Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2021;33(1):138-145
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20210015
To double the percentage of time within the 100 - 180mg/dL blood glucose range in the first three months following a phased implementation of a formal education program, and then, of an insulin therapy protocol, without entailing an increased incidence of hypoglycemia.
The pre-intervention glycemic control was assessed retrospectively. Next, were carried out the implementation of a formal education program, distribution of manual algorithms for intravenous insulin therapy - optimized by the users, based on the modified Yale protocol - and informal training of the nursing staff. The use of electronic blood glucose control systems was supported, and the results were recorded prospectively.
The first phase of the program (formal education) lead to improvement of the time within the euglycemic interval (28% to 37%). In the second phase, euglycemia was achieved 66% of the time, and the incidence of hypoglycemia was decreased. The percentage of patients on intravenous insulin infusion at 48 hours from admission increased from 6% to 35%.
The phased implementation of a formal education program, fostering the use of electronic insulin therapy protocols and dynamic manuals, received good adherence and has shown to be safe and effective for blood glucose control in critically ill patients, with a concomitant decrease in hypoglycemia.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2014;26(1):71-76
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20140011
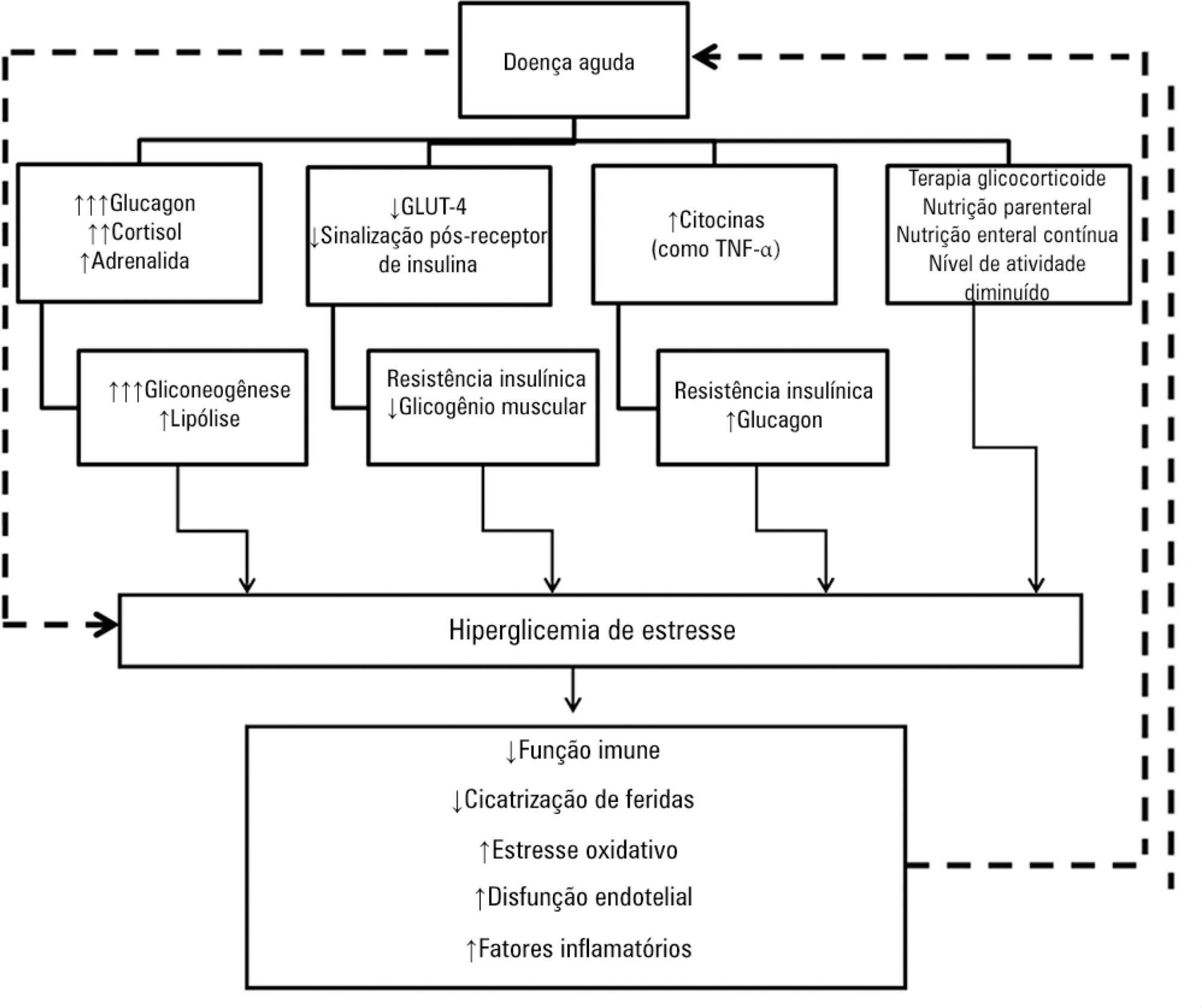
Hyperglycemia is a commonly encountered issue in critically ill patients in the intensive care setting. The presence of hyperglycemia is associated with increased morbidity and mortality, regardless of the reason for admission (e.g., acute myocardial infarction, status post-cardiovascular surgery, stroke, sepsis). However, the pathophysiology and, in particular, the treatment of hyperglycemia in the critically ill patient remain controversial. In clinical practice, several aspects must be taken into account in the management of these patients, including blood glucose targets, history of diabetes mellitus, the route of nutrition (enteral or parenteral), and available monitoring equipment, which substantially increases the workload of providers involved in the patients' care. This review describes the epidemiology, pathophysiology, management, and monitoring of hyperglycemia in the critically ill adult patient.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2007;19(4):490-493
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2007000400015
BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: Hepatic infarction is characterized by parenchyma ischemic necrosis involving at least two acinis. It is extremely uncommon due to the arterial and portal venous blood supply. We report a case of a patient not know to have diabetes who developed massive areas of ischemic infarcts of the liver after episode of acutely diabetes decompensated. CASE REPORT: A 67 year-old hypertensive female who has been presenting, for the last 10 days, polydipsia, high urinary volume, visual and gait impairment, nausea and vomiting was admitted to the emergency room (ER). During the physical examination it was observed dehydration, skin discoloration, peripheral cyanosis, hypothermia, tachycardia, hypotension and mild diffuse abdominal pain. Admissional laboratory exams demonstrated total leukocytes: 16.800, Cr: 3.7, Ur: 167, Na: 133, K: 6.9, glucose: 561; arterial gasometry (O2 catheter: 2 L/min): pH: 6.93, pCO2: 12.1, pO2: 107, B.E.: -28.8, HCO3: 2.4, Sat 91.3%, lactato: 79; urinalysis: pH: 6; leukocytes: 13; density: 1015; erythrocytes: 19; protein: ++; glucose: +++; bilirubin: negative; ketonic bodies: + denote ketonemia. EKG: sharp T wave, right branch block. Patient was treated with intravenous insulin, hydration, sodium bicarbonate and ceftriaxone. After initial treatment, the laboratory exams showed Cr: 2.2, Ur: 122, Na: 162, K: 4.3, Ca: 6.4, glucose: 504, pH: 7.01, HCO3: 7.1, B.E.: -22. One day after admission the patient presented with important abdominal pain and peritoneal irritation, followed by difficulty for talking and somnolence; routine laboratory exams showed arterial gasometry: pH: 7.4, pCO2: 31, pO2: 68, BE: -4.4, HCO3: 19, SatO2: 93.5%; Ur: 95,Cr: 1.4, albumin: 2.4, Ca: 0.95, Na: 166, K:4, bilirubin: 0.5, bilirubin D/I: 0.2/0.3, Amylase: 1157, Gamma-GT: 56, AST 7.210, ALT: 2.470, SR (sedimentation rate): 15, Lipase: 84. Abdominal ultrasound was unremarkable. Patient respiratory function and conscience level worsened, requiring intubation. Despite all resuscitation efforts, she died. Necropsy showed multiple ischemic infarcts of the liver with vascular thrombosis, splenic infarcts, generalized visceral congestion and atherosclerosis of aorta and its branches. Pancreas was normal. CONCLUSIONS: The mechanisms of hepatic and splenic infarctions in this case were unclear. The following factors may have contributed to necrosis: vomiting and fever should be considered to induce dehydration and hypotension, which further decreased portal and hepatic arterial inflows; elevated level of catecholamine in hyperglycemic states might induce vasoconstriction effects; widespread atherosclerosis is commonly seen in diabetic and hypertensive patients. This case underlies the importance of searching for hepatic necrosis or infarction in any diabetic patient with elevated liver enzymes. Anticoagulation therapy should be instituted promptly upon recognition of vascular thromboses.

Search
Search in:
Case reports (56) Child (53) Coronavirus infections (34) COVID-19 (46) Critical care (116) Critical illness (54) Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (26) Infant, newborn (27) Intensive care (72) Intensive care units (256) Intensive care units, pediatric (31) mechanical ventilation (38) Mortality (76) Physical therapy modalities (28) Prognosis (61) Respiration, artificial (119) Respiratory insufficiency (26) risk factors (34) SARS-CoV-2 (28) Sepsis (98)