Abstract
Crit Care Sci. 2023;35(4):377-385
DOI 10.5935/2965-2774.20230215-pt
To evaluate the occurrence of adverse events in the postoperative period of cardiac surgery in a pediatric intensive care unit and to find any patient characteristics that can predict such events.
This was a historical cohort study of patients recovering in the pediatric intensive care unit for the first 7 days after cardiac surgery between April and December 2019, by reviewing the medical records. The following were reviewed: demographic, clinical, and laboratory characteristics; patient severity scores; and selected adverse events, grouped into device-related, surgical, and nonsurgical.
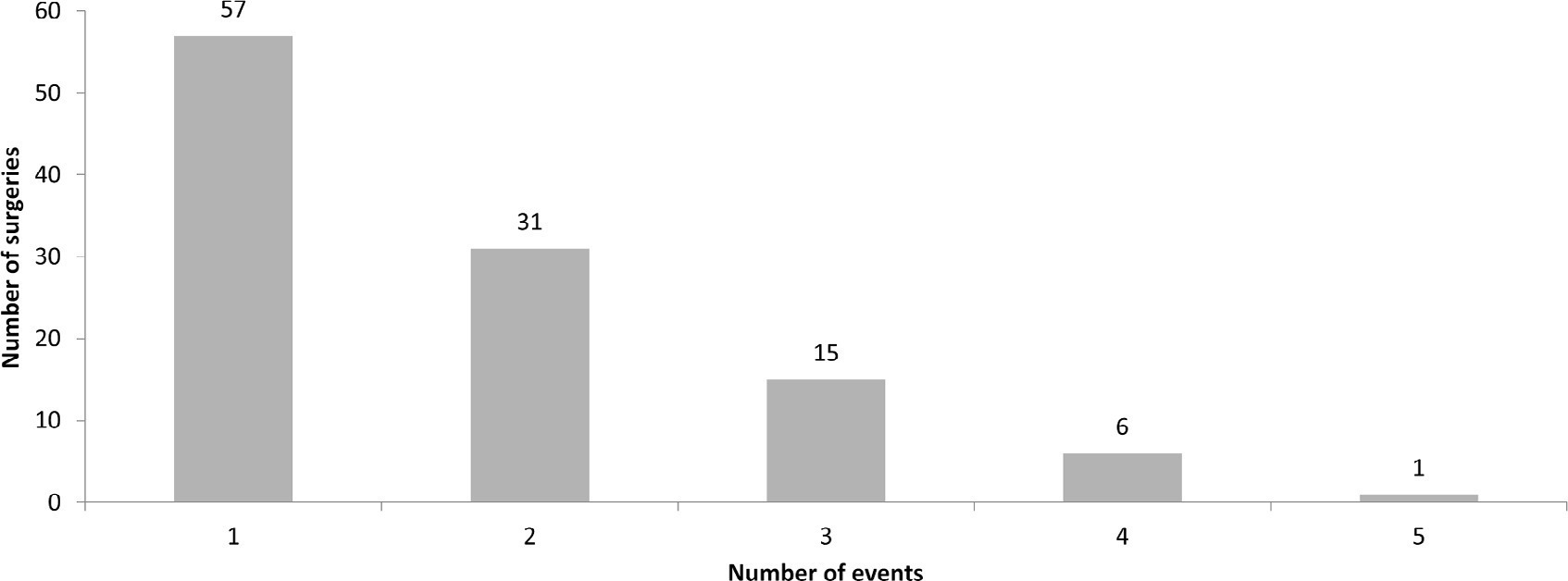
A total of 238 medical records were included. At least one adverse event occurred in 110 postoperative patients (46.2%). The total number of adverse events was 193 (81%). Vascular catheters were the most common cause, followed by cardiac arrest, bleeding, and surgical reexploration. In the univariate analysis, the vasoactive-inotropic score (VIS), Risk Adjustment in Congenital Heart Surgery (RACHS-1) score, age, Pediatric Index of Mortality (PIM-2), cardiopulmonary bypass and aortic clamping duration were significantly associated with adverse events. In the multivariate analysis, VIS ≥ 20 (OR 2.90; p = 0.004) and RACHS-1 ≥ 3 (OR 2.11; p = 0.019) were significant predictors, while age and delayed sternal closure showed only trends toward significance. To predict the occurrence of adverse events from VIS and RACHS-1, the area under the curve was 0.73 (95%CI 0.66 - 0.79).
Adverse events were quite frequent in children after cardiac surgery, especially those related to devices. The VIS and RACHS-1, used together, predicted the occurrence of adverse events well in this pediatric sample.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2020;32(4):551-556
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20200092
To analyze the clinical outcome of children with fluid-refractory septic shock initially treated with dopamine or epinephrine.
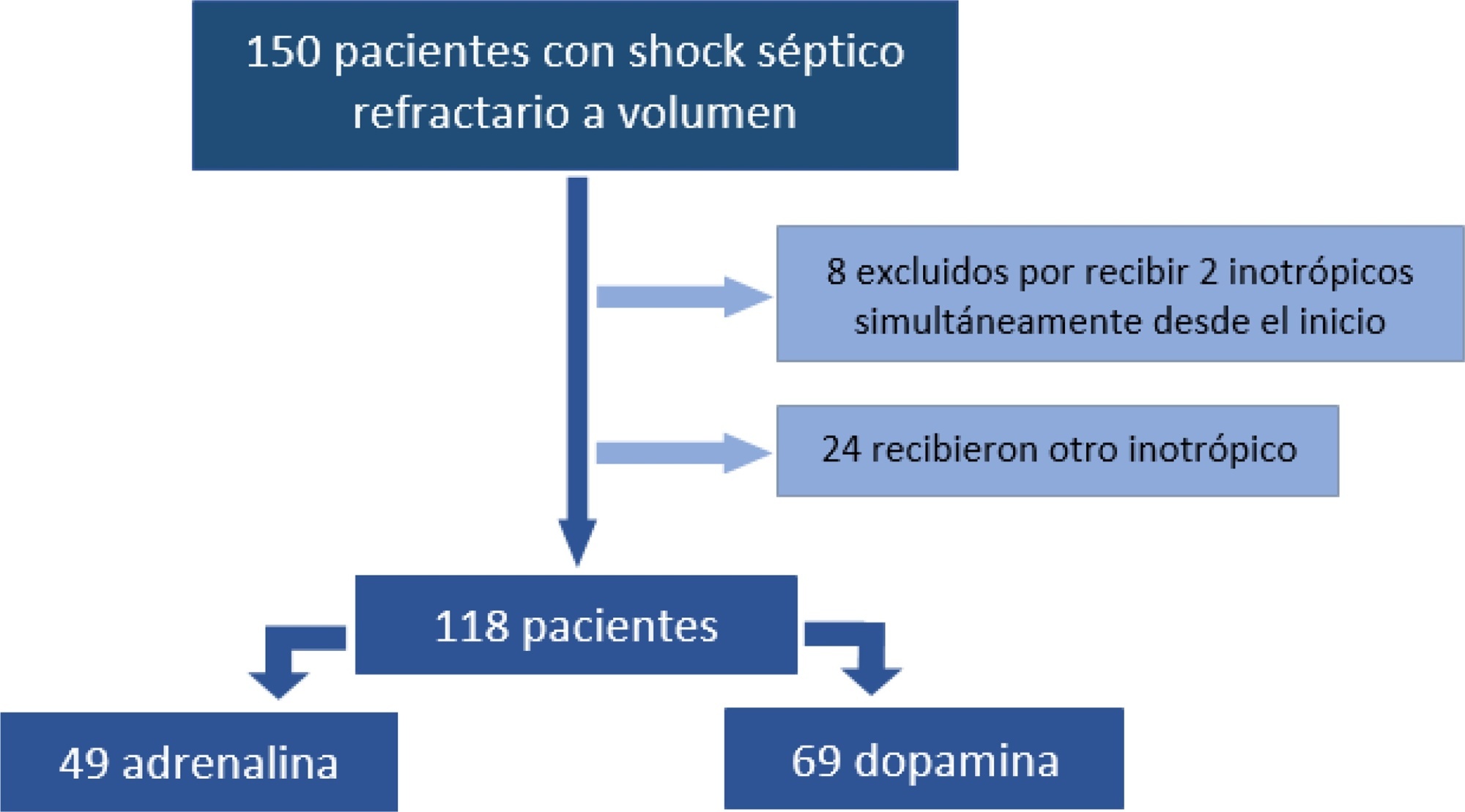
A retrospective cohort study was conducted at a pediatric emergency department of a tertiary hospital. Population: children admitted because of fluid-refractory septic shock. Clinical outcome was compared between two groups: Dopamine and Epinephrine. Variables evaluated were use of invasive mechanical ventilation, days of inotropic therapy, length of hospital stay, intensive care stay, and mortality. For numerical and categorical variables, we used measures of central tendency. They were compared by the Mann-Whitney U-test and the (2 test.
We included 118 patients. A total of 58.5% received dopamine and 41.5% received epinephrine. The rate of invasive mechanical ventilation was 38.8% for epinephrine versus 40.6% for dopamine (p = 0.84), with a median of 4 days for the Epinephrine Group and 5.5 for the Dopamine Group (p = 0.104). Median time of inotropic therapy was 2 days for both groups (p = 0.714). Median hospital stay was 11 and 13 days for the Epinephrine and Dopamine groups, respectively (p = 0.554), and median stay in intensive care was 4 days (0 - 81 days) in both groups (p = 0.748). Mortality was 5% for the Epinephrine Group versus 9% for the Dopamine Group (p = 0.64).
At our center, no differences in use of invasive mechanical ventilation, time of inotropic therapy, length of hospital stay, length of intensive care unit stay, or mortality were observed in children admitted to the pediatric emergency department with a diagnosis of fluid-refractory septic shock initially treated with dopamine versus epinephrine.
Search
Search in:
Case reports (56) Child (53) Coronavirus infections (34) COVID-19 (46) Critical care (116) Critical illness (54) Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (26) Infant, newborn (27) Intensive care (72) Intensive care units (256) Intensive care units, pediatric (31) mechanical ventilation (38) Mortality (76) Physical therapy modalities (28) Prognosis (61) Respiration, artificial (119) Respiratory insufficiency (26) risk factors (34) SARS-CoV-2 (28) Sepsis (98)