Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2022;34(3):327-334
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20220070-en
To describe the implementation and results of the collaborative PROADI-SUS project by the Brazilian Ministry of Health to reduce healthcare-associated infections: ventilator-associated pneumonia, primary central line-associated bloodstream infection and catheter-associated urinary tract infections.
This was a prospective observational study that investigated the implementation stages and outcomes during 18 months in five intensive care units in the city of Recife. Reductions in healthcare-associated infections in each unit were calculated using previous medians compared to those of the study period.
The goal of reducing the three healthcare-associated infections, i.e., 30% in 18 months, was achieved in at least one of the healthcare-associated infections and was also achieved for two healthcare-associated infections in two hospitals and three healthcare-associated infections in just one hospital; the latter reached the target of 36 months. Implementing the bundles and monitoring the results by the professionals were considered essential actions by the local management teams. In addition, the acquisition of supplies and their availability alongside the beds, signage, checklists, staff awareness, adaptation, team building, training and celebration of achievements were assessed as being relevant for reducing healthcare-associated infections.
The collaborative approach reduced healthcare-associated infections, despite partial adherence to the bundles. The hypothesis is that success is related to the project methodology and motivated multidisciplinary teams, especially nursing teams.
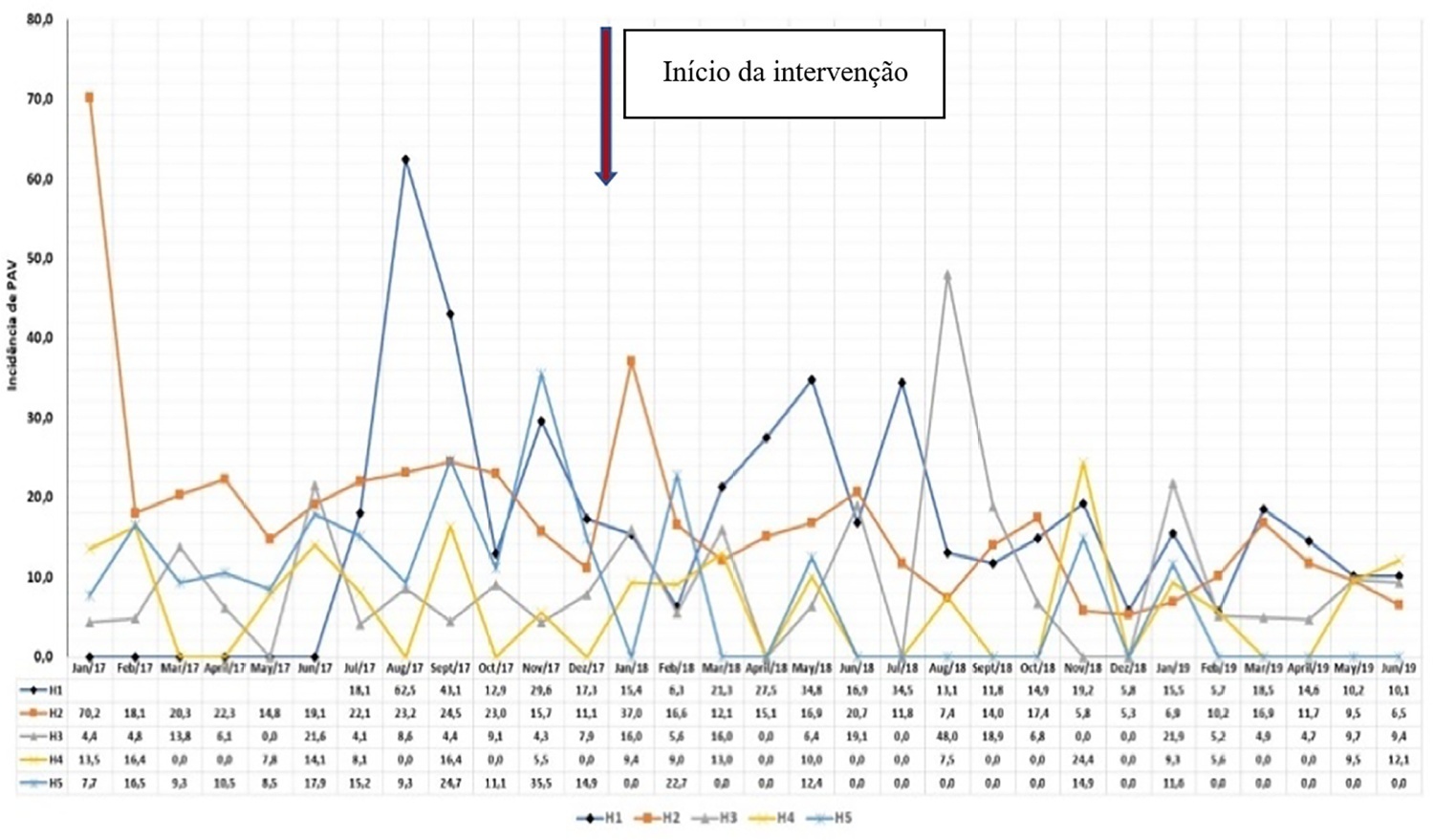
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2014;26(1):7-13
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20140002
To evaluate the role of quality indicators and adverse events registering in the quality assessment of intensive care physiotherapy and to evaluate the impact of implementing protocolized care and professional training in the quality improvement process.
A prospective before-after study was designed to assess 15 indicators of the quality of care. Baseline compliance and adverse events were collected before and after the implementation of treatment protocols and staff training.
Eighty-nine patients admitted, being 48 in the pre-intervention period and 41 in the post-intervention period with a total of 1246 and 1191 observations respectively. Among the indicators related to the global population, there was a significant improvement in chest x-ray control, multidisciplinary rounds and shift changes as well as in compliance with these decisions. Indicators related to the population under mechanical ventilation, obtained by direct observation at bedside, showed a significant improvement in the compliance with the tidal volume of 6-8mL/Kg, plateau pressure <30cmH2O, adequate mechanical ventilation alarm setting, mechanical ventilation humidification control, adequate humidification line exchange and orotracheal tube position. Among the mechanical ventilation indicators collected through the physiotherapy records, there was significantly improved compliance with the predicted tidal volume registry and cuff pressure registry. There was a significant reduction in the number of adverse events. There was no impact on intensive care unit mortality, length of stay, duration of mechanical ventilation and ventilator-free days.
It is possible to measure the quality of physiotherapy care using indicators of quality control. The implementation of care protocols and training of the professionals can improve team performance.
Search
Search in:
Case reports (56) Child (53) Coronavirus infections (34) COVID-19 (46) Critical care (116) Critical illness (54) Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (26) Infant, newborn (27) Intensive care (72) Intensive care units (256) Intensive care units, pediatric (31) mechanical ventilation (38) Mortality (76) Physical therapy modalities (28) Prognosis (61) Respiration, artificial (119) Respiratory insufficiency (26) risk factors (34) SARS-CoV-2 (28) Sepsis (98)