Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2013;25(2):99-105
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20130020
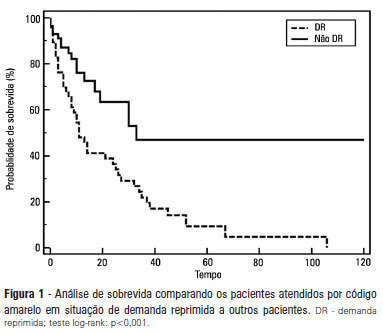
OBJECTIVE: To describe the epidemiological data of the clinical instability events in patients attended to by the rapid response team and to identify prognostic factors. METHODS: This was a longitudinal study, performed from January to July 2010, with an adult inpatient population in a hospital environment. The data collected regarding the code yellow service included the criteria of the clinical instability, the drug and non-drug therapies administered and the activities and procedures performed. The outcomes evaluated were the need for intensive care unit admission and the hospital mortality rates. A level of p=0.05 was considered to be significant. RESULTS: A total of 150 code yellow events that occurred in 104 patients were evaluated. The most common causes were related to acute respiratory insufficiency with hypoxia or a change in the respiratory rate and a concern of the team about the patient's clinical condition. It was necessary to request a transfer to the intensive care unit in 80 of the 150 cases (53.3%). It was necessary to perform 42 procedures. The most frequent procedures were orotracheal intubation and the insertion of a central venous catheter. The patients who were in critical condition and had to wait for an intensive care unit bed had a higher risk of death compared to the other patients (hazard ratio: 3.12; 95% CI: 1.80-5.40; p<0.001). CONCLUSIONS: There are patients in critical condition that require expert intensive care in the regular ward unit hospital beds. The events that most frequently led to the code yellow activation were related to hemodynamic and respiratory support. The interventions performed indicate the need for a physician on the team. The situation of pent-up demand is associated with a higher mortality rate.
Search
Search in:
Case reports (56) Child (53) Coronavirus infections (34) COVID-19 (46) Critical care (116) Critical illness (54) Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (26) Infant, newborn (27) Intensive care (72) Intensive care units (256) Intensive care units, pediatric (31) mechanical ventilation (38) Mortality (76) Physical therapy modalities (28) Prognosis (61) Respiration, artificial (119) Respiratory insufficiency (26) risk factors (34) SARS-CoV-2 (28) Sepsis (98)