Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2014;26(1):57-64
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20140009
To describe the characteristics of physical therapy assistance to newborns and to provide a profile of physical therapists working in intensive care units in the city of São Paulo, Brazil.
This cross-sectional study was conducted in every hospital in São Paulo city that had at least one intensive care unit bed for newborns registered at the National Registry of Health Establishments in 2010. In each unit, three types of physical therapists were included: an executive who was responsible for the physical therapy service in that hospital (chief-physical therapists), a physical therapist who was responsible for the physical therapy assistance in the neonatal unit (reference-physical therapists), and a randomly selected physical therapist who was directly involved in the neonatal care (care-physical therapists).
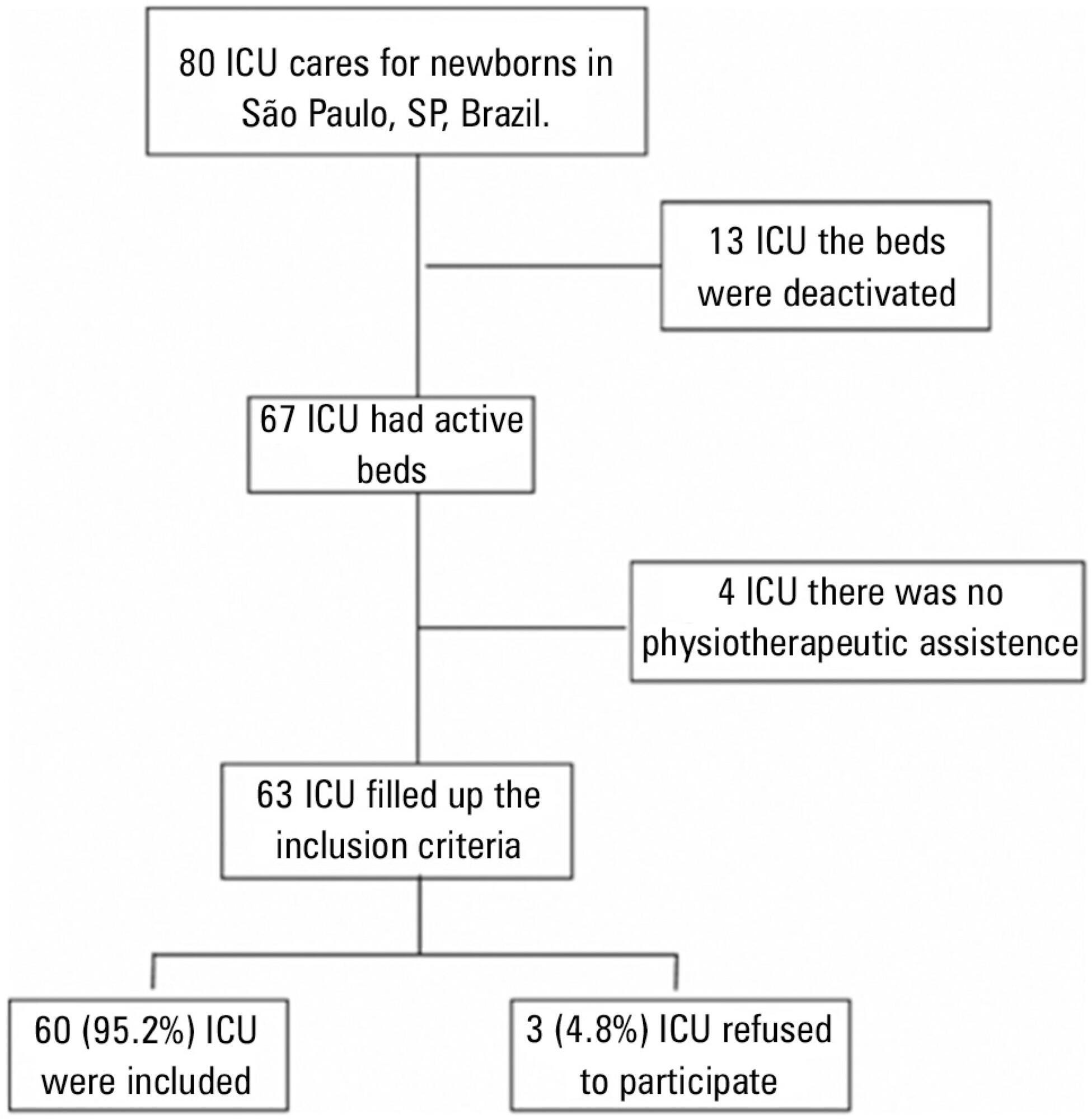
Among the 67 hospitals eligible for the study, 63 (94.0%) had a physical therapy service. Of those hospitals, three (4.8%) refused to participate. Thus, 60 chief-PTs, 52 reference-physical therapists, and 44 care-physical therapists were interviewed. During day shifts, night shifts, and weekends/holidays, there were no physical therapists in 1.7%, 45.0%, and 13.3% of the intensive care units, respectively. Physical therapy assistance was available for 17.8±7.2 hours/day, and each physical therapist cared for 9.4±2.6 newborns during six working hours. Most professionals had completed at least one specialization course.
Most neonatal intensive care units in the city of São Paulo had physical therapists working on the day shift. However, other shifts had incomplete staff with less than 18 hours of available physical therapy assistance per day.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2012;24(1):64-70
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2012000100010
OBJECTIVE: To assess the consciousness level, pulmonary and hemodynamic effects of orthostatic position in intensive care patients. METHODS: This study was conducted from April 2008 to July 2009 in the Adult Intensive Care Unit, Hospital das Clínicas, Universidade Estadual de Campinas, São Paulo, Brazil. Fifteen patients were included who were mechanically ventilated for more than seven days and had the following characteristics: tracheotomized; receiving intermittent nebulization; maximal inspiratory pressure of less than -25 cm H2O; Tobin score less than 105; preserved respiratory drive; not sedated; partial arterial oxygen pressure greater than 70 mm Hg; oxygen saturation greater than 90%; and hemodynamically stable. With inclinations of 0º, 30º and 50º, the following parameters were recorded: consciousness level; blinking reflex; thoracoabdominal cirtometry; vital capacity; tidal volume; minute volume; respiratory muscle strength; and vital signs. RESULTS: No neurological level changes were observed. Respiratory rate and minute volume (V E) decreased at 30% and later increased at 50%; however, these changes were not statistically significant. Abdominal cirtometry and maximal expiratory pressure increased, but again, the changes were not statistically significant. Regarding maximal inspiratory pressure and vital capacity, statistically significant increases were seen in the comparison between the 50º and 0º inclinations. However, tidal volume increased with time in the comparisons between 30º and 0º and between 50º and 0º. Mean blood pressure increased only for the comparison of 50º versus 0º. Heart rate increased with time for the comparisons between 30º and 0º, between 50º and 0º and between 50º and 30º. CONCLUSION: Passive orthostatism resulted in improved tidal volume and vital capacity, maximal inspiratory pressure and increased heart rate and mean blood pressure in critically ill patients.
Search
Search in:
Case reports (56) Child (53) Coronavirus infections (34) COVID-19 (46) Critical care (116) Critical illness (54) Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (26) Infant, newborn (27) Intensive care (72) Intensive care units (256) Intensive care units, pediatric (31) mechanical ventilation (38) Mortality (76) Physical therapy modalities (28) Prognosis (61) Respiration, artificial (119) Respiratory insufficiency (26) risk factors (34) SARS-CoV-2 (28) Sepsis (98)