You searched for:"Elias Ferreira Porto"
We found (2) results for your search.-
Original Articles
Comparative analysis between the alveolar recruitment maneuver and breath stacking technique in patients with acute lung injury
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2014;26(2):163-168
Abstract
Original ArticlesComparative analysis between the alveolar recruitment maneuver and breath stacking technique in patients with acute lung injury
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2014;26(2):163-168
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20140024
Views0Objective:
To compare the effectiveness of the alveolar recruitment maneuver and the breath stacking technique with respect to lung mechanics and gas exchange in patients with acute lung injury.
Methods:
Thirty patients were distributed into two groups: Group 1 – breath stacking; and Group 2 – alveolar recruitment maneuver. After undergoing conventional physical therapy, all patients received both treatments with an interval of 1 day between them. In the first group, the breath stacking technique was used initially, and subsequently, the alveolar recruitment maneuver was applied. Group 2 patients were initially subjected to alveolar recruitment, followed by the breath stacking technique. Measurements of lung compliance and airway resistance were evaluated before and after the use of both techniques. Gas analyses were collected before and after the techniques were used to evaluate oxygenation and gas exchange.
Results:
Both groups had a significant increase in static compliance after breath stacking (p=0.021) and alveolar recruitment (p=0.03), but with no significant differences between the groups (p=0.95). The dynamic compliance did not increase for the breath stacking (p=0.22) and alveolar recruitment (p=0.074) groups, with no significant difference between the groups (p=0.11). The airway resistance did not decrease for either groups, i.e., breath stacking (p=0.91) and alveolar recruitment (p=0.82), with no significant difference between the groups (p=0.39). The partial pressure of oxygen increased significantly after breath stacking (p=0.013) and alveolar recruitment (p=0.04), but there was no significant difference between the groups (p=0.073). The alveolar-arterial O2 difference decreased for both groups after the breath stacking (p=0.025) and alveolar recruitment (p=0.03) interventions, and there was no significant difference between the groups (p=0.81).
Conclusion:
Our data suggest that the breath stacking and alveolar recruitment techniques are effective in improving the lung mechanics and gas exchange in patients with acute lung injury.
Keywords:Breathing exercisesPhysical therapy modalitiesPositive-pressure respiration/methodsPulmonary gas exchangeRespiratory mechanicsSee more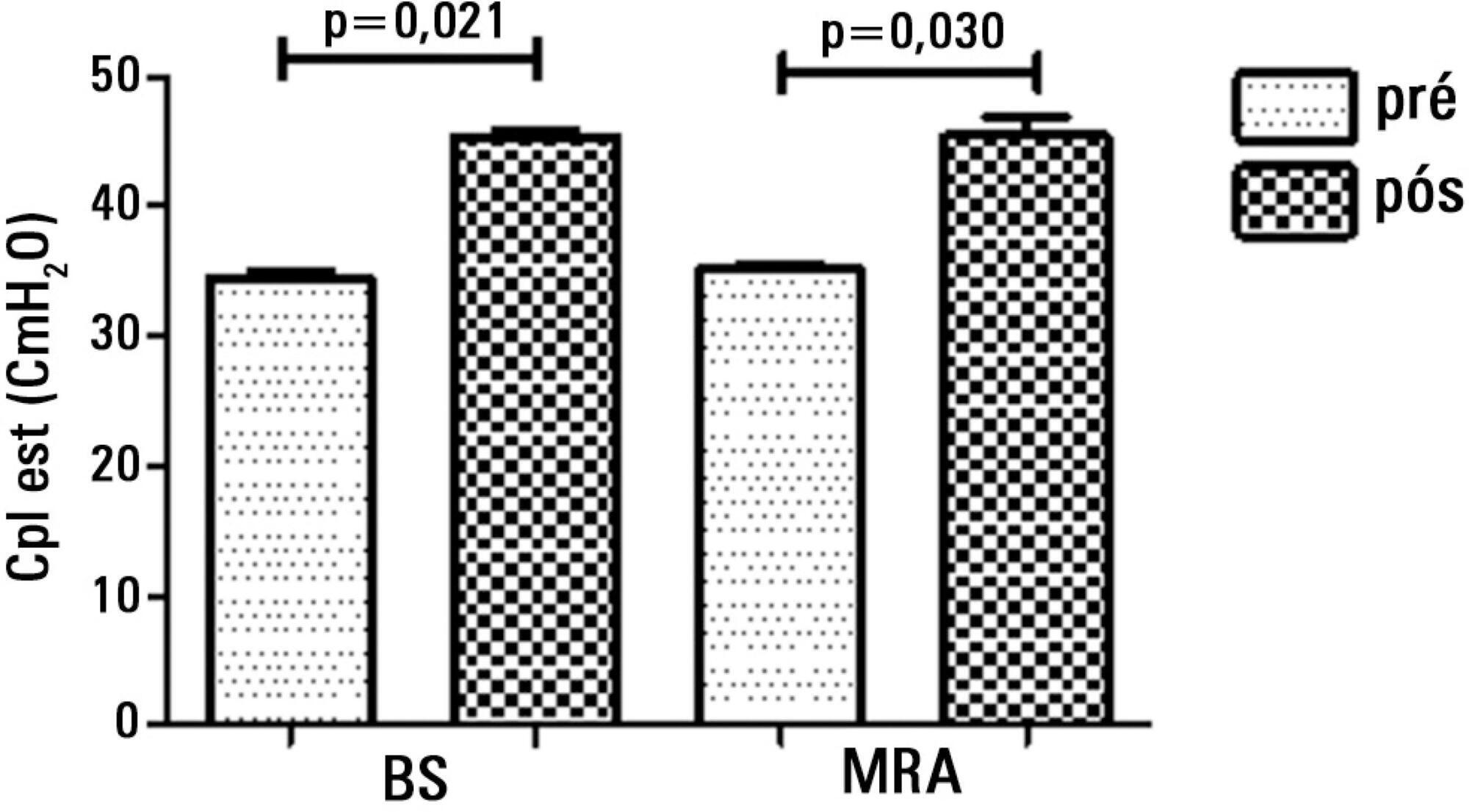
-
Original Articles
Comparative analysis of respiratory systems compliance in three different positioning (lateral, dorsal and sitting) in patients in prolonged invasive mechanical ventilation
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2008;20(3):213-219
Abstract
Original ArticlesComparative analysis of respiratory systems compliance in three different positioning (lateral, dorsal and sitting) in patients in prolonged invasive mechanical ventilation
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2008;20(3):213-219
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2008000300002
Views0See moreOBJECTIVES: This study is justified by the fact that in clinical practice, changes occur in patient’s positioning in the bed during hospitalization in intensive care unity, it’s necessary better understanding about possible adverse effects that such changes might cause mainly on the respiratory system condition. The objective this study was to evaluate if the patients positioning in bed can to alter the pulmonary complacency. METHODS: All included patients were submitted to mechanical ventilation and were sedated and curarized respiratory system compliance was assessed in three different positioning: lateral, dorsal and sitting. After an alveolar recruitment maneuver, patients were placed to a position throughout two hours, and in the last five minutes the data was collected from the mechanical ventilator display. RESULTS: twenty eight patients were prospectively assessed. Values of respiratory system compliance in the lateral position were 37,07 ± 12,9 in the dorsal were 39,2 ± 10,5 and in the sitting 43,4 ± 9,6 mL/cmH2O. There were a statistical difference when we compared to the sitting and dorsal with lateral positioning for respiratory system compliance (p = 0.0052) and tidal volume (p < 0.001). There was a negative correlation between mean values of positive end expiratory pressure a respiratory system compliance (r = 0.59, p = 0.002). The FIO2 administered was 0.6 for the lateral positioning and 0.5 for the dorsal and sitting positioning (p = 0.049). CONCLUSIONS: That body positioning in patients restrained to a bed and submitted to invasive mechanical ventilation leads to pulmonary compliance, tidal volume and SpO2 oscillations. In the sitting position the pulmonary compliance is higher than in others positions.

Search
Search in:
KEY WORDS
Case reports Child Coronavirus infections COVID-19 Critical care Critical illness Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation Infant, newborn Intensive care Intensive care units Intensive care units, pediatric mechanical ventilation Mortality Physical therapy modalities Prognosis Respiration, artificial Respiratory insufficiency risk factors SARS-CoV-2 Sepsis




