Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2008;20(1):43-48
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2008000100007
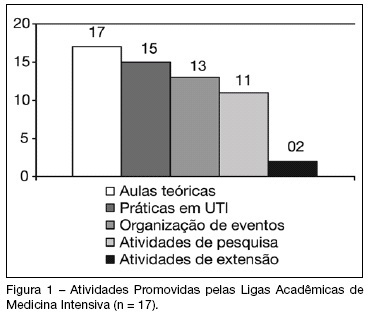
BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: The Brazilian Intensive Care Medicine Association (AMIB) has been stimulating the creation of undergraduate associations/study groups on Critical Care Medicine (CCM), considering them a useful instrument to fill gaps in professional formation. The aim of this study was to evaluate the activities developed by CCM undergraduate study groups in Brazil. METHODS: The analyzed information was obtained on answers to a standard questionnaire. Contact by e-mail and/or telephone was made with representatives of all study groups registered on AMIB Committee of Undergraduate Study Groups on CCM (LIGAMI-AMIB) in September of 2007. In that period, there were 33 groups associated to LIGAMI, which 4 doesn't exist anymore, 17 answered to the sent questionnaire and the remaining 12 didn't answer the questionnaire or it was not obtained contact. RESULTS: Most study groups were founded after 2005, coinciding with the LIGAMI-AMIB Committee creation, and they are linked to one or more medical schools. Among the group's activities, the most frequent was theoretical classes (100%), usually supplied by teachers or invited physicians (69%). Other activities include practices on Intensive Care Units (88%), organization of scientific events (77%) and research projects (65%). Most study groups (65%) had already organized some scientific event such as courses and symposia; however, only three had already accomplished the AMIB CCM Introductory Course. CONCLUSIONS: The growing number of CCM undergraduate study groups in Brazil demonstrates students' interest for this specialty. Besides, there is a necessity of larger integration between existing groups to change experiences, cooperate in the accomplishment of research projects and participation on national and international events.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2008;20(1):68-76
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2008000100011
BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: In this study we discuss about risks to health of intensive care unity staff and suggest a proposal of integral approach of health. CONTENTS: Literature review, from 1997 to 2007, at Bireme database about "health education", "intensive care unity", "nursing" and "occupational health", regardless of design of study. CONCLUSIONS: All studies show that the environment of intensive care unity is unhealthy, which is also due to habits and attitudes of ICU health professionals. An approach to health education would be beneficial to minimize the problem. Strategies for continuing education are appropriate both in the prevention of occupational and environmental risks in intensive care units.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2008;20(1):106-109
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2008000100018
BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: Infection with the non-Candida yeast species Trichosporon have been recognized with increasing frequency over the last two decades. Invasive disease due to trichosporonosis has been reported from neutropenic patients with cancer and the mortality is high. Recently, others groups of patients have become susceptible to this rare fungi. We report the emerging of infection with pathogenic Trichosporon asahii in severely ill heart failure patients in a tertiary cardiological intensive care unit (CICU). We describe our data, and report a fatal case of disseminated trichosporonosis in a patient with heart failure. We also review literature pertaining to T. asahii infections. CASE REPORT: An 85 year-old woman with a history of hypertension, heart failure (ejection fraction (EJ): 30%) and pulmonary embolism was admitted to a medical cardiological ICU after cardiac arrest (ventricular fibrillation) resuscitated during a routine consultation. There were no neurological sequelae and the echocardiogram revels no changes, neither the cardiac biomarkers. Ventricular fibrillation was considered secondary to heart failure. The patient had extubation failure and difficult weaning needing long term mechanical ventilation even after tracheostomy. Her hospital course was complicated by acute renal failure and recurrent respiratory, urinary and systemic bacterial infections, which responded to broad-spectrum antibiotics. After a temporary improvement she developed urinary infection and subsequent septic shock. Cultures of urine and blood specimens grew T. asahii. Treatment with liposome amphotericin B (5 mg/kg/day) was started. Despite receiving vancomycin and imipenem, the clinical condition of the patient deteriorates. Blood taken for culture on the seventh day of amphotericin B therapy were negative but urine specimen still grew T. asahii. On the eighteenth day of antifungal therapy, the patient died with multiorgan failure. CONCLUSIONS: The increasing of severely ill patients, and the use of broad spectrum antibiotics, has predisposed the emerging of invasive infections by rare and new opportunistic fungal pathogens. Severe infection related to T. asahii, until recently restricted to neutropenic patients with cancer, has been frequently identified in heart failure patients with advanced age. The mortality is high. These data highlights the importance of considering this group of patients as a risk group for T. asahii infection.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2006;18(4):412-417
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2006000400016
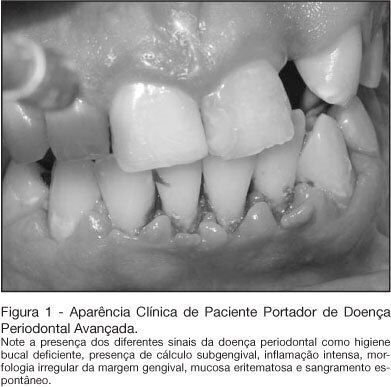
BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: In the intensive care unit, the nosocomial respiratory infection is responsible for high rates of morbidity, mortality and expressive increase in hospitals costs. Its establishment feels more commonly by the aspiration of the content present within the mouth and the pharynx. Thus we intended to review the literature on the participation of the oral condition in the establishment of the nosocomial respiratory infection. CONTENTS: Deficient oral hygiene is common in patients under intensive care, which provides the colonization of oral biofilm for pathogenic microorganisms, especially for respiratory pathogens. The studies clearly show that the amount of oral biofilm in patients under intensive care increases according to period hospitalization meanwhile there also is an increase in respiratory pathogens. That colonizes the oral biofilm. This biofilm is an important resource of pathogens in patients under intensive care. CONCLUSIONS: In spite of well-established hypotheses that narrow down the relationships between lung infections and the oral condition, the studies are not still completely defined. However, due to strong possibilities that these hypotheses are true, it is necessary to have and maintain the oral health, in addition to more integration of dentistry and of Medicine, seeking patients' global treatment, the prevention of diseases, and more humanization at the intensive care unit.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2007;19(4):434-436
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2007000400005
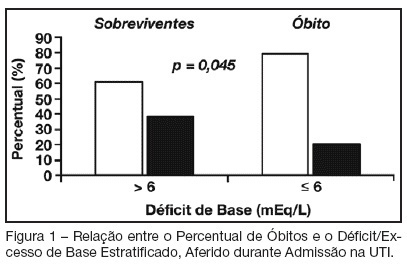
BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: Base deficit is considered an indicator of tissue injury, shock and resuscitation. The objective of this study was to establish an association between base deficit obtained on the admission of patients in intensive care unit (ICU) and their prognosis. METHODS: A retrospective study with analysis of 110 patients admitted consecutively in the ICU, during the period of June to December 2006. RESULTS: There was a predominance of women, with age mean 54.2 ± 18.7 years old. Length of stay in ICU was 6.5 ± 7.4 days and the mean APACHE II score was 21 ± 8.1 points. The standardized mortality ratio was 0.715. Mortality was higher in patients with base deficit > 6 mEq/L (38.9%) than in those with base deficit < 6 mEq/L (20.6%); p < 0.05. Patients with early mortality had lower base deficit (7.75 ± 8.33 mEq/L) than survivors (3.17 ± 5.43 mEq/L); p < 0.05. Patients with permanence in ICU until 7 days and patients that stayed in this unit for more than 7 days had similar base deficit. CONCLUSIONS: Base deficit had been associated with early mortality during ICU internment. Base deficit > 6 mEq/L is a marker of significant mortality.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2007;19(4):485-489
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2007000400014
BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: The suffering with the death and the prolonged time of patient's admission in a intensive care unit (ICU) are factors that leads to necessity the best communication with the personal that works in ICU, patients and their family, and its justify this work, whose objective is discuss this subject. CONTENTS: The professional experience of the author was used in this issue and the articles written during the last five years about death, communication and ICU were reviewed by means of MedLine, Up to Date, Google and Brazilian Journal of Intensive Therapy. CONCLUSIONS: It was concluded that the physician, the patient together with her/his family, and the multiprofessional staff of the ICU is one of the main factors that interferes with the process of satisfying both the patient and the ones who work on such unities. For adequate information, the physician must be conscious about therapeutic limits, and must learn how to treat the patient during the process of dying. In this way, the physician will be apt to talk about death. The ideal situation would be that the professional, responsible to give the news, should be experience, from the technical point of view as well as ethical, and should be the same person, as always as possible, when necessary. The patient mostly little be able to influence in her/his process of dying, but if communication is possible, it be simple, honest and humane. The patient's family members have the right of being together with the one who they love, and of being steadily informed about the real situation. All the members in the process must know the truth and the chosen therapeutic orientation to be taken. Communication should be done in a quiet and prived place.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2007;19(4):444-449
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2007000400007
BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: To assess the incidence of tracheostomy in patients submitted to mechanic ventilation (MV); to compare the length of stay (LOS), duration of MV, APACHE II and mortality among patients submitted to tracheostomy, according to the moment of its application (early or late). METHODS: A retrospective observation study type cohort was done from April thru October 2005 including 190 patients at the adult intensive care unit (ICU) of Hospital Estadual do Grajaú. RESULTS: Among the 190 patients, 32 (16.84%) were submitted to tracheostomy with a longer LOS (30.16 days) as compared to those that were not (p < 0.001). The mean time of the tracheostomy procedure was 13.5 days from the starting of the MV. It is known that there still is no guidance for defining an ideal period for the operation. On this study, the prevalence of early tracheostomy (<13 days) was 46.87% (n = 15) and the late tracheostomy (> 13 days) was 53.13% (n = 17). In a meaningful way, the patients with early tracheostomy obtained APACHE II superior to those with late tracheostomy (18.2 versus 13.47), however there was no difference regarding the mortality rate. There was no difference regarding the time of ICU LOS (28.9 versus 31.28 days) and the MV time (29.73 versus 32.23 days) for both groups. CONCLUSIONS: The incidence of tracheostomy was high, being associated to a smaller ICU mortality but with a longer LOS and more complications. There was no significant difference regarding the destination of the patients when submitted to early or late tracheostomy.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2007;19(4):450-455
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2007000400008
BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: The headquarters of mechanical fans is the unit of the hospital with purpose of organizing ventilation resources promoting control and preventive maintenance and organizational of these equipments. The objective of this study was to elaborate a proposal of implantation of a headquarters of mechanical fans in an academical hospital, subsidized by the identification of the male nurse's scientific technical knowledge on the theme ventilation mechanics and for the detection of problems originating from of the decentralized administration of the fans. METHODS: It is treated of exploratory descriptive study with quantitative approach, accomplished with 13 male nurses of ICU. The information was collected through structured interviews and submitted the descriptive analysis of the content. RESULTS: The results reveal that the male nurses possess several doubts, fact evidenced by 100% of the interviewees that mentioned the need of training courses gone back to the nursing attendance to the patient in ventilation mechanics. The situations described by the male nurses in the daily they demonstrate that the decentralization of the administration of the mechanical fans is shown ineffective as the organization, safety and quality. The proposal of implantation of a headquarters of fans appears for improvements in the attendance, in the formation of human resources and in the production of the knowledge. CONCLUSÕES: It is ended that the current profile can be changed through the breaking of institutional paradigms and of the institution of innovative practices that you/they will reinforce the purpose of a hospital of great load gone back to teaching, he/she researches and extension.