You searched for:"Mansueto Gomes Neto"
We found (2) results for your search.-
Original Article
Influence of different degrees of head elevation on respiratory mechanics in mechanically ventilated patients
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2015;27(4):347-352
Abstract
Original ArticleInfluence of different degrees of head elevation on respiratory mechanics in mechanically ventilated patients
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2015;27(4):347-352
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20150059
Views0See moreRESUMO
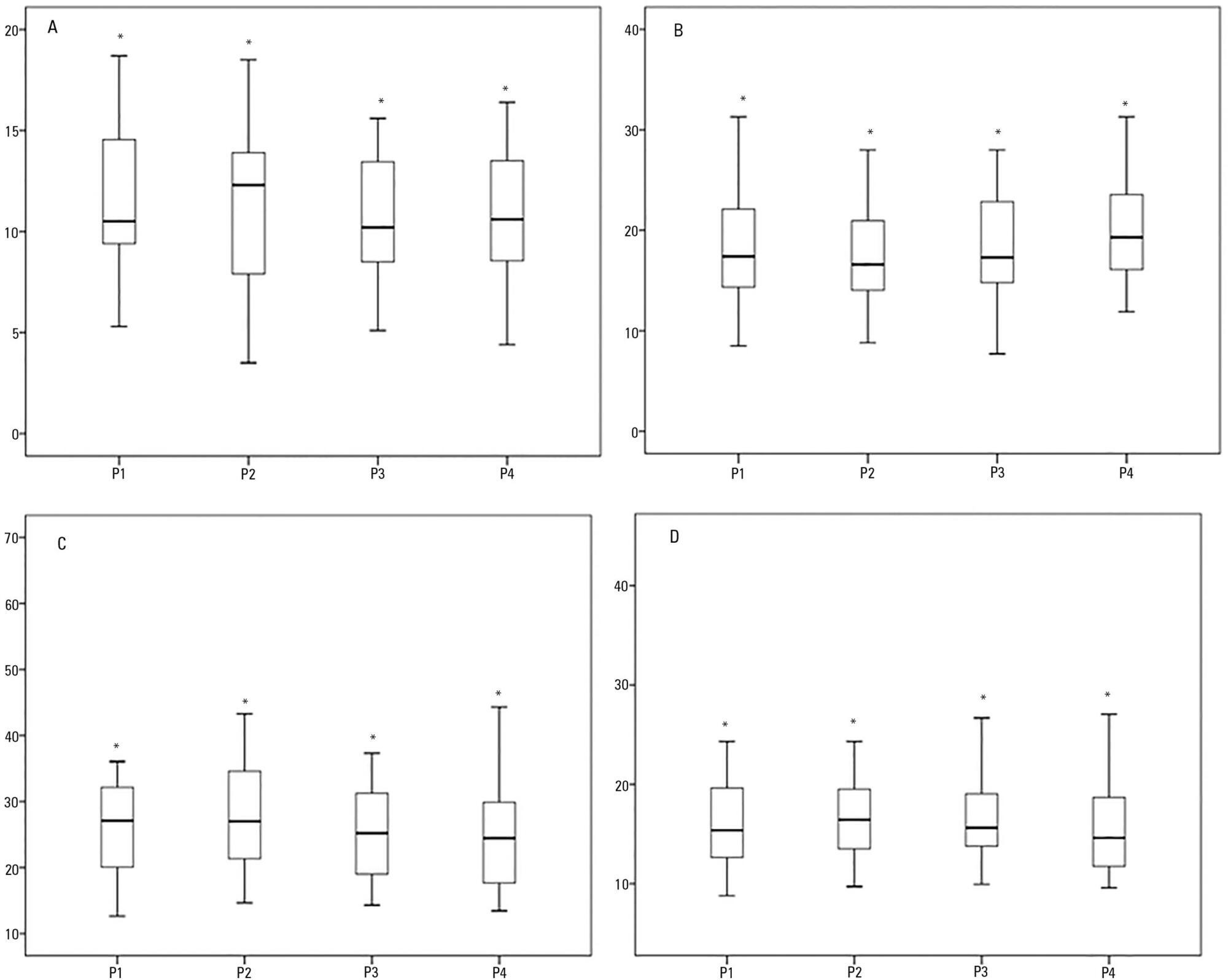
Objective:
The positioning of a patient in bed may directly affect their respiratory mechanics. The objective of this study was to evaluate the respiratory mechanics of mechanically ventilated patients positioned with different head angles hospitalized in an intensive care unit.
Methods:
This was a prospective physiological study in which static and dynamic compliance, resistive airway pressure, and peripheral oxygen saturation were measured with the head at four different positions (0° = P1, 30° = P2, 45° = P3, and 60° = P4). Repeated-measures analysis of variance (ANOVA) with a Bonferroni post-test and Friedman analysis were used to compare the values obtained at the different positions.
Results:
A comparison of the 35 evaluated patients revealed that the resistive airway pressure values in the 0° position were higher than those obtained when patients were positioned at greater angles. The elastic pressure analysis revealed that the 60° position produced the highest value relative to the other positions. Regarding static compliance, a reduction in values was observed from the 0° position to the 60° position. The dynamic compliance analysis revealed that the 30° angle produced the greatest value compared to the other positions. The peripheral oxygen saturation showed little variation, with the highest value obtained at the 0° position.
Conclusion:
The highest dynamic compliance value was observed at the 30° position, and the highest oxygenation value was observed at the 0° position.
-
Original Articles
Impact of hospitalization in an intensive care unit on range of motion of critically ill patients: a pilot study
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2014;26(1):65-70
Abstract
Original ArticlesImpact of hospitalization in an intensive care unit on range of motion of critically ill patients: a pilot study
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2014;26(1):65-70
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20140010
Views0See moreObjective:
To evaluate the joint range of motion of critically ill patients during hospitalization in the intensive care unit.
Methods:
This work was a prospective longitudinal study conducted in a critical care unit of a public hospital in the city of Salvador (BA) from September to November 2010. The main variable evaluated was the passive joint range of motion. A goniometer was used to measure the elbows, knees and ankles at the time of admission and at discharge. All patients admitted in the period were included other than patients with length of stay <72 hours and patients with reduced joint range of motion on admission.
Results:
The sample consisted of 22 subjects with a mean age of 53.5±17.6 years, duration of stay in the intensive care unit of 13.0±6.0 days and time on mechanical ventilation of 12.0±6.3 days. The APACHE II score was 28.5±7.3, and the majority of patients had functional independence at admission with a prior Barthel index of 88.8±19. The losses of joint range of motion were 11.1±2.1°, 11.0±2.2°, 8.4±1.7°, 9.2±1.6°, 5.8±0.9° and 5.1±1.0°, for the right and left elbows, knees and ankles, respectively (p<0.001).
Conclusion:
There was a tendency towards decreased range of motion of large joints such as the ankle, knee and elbow during hospitalization in the intensive care unit.
Search
Search in:
KEY WORDS
Case reports Child Coronavirus infections COVID-19 Critical care Critical illness Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation Infant, newborn Intensive care Intensive care units Intensive care units, pediatric mechanical ventilation Mortality Physical therapy modalities Prognosis Respiration, artificial Respiratory insufficiency risk factors SARS-CoV-2 Sepsis




