Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2010;22(3):213-219
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2010000300001
OBJECTIVE: To analyze the economic impact of an early sepsis detection protocol in two general hospitals. METHODS: We analyzed data collected from a prospective study of septic patients before and after the implementation of a protocol for early diagnosis of severe sepsis. We conducted a cost-effectiveness analysis comparing: mortality rate, cost of sepsis treatment and indirect costs attributed to years of productive life lost to premature death in both phases. RESULTS: Two hundred seventeen patients were included, 102 in phase I and 115 in phase II. After protocol implementation, in private and public hospital, mortality rates decreased from 50% to 32.2% and from 67.6% to 41% (p < 0.05). The mean years of productive life lost due to sepsis decreased from 3.18 to 0.80 and 9.81 to 4.65 (p < 0.05), with a mean gain of 2.38 and 5.16 years of productive life, for each septic patient. Considering Brazilian gross domestic product per capita, estimated productivity loss due to sepsis decreased between 3.2 and 9.7 billion US dollars, varying based on the incidence of sepsis. Hospital costs were similar in both phases. CONCLUSION: A protocol for early detection and treatment of in-hospital septic patients is highly cost-effective from a societal perspective.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2008;20(4):331-338
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2008000400003
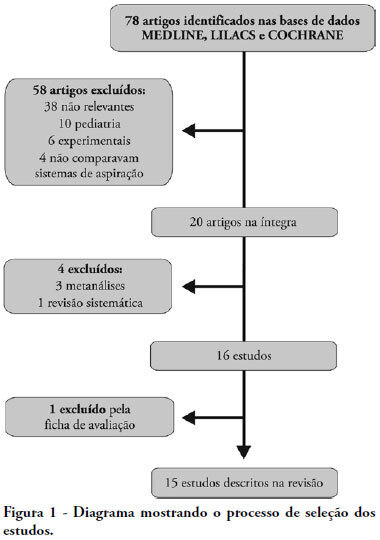
OBJECTIVES: This study attempted to identify which is the more effective suction system. The objective was to compare open versus closed suction systems according to a systematic review. METHODS: A search of scientific literature was conducted in MedLine, LILACS and Cochrane between 1997 and August 2007 using the key words: endotracheal suction and closed suction. Included were articles that compared the open and closed suction systems used in adult humans and that were randomized and controlled trials. RESULTS: From the 78 articles identified, only 15 were accepted and described in this review. Nine compared incidence of ventilator-associated pneumonia, six compared oxygen saturation, four compared blood pressure and heart rate, three compared pulmonary volumes, two compared secretion removal and four compared costs. No difference was found in these variables compared: incidence of ventilator associated pneumonia, mortality, intensive care unit length of stay, duration of mechanical ventilation, PaCO2, PaO2, mean blood pressure, heart rate and secretion removal. However, there were always SpO2 and pulmonary volume decreases when using the open suction system; and costs were lower in most of the studies that used the closed suction system. CONCLUSIONS: Closed suction system seems to increase the risk of colonization, but has the advantage of not reducing the pulmonary volumes and not entailing a drop of saturation, especially in patients with severe respiratory failure and in the use of higher levels of positive end expiratory pressure.