confirmed with enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) test, titers being higher than 1:160. The treatment is usually a surgery, followed with antibiotics for long period of time. Some cases can be cured with antibiotic treatment only, with antibiotics such as doxiciclin, rifampicin, ciprofloxacin, gentamicin and tetracycline. We present a case report of a patient with brucellose endocarditis. CASE REPORT: Fifty one year old male patient, a farmer, was admitted with clinical history of fever and weight loss. Echocardiography showed thickening and vegetation on the aortic valve and blood culture was positive for Staphylococcus epidermidis. The treatment with crystal penicillin and garamycin was initiated with no improval during three weeks. Endocarditis caused by human brucellosis was suspected and a new treatment with rifampicin and ciprofloxacin, associated with vancomycin because of the first blood culture, was initiated. Agglutination sorology was positive for brucellosis, with titers of 1:360. The patient got better with new treatment and was dismissed from the intensive care unit clinically stable, taking ciprofloxacin and gentamicin. CONCLUSIONS: Endocarditis caused by human brucellosis is rare; however it should always be considered when conservative antibiotic treatment fails, especially in patients that have contact with animals and dairy products.