Abstract
Crit Care Sci. 2023;35(4):377-385
DOI 10.5935/2965-2774.20230215-pt
To evaluate the occurrence of adverse events in the postoperative period of cardiac surgery in a pediatric intensive care unit and to find any patient characteristics that can predict such events.
This was a historical cohort study of patients recovering in the pediatric intensive care unit for the first 7 days after cardiac surgery between April and December 2019, by reviewing the medical records. The following were reviewed: demographic, clinical, and laboratory characteristics; patient severity scores; and selected adverse events, grouped into device-related, surgical, and nonsurgical.
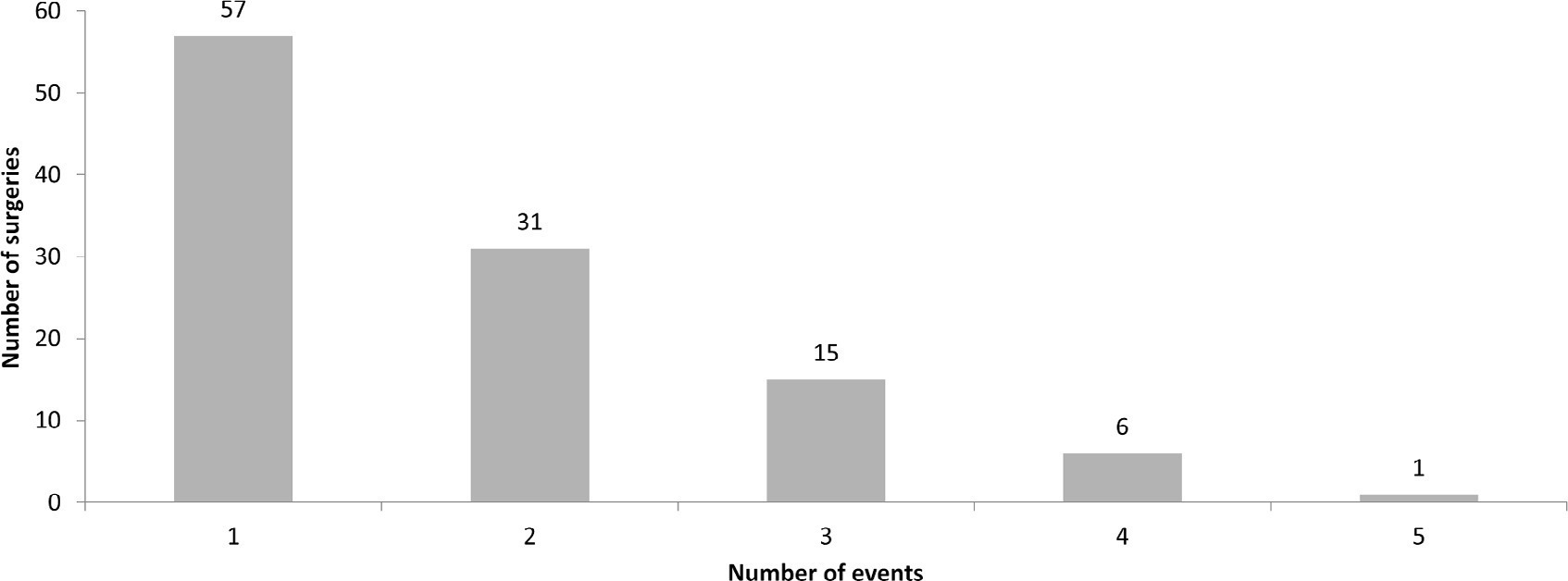
A total of 238 medical records were included. At least one adverse event occurred in 110 postoperative patients (46.2%). The total number of adverse events was 193 (81%). Vascular catheters were the most common cause, followed by cardiac arrest, bleeding, and surgical reexploration. In the univariate analysis, the vasoactive-inotropic score (VIS), Risk Adjustment in Congenital Heart Surgery (RACHS-1) score, age, Pediatric Index of Mortality (PIM-2), cardiopulmonary bypass and aortic clamping duration were significantly associated with adverse events. In the multivariate analysis, VIS ≥ 20 (OR 2.90; p = 0.004) and RACHS-1 ≥ 3 (OR 2.11; p = 0.019) were significant predictors, while age and delayed sternal closure showed only trends toward significance. To predict the occurrence of adverse events from VIS and RACHS-1, the area under the curve was 0.73 (95%CI 0.66 - 0.79).
Adverse events were quite frequent in children after cardiac surgery, especially those related to devices. The VIS and RACHS-1, used together, predicted the occurrence of adverse events well in this pediatric sample.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2022;34(3):386-392
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20220446-en
To analyze the association of patient safety culture perceived by nursing professionals with incidents recorded during nursing shifts in intensive care units.
This was a cross-sectional study that investigated patient safety culture measured by the Hospital Survey on Patient Safety Culture instrument. Descriptive statistics, chi-square tests, Student’s t-test and multiple linear regression models were analyzed considering a significance level of 5%.
The study reported a mean of 3.1 (standard deviation of 0.4) for the culture of patient safety in the perception of nursing professionals and 480 incidents with and without damage recorded during the nursing shifts. The variables patient safety culture with a difference between means of 0.543 (95%CI 0.022 - 1.065; p < 0.05) and nursing assistants with a difference between means of -0.133 (95%CI -0.192 - -0.074; p < 0.05) were associated with the incidents recorded during the nursing shifts. Further, nursing assistants had a lower tendency to record incidents than did the nurses.
The strengthening of the patient safety culture and the aspects tangential to the nursing professionals represent a possible target for interventions to encourage the recording of incidents during the nursing shift shifts and improve patient safety.
Search
Search in:
Case reports (56) Child (53) Coronavirus infections (34) COVID-19 (46) Critical care (116) Critical illness (54) Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (26) Infant, newborn (27) Intensive care (72) Intensive care units (256) Intensive care units, pediatric (31) mechanical ventilation (38) Mortality (76) Physical therapy modalities (28) Prognosis (61) Respiration, artificial (119) Respiratory insufficiency (26) risk factors (34) SARS-CoV-2 (28) Sepsis (98)