Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2011;23(1):78-86
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2011000100013
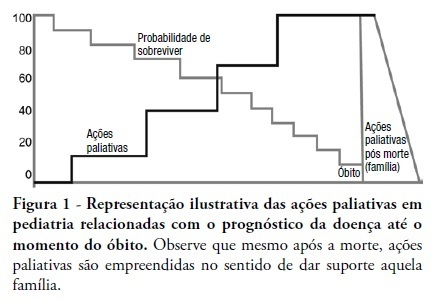
This review discusses the main dilemmas and difficulties related to end-of-life decision's in children with terminal and irreversible diseases and propose a rational sequence for delivering palliative care to this patients' group. The Medline and Lilacs databases were searched using the terms 'end of life', 'palliative care', 'death' and 'terminal disease' for articles published in recent years. The most relevant articles and those enrolling pediatric patients were selected and compared to previous authors' studies in this field. The current Brazilian Medical Ethics Code (2010) was analyzed regarding end-oflife practices and palliative care for terminal patients. Lack of knowledge, insufficient specific training, and legal concerns are the main reasons why end-of-life decisions in terminal children are based on medical opinion with scarce family participation. The current Brazilian Medical Ethics Code (2010) fully supports end-of-life decisions made consensually with active family participation. Honest dialogue with the family regarding diagnostic, prognostic, therapeutic and palliative care measures should be established gradually to identify the best strategy to meet the child's end-of-life needs. Treatment focused on the child's welfare combined with the family's participation is the basis for successful palliative care of children with terminal diseases.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2011;23(1):87-95
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2011000100014
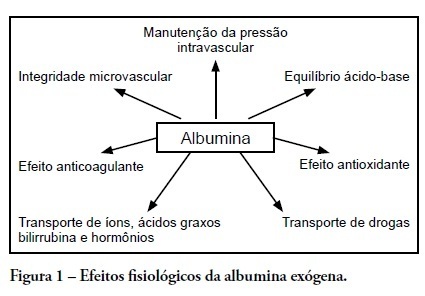
Human albumin has been used as a therapeutic agent in intensive care units for more than 50 years. However, clinical studies from the late 1990s described possible harmful effects in critically ill patients. These studies' controversial results followed other randomized controlled studies and meta-analyses that showed no harmful effects of this colloid solution. In Brazil, several public and private hospitals comply with the Agência Nacional de Vigilância Sanitária (the Brazilian Health Surveillance Agency) recommendations for appropriate administration of intravenous albumin. This review discusses indications for albumin administration in critically ill patients and analyzes the evidence for metabolic and immunomodulatory effects of this colloid solution. We also describe the most significant studies from 1998 to the present time; these reveal an absence of incremental mortality from intravenous albumin administration as compared to crystalloid solutions. The National Health Surveillance Agency indications are discussed relative to the current body of evidence for albumin use in critically ill patients.