You searched for:"Cibelle Andrade Lima"
We found (2) results for your search.-
Original Articles
Impact of fast-track management on adult cardiac surgery: clinical and hospital outcomes
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2019;31(3):361-367
Abstract
Original ArticlesImpact of fast-track management on adult cardiac surgery: clinical and hospital outcomes
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2019;31(3):361-367
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20190059
Views0ABSTRACT
Objective:
To compare the impact of two fast-track strategies regarding the extubation time and removal of invasive mechanical ventilation in adults after cardiac surgery on clinical and hospital outcomes.
Methods:
This was a retrospective cohort study with patients undergoing cardiac surgery. Patients were classified according to the extubation time as the Control Group (extubated 6 hours after admission to the intensive care unit, with a maximum mechanical ventilation time of 18 hours), Group 1 (extubated in the operating room after surgery) and Group 2 (extubated within 6 hours after admission to the intensive care unit). The primary outcomes analyzed were vital capacity on the first postoperative day, length of hospital stay, and length of stay in the intensive care unit. The secondary outcomes were reintubation, hospital-acquired pneumonia, sepsis, and death.
Results:
For the 223 patients evaluated, the vital capacity was lower in Groups 1 and 2 compared to the Control (p = 0.000 and p = 0.046, respectively). The length of stay in the intensive care unit was significantly lower in Groups 1 and 2 compared to the Control (p = 0.009 and p = 0.000, respectively), whereas the length of hospital stay was lower in Group 1 compared to the Control (p = 0.014). There was an association between extubation in the operating room (Group 1) with reintubation (p = 0.025) and postoperative complications (p = 0.038).
Conclusion:
Patients undergoing fast-track management with extubation within 6 hours had shorter stays in the intensive care unit without increasing postoperative complications and death. Patients extubated in the operating room had a shorter hospital stay and a shorter stay in the intensive care unit but showed an increase in the frequency of reintubation and postoperative complications.
Keywords:Airway extubationCardiac surgical proceduresIntensive care unitsLength of stayRespiration, artificialVital capacitySee more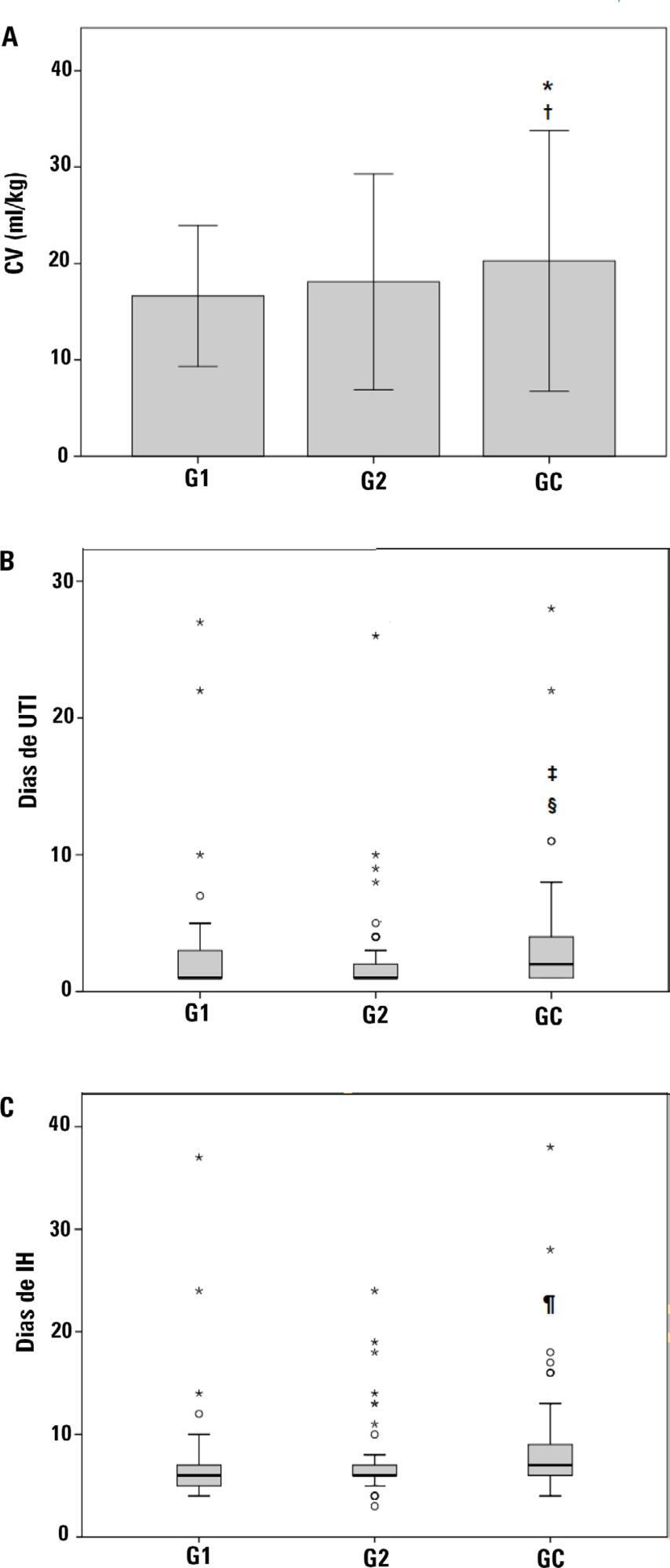
-
Influence of peripheral muscle strength on the decannulation success rate
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2011;23(1):56-61
Abstract
Influence of peripheral muscle strength on the decannulation success rate
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2011;23(1):56-61
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2011000100010
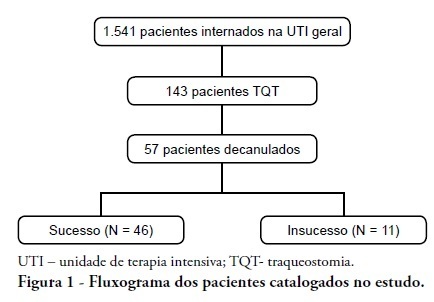
Views0See moreINTRODUCTION: Tracheostomy is probably the most common surgical procedure in critically ill patients and is generally performed to facilitate mechanical ventilation weaning. Evidence-based guidelines have confirmed the benefits of tracheostomy weaning protocols and of the physiotherapists engagement in this process; however, no consensus decannulation criteria are currently available. Therefore, this study aimed to evaluate the influence of peripheral muscle strength and other indicators on decannulation success. METHODS: This was an observational retrospective study that analyzed the medical records of patients admitted to the medical and surgical intensive care unit of Hospital Agamenon Magalhães between March 2007 and August 2009. Respiratory and peripheral muscle strengths were evaluated in decannulated patients. RESULTS: Overall, 1,541 patients were evaluated, 143 of which had been tracheostomized, and only 57 of which had been decannulated. Forty-six patients had a satisfactory decannulation outcome, while 11 had decannulation failure, requiring the return to an artificial airway within 2 weeks. The calculated Medical Research Council peripheral muscle strength score was significantly lower for the failure group than for the successful decannulation group (28.33 ± 15.31 vs. 41.11 ± 11.52; P = 0.04). Scores above or equal 26 had 94.4% sensitivity and 50.0% specificity for the decannulation outcome, with an area under the ROC curve of 0.7593. In addition, white blood cell counts were higher in decannulation failure group patients (14,070 ± 3,073 vs. 10,520 ± 3,402 cells/μL; P = 0.00). CONCLUSION: This study has shown that peripheral muscle strength and blood leucocyte counts evaluated on the day of decannulation may influence the tracheostomy decannulation success rate.
Search
Search in:
KEY WORDS
Case reports Child Coronavirus infections COVID-19 Critical care Critical illness Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation Infant, newborn Intensive care Intensive care units Intensive care units, pediatric mechanical ventilation Mortality Physical therapy modalities Prognosis Respiration, artificial Respiratory insufficiency risk factors SARS-CoV-2 Sepsis




