Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2017;29(1):47-54
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20170008
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the clinical/functional aspects and quality of life of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients who were discharged after an intensive care unit admission for acute respiratory failure.
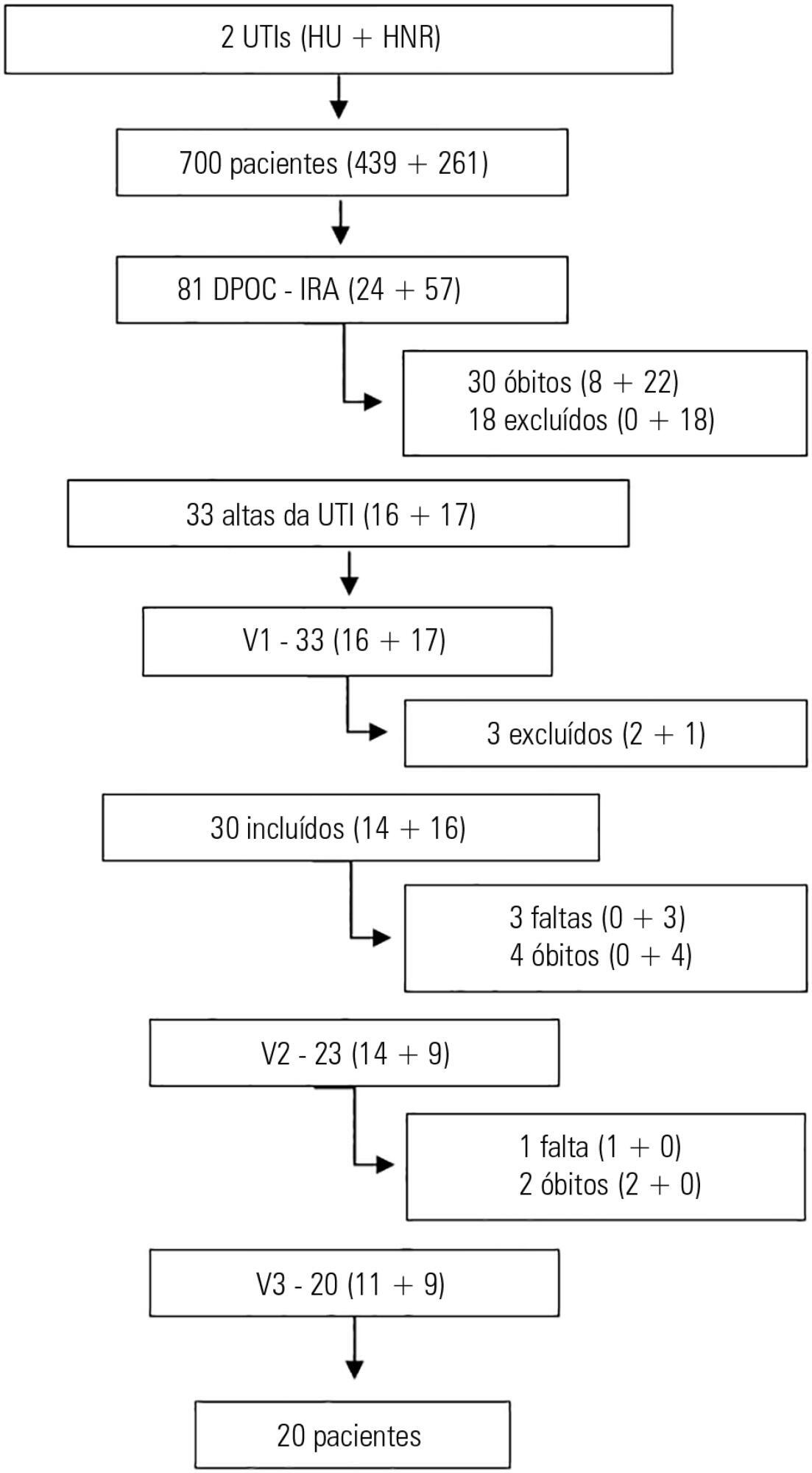
This prospective study included chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients who were admitted to two intensive care units between December of 2010 and August of 2011 and evaluated over three visits after discharge. Thirty patients were included, and 20 patients completed the three-month follow up.
There was a significant improvement in the following: forced expiratory flow in one second (L) (1.1/1.4/1.4; p = 0.019), six-minute walk test (m) (- /232.8 /272.6; p = 0.04), BODE score (7.5/5.0/3.8; p = 0.001), cognition measured by the Mini Mental State Examination (21/23.5/23.5; p = 0.008) and quality of life measured by the total Saint George Respiratory Questionnaire score (63.3/56.8/51, p = 0.02). The mean difference in the total score was 12.3 (between visits 1 and three). Important clinical differences were observed for the symptom score (18.8), activities score (5.2) and impact score (14.3). The majority of participants (80%) reported they would be willing to undergo a new intensive care unit admission.
Despite the disease severity, there was a significant clinical, functional and quality of life improvement at the end of the third month. Most patients would be willing to undergo a new intensive care unit admission.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2008;20(2):184-189
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2008000200012
BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is defined as a syndrome characterized by usually progressive chronic airflow limitation which is associated to a bronchial hyperresponsiveness and is partially reversible. Noninvasive mechanical ventilation is an alternative treatment for patients with COPD exacerbations. The objective of the literature reviews was to verify noninvasive mechanical ventilation benefits and complications in acute exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in patients. CONTENTS: This national and international's scientific literature review was developed according to criteria established for documentary research in the MedLine, LILACS, SciElo, PubMed and Cochrane, databases using the key words: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and noninvasive mechanical ventilation. Inclusion criteria were articles published from 1995 to 2007; in English, Spanish and Portuguese; studies in the human model and with no gender restriction. CONCLUSIONS: Noninvasive mechanical ventilation can reduce partial pressure of carbon dioxide, improve gas exchange, alleviate symptoms as dyspnea caused by fatigue of the respiratory muscles, reduce duration of hospitalization, decrease need for invasive mechanical ventilation, reduce number of complications and also lessen hospital mortality. The main complications found were: facial skin erythema, claustrophobia, nasal congestion, face pain, eye irritation, aspiration pneumonia, hypotension, pneumothorax, aerophagia, hypercapnia, gastric insufflation, vomit, bronchoaspiration, morning headaches, face injuries, air embolism and, last but not least, discomfort of the patient. Noninvasive mechanical ventilation can be more effective in patients with moderate-severe exacerbations of COPD and these complications can be minimized by an adequate interface also by the contribution of the physiotherapist experience.