Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2006;18(2):121-125
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2006000200003
BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: Weaning from mechanical ventilation (MV) is an important strategy to reduce morbidity and mortality in critical care patients. In this setting, this study aimed at evaluation of T-tube trial (TT) in weaning from MV. METHODS: Patient admitted in the ICU were included if they present the following inclusion criteria: MV > 24 hours, no neuromuscular disorders, PaO2/FiO2 ratio >200, hemodynamic stability, reversion of the cause of respiratory failure, adequate respiratory drive. All were submitted to TT. Failure was defined by the presence of one of these symptoms: RR > 30 ipm, hypoxemia, tachycardia, arrhythmia, hypertension or hypotension. After two hours of TT, patients without failure criteria were extubated. After 48 hours of adequate spontaneous respiration the patient was considered successful weaned. Results were considered significant if p < 0.05. RESULTS: Forty-nine patients were included with a mean age 51.8 ± 21.7 years. The incidence of ARDS and septic shock were 26.5% and 32.7% and mean duration of MV was 11.9 ± 13 days. Discontinuation of MV occurred in 79.2%, reintubation in 31.6%, in a mean time of 13 ± 8.7 hours and in 75% of the cases it was due to respiratory failure. There was no correlation between success in TT and hemoglobin levels, PaO2/FiO2 ratio, age, gender, prior ARDS or septic shock. Weaning success was not correlated with none of the above variables. CONCLUSIONS: TT was adequated for weaning from mechanical ventilation in the majority of the cases. However, reintubation rate was high. Possible causes are the long period of TT, prior mechanical ventilation or the failure in the criteria used to indicate extubation.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2007;19(3):331-336
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2007000300011
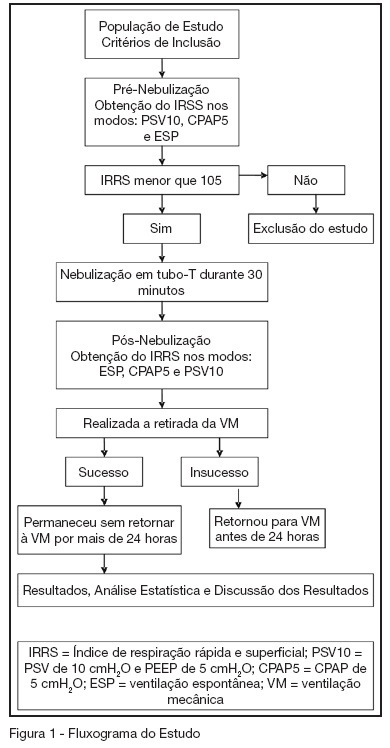
BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: To compare the attainment of the rapid shallow breathing index (IRRS) in modalities PSV 10 cmH2O and PEEP 5 cmH2O (PSV10), CPAP 5 cmH2O (CPAP5) and spontaneous breathing (SB), correlating them with success on failure in the withdrawal of mechanical ventilation (MV). METHODS: Prospective study including 54 patients in MV > 48 hours, submitted to the IRRS in three ventilatory modalities: PSV10, CPAP5 and SB at the moments before and after T-tube spontaneous breathing. The patients were removed from MV when IRRS was < 105. RESULTS: There wasn't statistically significant difference between IRRS values at the moments before and after T-tube SB. There was statistically significant difference IRRS value between the modalities CPAP5 and PSV10 (p = 0.008), and between the modalities SB and PSV10 (p = 0.01) at the moment before T-Tube SB and of IRRS value, gotten between CPAP5 and PSV10 (p = 0.01) at the moment after T-tube SB. CONCLUSIONS: From this sample, it can be observed that IRRS values are overestimated when gotten in modality PSV10. It was also evidenced that there is no need of a 30 min T-tube SB before extubation, when the weaning is performed with the technique of gradual reduction of PSV. This study suggested that IRRS is able to predict weaning success; however it is not able to determine failure when it was < 105. It is recommended that IRRS must be analyzed in association with other predictive weaning parameters.