You searched for:"Ana Ribeiro"
We found (4) results for your search.-
Review Article
Efficacy and safety of milrinone in the treatment of cerebral vasospasm after subarachnoid hemorrhage: a systematic review
- Alex Goes Santos-Teles
 ,
, - Clara Ramalho,
- João Gabriel Rosa Ramos,
- Rogério da Hora Passos,
- André Gobatto, [ … ],
- Juliana Ribeiro Caldas
Abstract
Review ArticleEfficacy and safety of milrinone in the treatment of cerebral vasospasm after subarachnoid hemorrhage: a systematic review
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2020;32(4):592-602
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20200097
- Alex Goes Santos-Teles
 ,
, - Clara Ramalho,
- João Gabriel Rosa Ramos,
- Rogério da Hora Passos,
- André Gobatto,
- Suzete Farias,
- Paulo Benígno Pena Batista,
- Juliana Ribeiro Caldas
Views0See moreABSTRACT
Objective:
To systematically review the current evidence on the efficacy of milrinone in the treatment of cerebral vasospasm after subarachnoid hemorrhage.
Methods:
The Pubmed®, Cochrane and Embase databases were screened for articles published from April 2001 to February 2019. Two independent reviewers performed the methodological quality screening and data extraction of the studies.
Results:
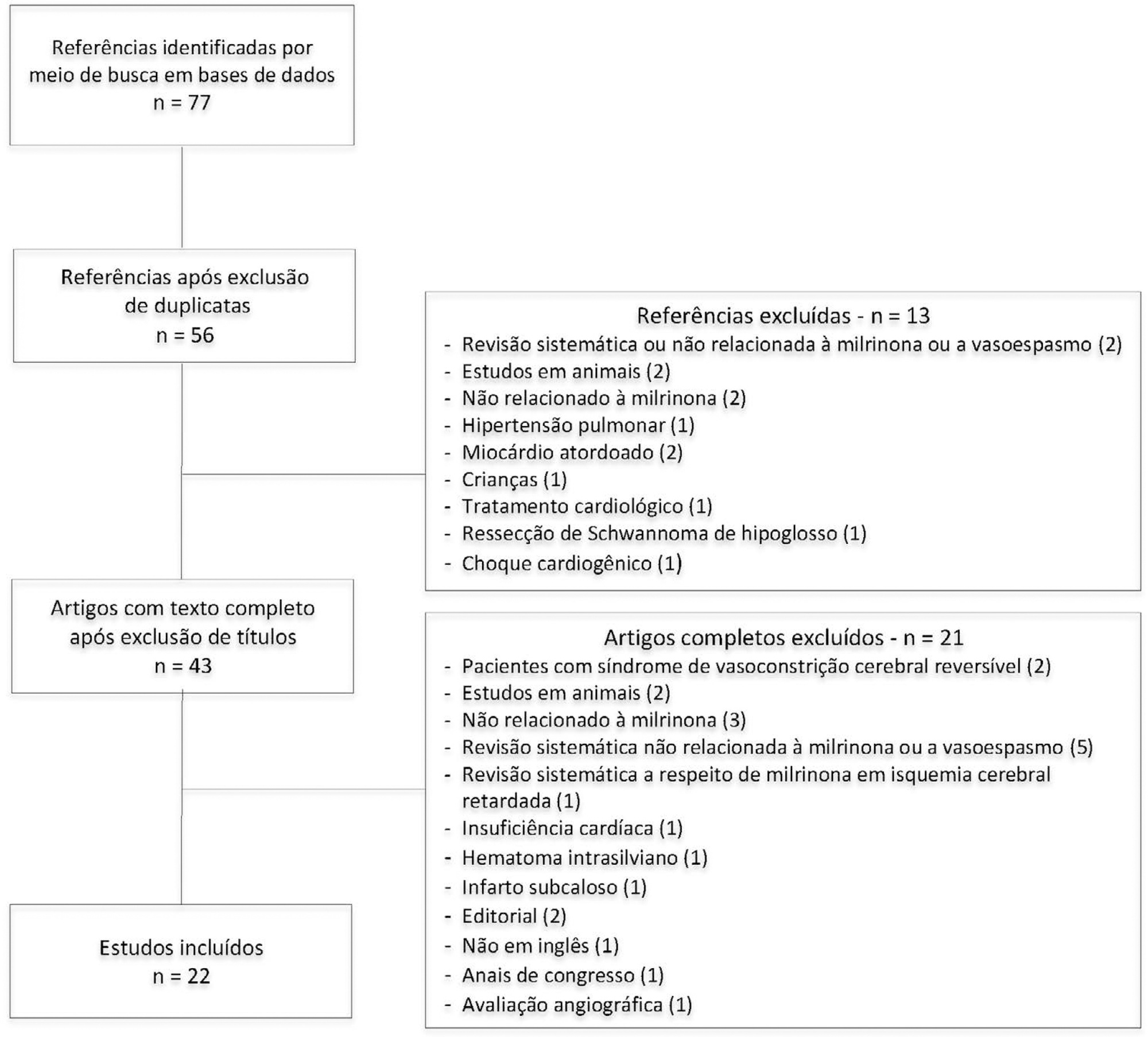
Twenty-two studies were found to be relevant, and only one of these was a randomized control trial. Studies showed marked heterogeneity and weaknesses in key methodological criteria. Most patients presented with moderate to severe vasospasm. Angiography was the main method of diagnosing vasospasm. Intra-arterial administration of milrinone was performed in three studies, intravenous administration was performed in nine studies, and both routes of administration in six studies; the intrathecal route was used in two studies, the cisternal route in one study and endovascular administration in one study. The side effects of milrinone were described in six studies. Twenty-one studies indicated resolution of vasospasm.
Conclusion:
The current evidence indicates that milrinone may have a role in treatment of vasospasm after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. However, only one randomized control trial was performed, with a low quality level. Our findings indicate the need for future randomized control trials with patient-centered outcomes to provide definitive recommendations.
Views0

Abstract
Review ArticleEfficacy and safety of milrinone in the treatment of cerebral vasospasm after subarachnoid hemorrhage: a systematic review
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2020;32(4):592-602
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20200097
- Alex Goes Santos-Teles
 ,
, - Clara Ramalho,
- João Gabriel Rosa Ramos,
- Rogério da Hora Passos,
- André Gobatto,
- Suzete Farias,
- Paulo Benígno Pena Batista,
- Juliana Ribeiro Caldas
Views0See moreABSTRACT
Objective:
To systematically review the current evidence on the efficacy of milrinone in the treatment of cerebral vasospasm after subarachnoid hemorrhage.
Methods:
The Pubmed®, Cochrane and Embase databases were screened for articles published from April 2001 to February 2019. Two independent reviewers performed the methodological quality screening and data extraction of the studies.
Results:
Twenty-two studies were found to be relevant, and only one of these was a randomized control trial. Studies showed marked heterogeneity and weaknesses in key methodological criteria. Most patients presented with moderate to severe vasospasm. Angiography was the main method of diagnosing vasospasm. Intra-arterial administration of milrinone was performed in three studies, intravenous administration was performed in nine studies, and both routes of administration in six studies; the intrathecal route was used in two studies, the cisternal route in one study and endovascular administration in one study. The side effects of milrinone were described in six studies. Twenty-one studies indicated resolution of vasospasm.
Conclusion:
The current evidence indicates that milrinone may have a role in treatment of vasospasm after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. However, only one randomized control trial was performed, with a low quality level. Our findings indicate the need for future randomized control trials with patient-centered outcomes to provide definitive recommendations.


- Alex Goes Santos-Teles
-
Review Articles
Approach to the liver transplant early postoperative period: an institutional standpoint
- Beatriz Amaral,
- Madalena Vicente,
- Carla Sofia Maravilha Pereira,
- Teresa Araújo,
- Ana Ribeiro, [ … ],
- Paulo Marcelino

Abstract
Review ArticlesApproach to the liver transplant early postoperative period: an institutional standpoint
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2019;31(4):561-570
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20190076
- Beatriz Amaral,
- Madalena Vicente,
- Carla Sofia Maravilha Pereira,
- Teresa Araújo,
- Ana Ribeiro,
- Rui Pereira
 ,
, - Rui Perdigoto,
- Paulo Marcelino

Views0ABSTRACT
The liver transplant program in our center started in 1992, and post-liver transplant patients are still admitted to the intensive care unit. For the intensive care physician, a learning curve started then, skills were acquired, and a specific practice was established. Throughout this time, several concepts changed, improving the care of these patients. The practical approach varies between liver transplant centers, according to local specificities. Hence, we wanted to present our routine practice to stimulate the debate between dedicated teams, which can allow the introduction of new ideas and potentially improve each local standard of care.
Keywords:Intensive careLiver transplantationLiver/surgeryPerioperative period/adverse effectsPostoperative periodSee moreViews0

Abstract
Review ArticlesApproach to the liver transplant early postoperative period: an institutional standpoint
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2019;31(4):561-570
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20190076
- Beatriz Amaral,
- Madalena Vicente,
- Carla Sofia Maravilha Pereira,
- Teresa Araújo,
- Ana Ribeiro,
- Rui Pereira
 ,
, - Rui Perdigoto,
- Paulo Marcelino

Views0ABSTRACT
The liver transplant program in our center started in 1992, and post-liver transplant patients are still admitted to the intensive care unit. For the intensive care physician, a learning curve started then, skills were acquired, and a specific practice was established. Throughout this time, several concepts changed, improving the care of these patients. The practical approach varies between liver transplant centers, according to local specificities. Hence, we wanted to present our routine practice to stimulate the debate between dedicated teams, which can allow the introduction of new ideas and potentially improve each local standard of care.
Keywords:Intensive careLiver transplantationLiver/surgeryPerioperative period/adverse effectsPostoperative periodSee more

-
Review Articles
Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for severe acute respiratory distress syndrome in adult patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Pedro Vitale Mendes,
- Livia Maria Garcia Melro,
- Ho Yeh Li,
- Daniel Joelsons
 ,
, - Rogerio Zigaib, [ … ],
- Marcelo Park
Abstract
Review ArticlesExtracorporeal membrane oxygenation for severe acute respiratory distress syndrome in adult patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2019;31(4):548-554
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20190077
- Pedro Vitale Mendes,
- Livia Maria Garcia Melro,
- Ho Yeh Li,
- Daniel Joelsons
 ,
, - Rogerio Zigaib,
- José Mauro da Fonseca Pestana Ribeiro,
- Bruno Adler Maccagnan Pinheiro Besen
 ,
, - Marcelo Park
Views0ABSTRACT
Objective:
The evidence of improved survival with the use of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) in acute respiratory distress syndrome is still uncertain.
Methods:
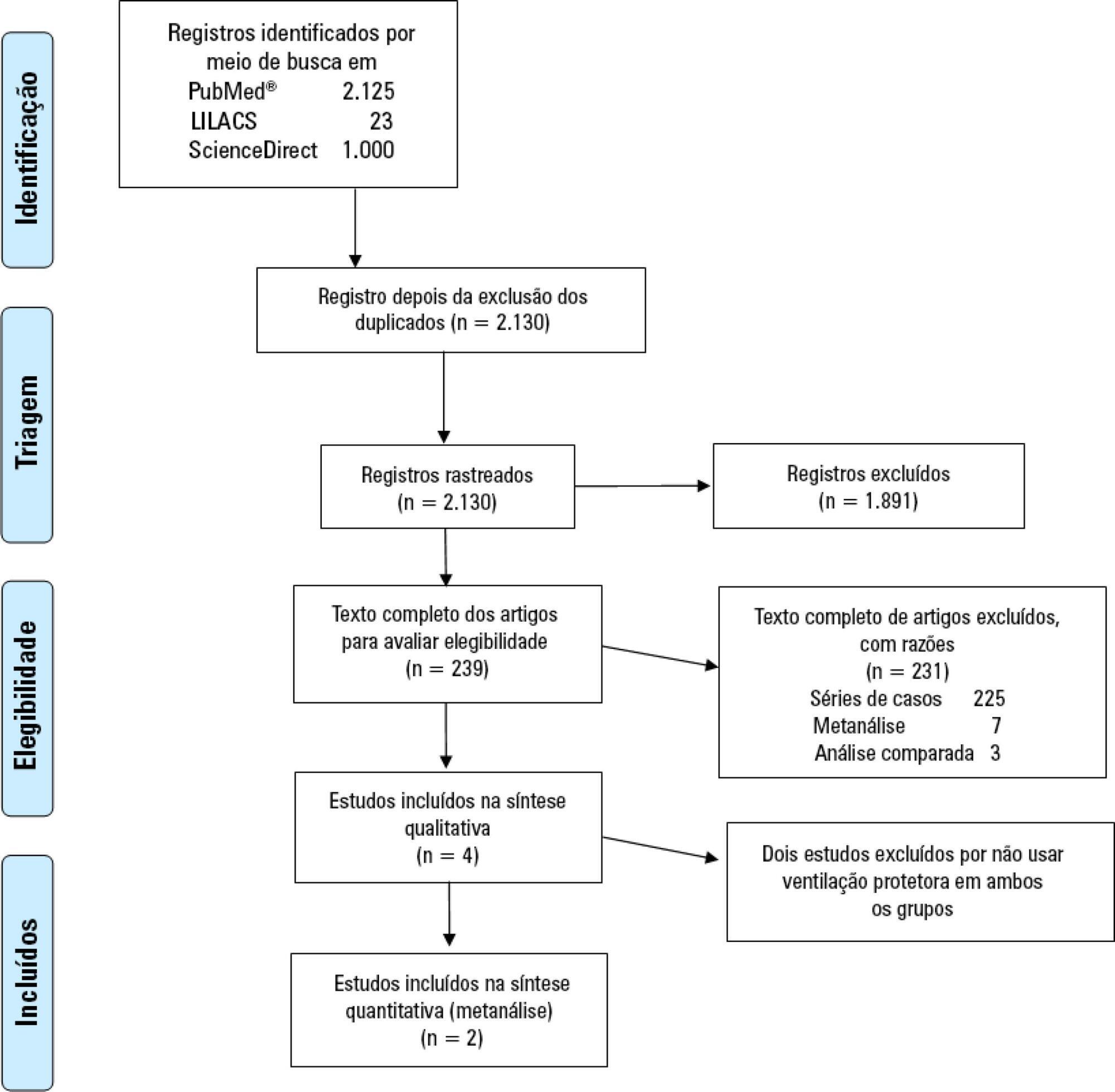
This systematic review and meta-analysis was registered in the PROSPERO database with the number CRD-42018098618. We performed a structured search of Medline, Lilacs, and ScienceDirect for randomized controlled trials evaluating the use of ECMO associated with (ultra)protective mechanical ventilation for severe acute respiratory failure in adult patients. We used the Cochrane risk of bias tool to evaluate the quality of the evidence. Our primary objective was to evaluate the effect of ECMO on the last reported mortality. Secondary outcomes were treatment failure, hospital length of stay and the need for renal replacement therapy in both groups.
Results:
Two randomized controlled studies were included in the meta-analysis, comprising 429 patients, of whom 214 were supported with ECMO. The most common reason for acute respiratory failure was pneumonia (60% – 65%). Respiratory ECMO support was associated with a reduction in last reported mortality and treatment failure with risk ratios (RR: 0.76; 95%CI 0.61 – 0.95 and RR: 0.68; 95%CI 0.55 – 0.85, respectively). Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation reduced the need for renal replacement therapy, with a RR of 0.88 (95%CI 0.77 – 0.99). Intensive care unit and hospital lengths of stay were longer in ECMO-supported patients, with an additional P50th 14.84 (P25th – P75th: 12.49 – 17.18) and P50th 29.80 (P25th – P75th: 26.04 – 33.56] days, respectively.
Conclusion:
Respiratory ECMO support in severe acute respiratory distress syndrome patients is associated with a reduced mortality rate and a reduced need for renal replacement therapy but a substantial increase in the lengths of stay in the intensive care unit and hospital. Our results may help bedside decision-making regarding ECMO initiation in patients with severe respiratory distress syndrome.
Keywords:Extracorporeal membrane oxygenationIntensive care unitsMeta-analysisRespiratory distress syndrome, adultRespiratory insufficiencySee moreViews0

Abstract
Review ArticlesExtracorporeal membrane oxygenation for severe acute respiratory distress syndrome in adult patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2019;31(4):548-554
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20190077
- Pedro Vitale Mendes,
- Livia Maria Garcia Melro,
- Ho Yeh Li,
- Daniel Joelsons
 ,
, - Rogerio Zigaib,
- José Mauro da Fonseca Pestana Ribeiro,
- Bruno Adler Maccagnan Pinheiro Besen
 ,
, - Marcelo Park
Views0ABSTRACT
Objective:
The evidence of improved survival with the use of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) in acute respiratory distress syndrome is still uncertain.
Methods:
This systematic review and meta-analysis was registered in the PROSPERO database with the number CRD-42018098618. We performed a structured search of Medline, Lilacs, and ScienceDirect for randomized controlled trials evaluating the use of ECMO associated with (ultra)protective mechanical ventilation for severe acute respiratory failure in adult patients. We used the Cochrane risk of bias tool to evaluate the quality of the evidence. Our primary objective was to evaluate the effect of ECMO on the last reported mortality. Secondary outcomes were treatment failure, hospital length of stay and the need for renal replacement therapy in both groups.
Results:
Two randomized controlled studies were included in the meta-analysis, comprising 429 patients, of whom 214 were supported with ECMO. The most common reason for acute respiratory failure was pneumonia (60% – 65%). Respiratory ECMO support was associated with a reduction in last reported mortality and treatment failure with risk ratios (RR: 0.76; 95%CI 0.61 – 0.95 and RR: 0.68; 95%CI 0.55 – 0.85, respectively). Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation reduced the need for renal replacement therapy, with a RR of 0.88 (95%CI 0.77 – 0.99). Intensive care unit and hospital lengths of stay were longer in ECMO-supported patients, with an additional P50th 14.84 (P25th – P75th: 12.49 – 17.18) and P50th 29.80 (P25th – P75th: 26.04 – 33.56] days, respectively.
Conclusion:
Respiratory ECMO support in severe acute respiratory distress syndrome patients is associated with a reduced mortality rate and a reduced need for renal replacement therapy but a substantial increase in the lengths of stay in the intensive care unit and hospital. Our results may help bedside decision-making regarding ECMO initiation in patients with severe respiratory distress syndrome.
Keywords:Extracorporeal membrane oxygenationIntensive care unitsMeta-analysisRespiratory distress syndrome, adultRespiratory insufficiencySee more

-
Original Articles – Clinical Research
Nutritional requirements of the critically ill patient
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2012;24(3):270-277
Abstract
Original Articles – Clinical ResearchNutritional requirements of the critically ill patient
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2012;24(3):270-277
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2012000300011
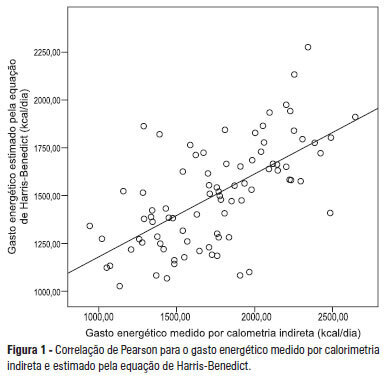
Views0OBJECTIVE: Given the inaccessibility of indirect calorimetry, intensive care units generally use predictive equations or recommendations that are established by international societies to determine energy expenditure. The aim of the present study was to compare the energy expenditure of critically ill patients, as determined using indirect calorimetry, to the values obtained using the Harris-Benedict equation. METHODS: A retrospective observational study was conducted at the Intensive Care Unit 1 of the Centro Hospitalar do Porto. The energy requirements of hospitalized critically ill patients as determined using indirect calorimetry were assessed between January 2003 and April 2012. The accuracy (± 10% difference between the measured and estimated values), the mean differences and the limits of agreement were determined for the studied equations. RESULTS: Eighty-five patients were assessed using 288 indirect calorimetry measurements. The following energy requirement values were obtained for the different methods: 1,753.98±391.13 kcal/day (24.48 ± 5.95 kcal/kg/day) for indirect calorimetry and 1,504.11 ± 266.99 kcal/day (20.72±2.43 kcal/kg/day) for the Harris-Benedict equation. The equation had a precision of 31.76% with a mean difference of -259.86 kcal/day and limits of agreement between -858.84 and 339.12 kcal/day. Sex (p=0.023), temperature (p=0.009) and body mass index (p<0.001) were found to significantly affect energy expenditure. CONCLUSION: The Harris-Benedict equation is inaccurate and tends to underestimate energy expenditure. In addition, the Harris-Benedict equation is associated with significant differences between the predicted and true energy expenditure at an individual level.
Keywords:Diet therapyEnergy metabolismIndirect calorimetryIntensive care unitsnutritional therapyRespiration, artificialSee moreViews0

Abstract
Original Articles – Clinical ResearchNutritional requirements of the critically ill patient
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2012;24(3):270-277
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2012000300011
Views0OBJECTIVE: Given the inaccessibility of indirect calorimetry, intensive care units generally use predictive equations or recommendations that are established by international societies to determine energy expenditure. The aim of the present study was to compare the energy expenditure of critically ill patients, as determined using indirect calorimetry, to the values obtained using the Harris-Benedict equation. METHODS: A retrospective observational study was conducted at the Intensive Care Unit 1 of the Centro Hospitalar do Porto. The energy requirements of hospitalized critically ill patients as determined using indirect calorimetry were assessed between January 2003 and April 2012. The accuracy (± 10% difference between the measured and estimated values), the mean differences and the limits of agreement were determined for the studied equations. RESULTS: Eighty-five patients were assessed using 288 indirect calorimetry measurements. The following energy requirement values were obtained for the different methods: 1,753.98±391.13 kcal/day (24.48 ± 5.95 kcal/kg/day) for indirect calorimetry and 1,504.11 ± 266.99 kcal/day (20.72±2.43 kcal/kg/day) for the Harris-Benedict equation. The equation had a precision of 31.76% with a mean difference of -259.86 kcal/day and limits of agreement between -858.84 and 339.12 kcal/day. Sex (p=0.023), temperature (p=0.009) and body mass index (p<0.001) were found to significantly affect energy expenditure. CONCLUSION: The Harris-Benedict equation is inaccurate and tends to underestimate energy expenditure. In addition, the Harris-Benedict equation is associated with significant differences between the predicted and true energy expenditure at an individual level.
Keywords:Diet therapyEnergy metabolismIndirect calorimetryIntensive care unitsnutritional therapyRespiration, artificialSee more

Search
Search in:
KEY WORDS
Case reports Child Coronavirus infections COVID-19 Critical care Critical illness Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation Infant, newborn Intensive care Intensive care units Intensive care units, pediatric mechanical ventilation Mortality Physical therapy modalities Prognosis Respiration, artificial Respiratory insufficiency risk factors SARS-CoV-2 Sepsis


