Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2022;34(1):96-106
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20220004-en
Early reversion of sepsis-induced tissue hypoperfusion is essential for survival in septic shock. However, consensus regarding the best initial resuscitation strategy is lacking given that interventions designed for the entire population with septic shock might produce unnecessary fluid administration. This article reports the rationale, study design and analysis plan of the ANDROMEDA-2 study, which aims to determine whether a peripheral perfusion-guided strategy consisting of capillary refill time-targeted resuscitation based on clinical and hemodynamic phenotypes is associated with a decrease in a composite outcome of mortality, time to organ support cessation, and hospital length of stay compared to standard care in patients with early (< 4 hours of diagnosis) septic shock.
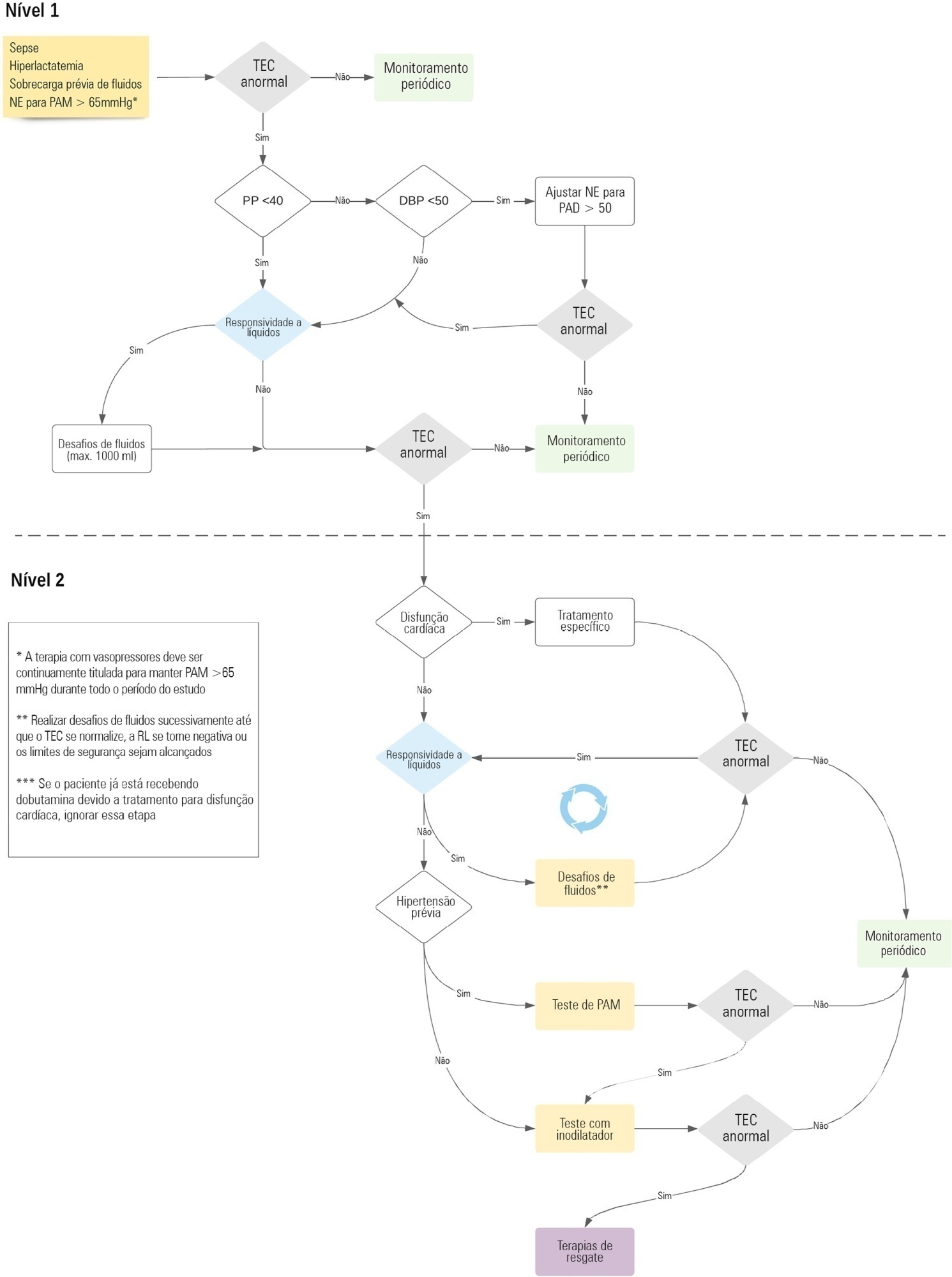
The ANDROMEDA-2 study is a multicenter, multinational randomized controlled trial. In the intervention group, capillary refill time will be measured hourly for 6 hours. If abnormal, patients will enter an algorithm starting with pulse pressure assessment. Patients with pulse pressure less than 40mmHg will be tested for fluid responsiveness and receive fluids accordingly. In patients with pulse pressure > 40mmHg, norepinephrine will be titrated to maintain diastolic arterial pressure > 50mmHg. Patients who fail to normalize capillary refill time after the previous steps will be subjected to critical care echocardiography for cardiac dysfunction evaluation and subsequent management. Finally, vasopressor and inodilator tests will be performed to further optimize perfusion. A sample size of 1,500 patients will provide 88% power to demonstrate superiority of the capillary refill time-targeted strategy.
If hemodynamic phenotype-based, capillary refill time-targeted resuscitation demonstrates to be a superior strategy, care processes in septic shock resuscitation can be optimized with bedside tools.
Search
Search in:
Case reports (56) Child (53) Coronavirus infections (34) COVID-19 (46) Critical care (116) Critical illness (54) Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (26) Infant, newborn (27) Intensive care (72) Intensive care units (256) Intensive care units, pediatric (31) mechanical ventilation (38) Mortality (76) Physical therapy modalities (28) Prognosis (61) Respiration, artificial (119) Respiratory insufficiency (26) risk factors (34) SARS-CoV-2 (28) Sepsis (98)