Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2020;32(3):444-457
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20200075
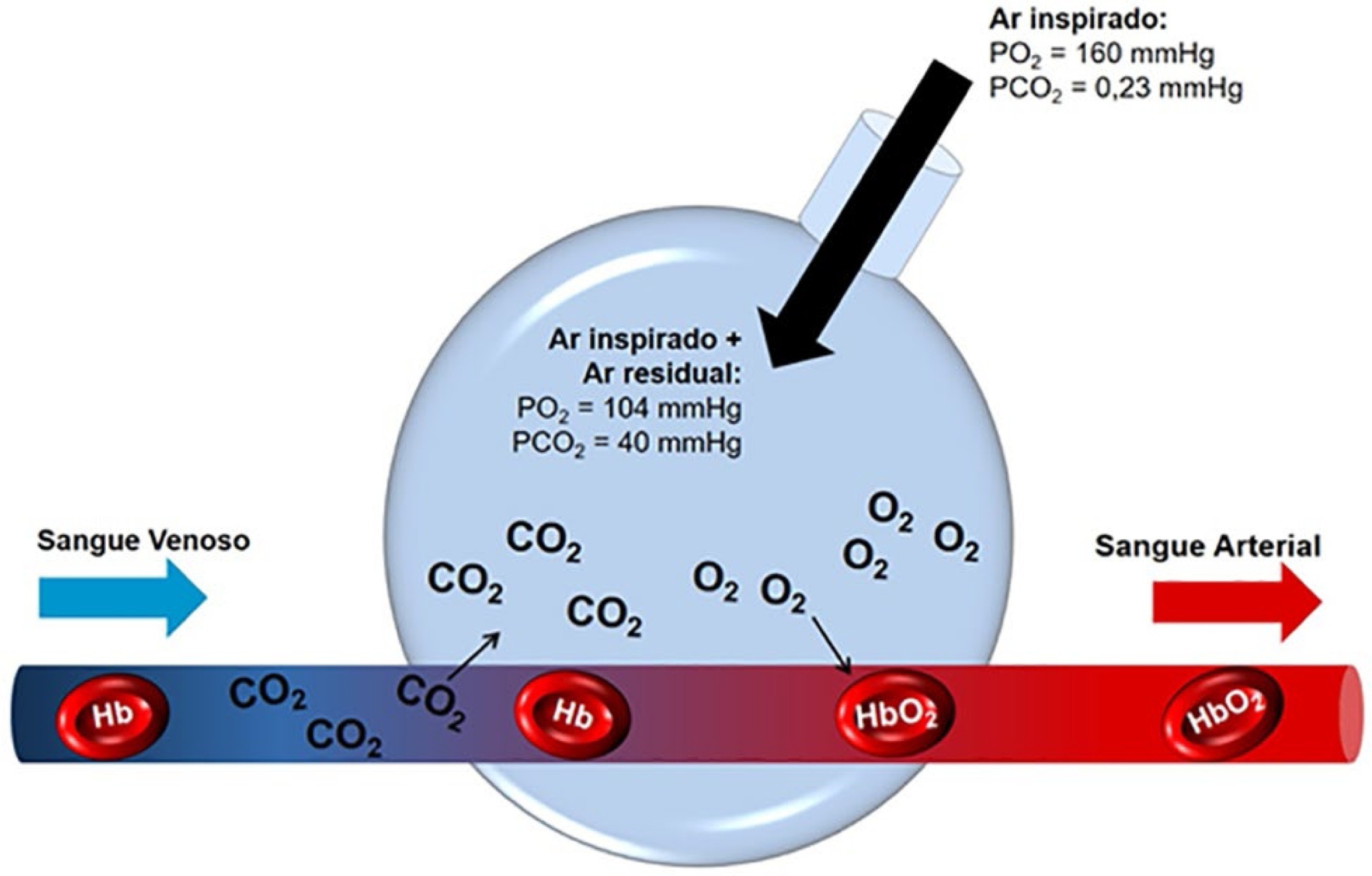
The COVID-19 pandemic has brought concerns to managers, healthcare professionals, and the general population related to the potential mechanical ventilators’ shortage for severely ill patients. In Brazil, there are several initiatives aimed at producing alternative ventilators to cover this gap. To assist the teams that work in these initiatives, we provide a discussion of some basic concepts on physiology and respiratory mechanics, commonly used mechanical ventilation terms, the differences between triggering and cycling, the basic ventilation modes and other relevant aspects, such as mechanisms of ventilator-induced lung injury, respiratory drive, airway heating and humidification, cross-contamination risks, and aerosol dissemination. After the prototype development phase, preclinical bench-tests and animal model trials are needed to determine the safety and performance of the ventilator, following the minimum technical requirements. Next, it is mandatory going through the regulatory procedures as required by the Brazilian Health Regulatory Agency (Agência Nacional de Vigilância Sanitária - ANVISA). The manufacturing company should be appropriately registered by ANVISA, which also must be notified about the conduction of clinical trials, following the research protocol approval by the Research Ethics Committee. The registration requisition of the ventilator with ANVISA should include a dossier containing the information described in this paper, which is not intended to cover all related matters but to provide guidance on the required procedures.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2019;31(1):39-46
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20190005
To compare the effects of vibrocompression and hyperinflation with mechanical ventilator techniques alone and in combination (hyperinflation with mechanical ventilator + vibrocompression) on the amount of aspirated secretion and the change in hemodynamic and pulmonary parameters.
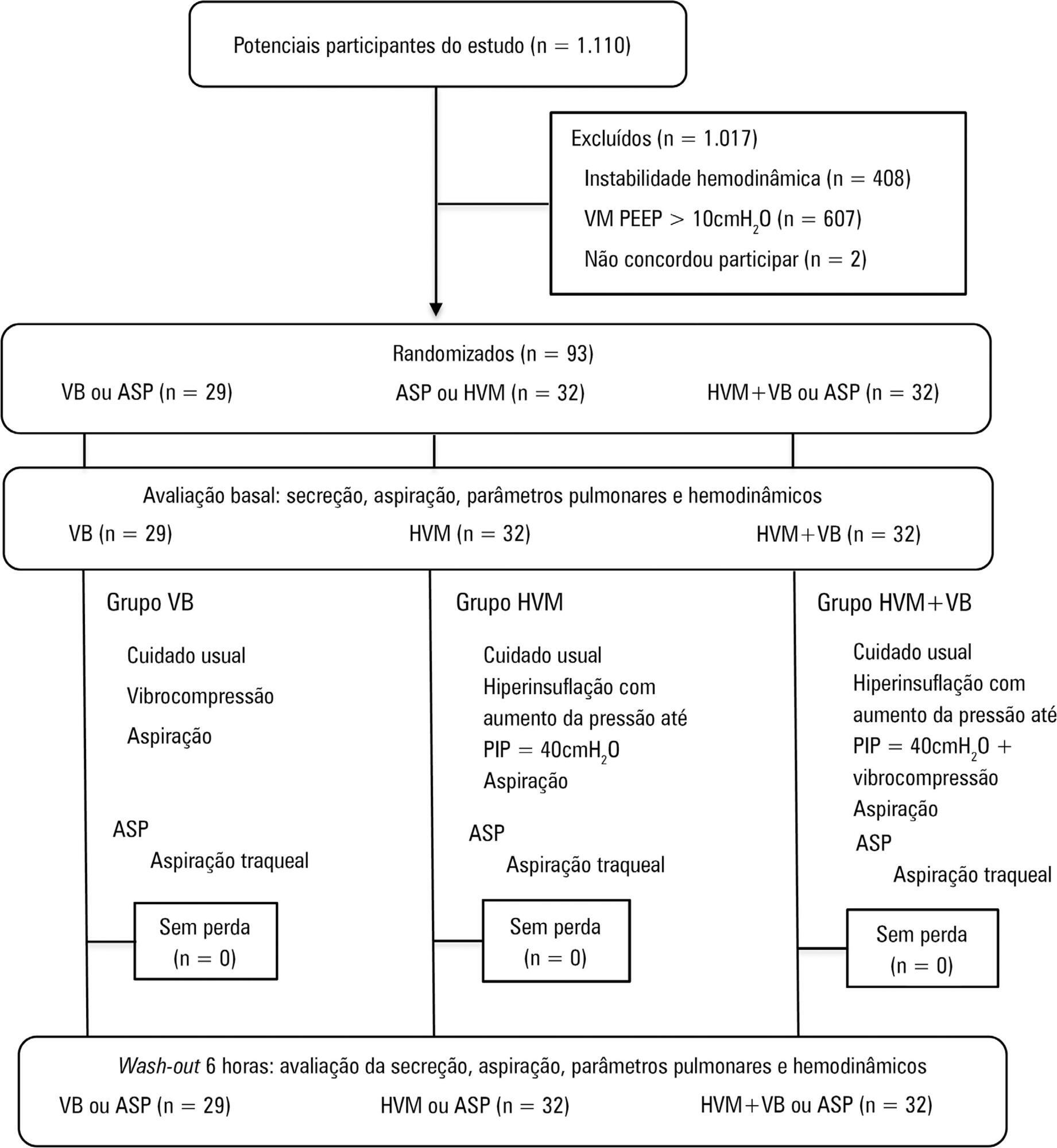
A randomized clinical trial with critically ill patients on mechanical ventilation conducted in the intensive care unit of a university hospital. The patients were randomly allocated to receive one of the bronchial hygiene techniques for 10 minutes (vibrocompression or hyperinflation with mechanical ventilator or hyperinflation with mechanical ventilator + vibrocompression). Afterwards, the patients were again randomly allocated to receive either the previous randomly allocated technique or only tracheal aspiration. The weight of aspirated secretions (in grams), ventilatory mechanics and cardiopulmonary data before and after the application of the techniques were analyzed. The tracheal reintubation frequency and time and mortality on mechanical ventilation were also evaluated.
A total of 93 patients (29 vibrocompression, 32 hyperinflation with mechanical ventilator and 32 hyperinflation with mechanical ventilator + vibrocompression) on mechanical ventilation for more than 24 hours were included. The hyperinflation with mechanical ventilator + vibrocompression group was the only one that presented a significant increase in aspirated secretions compared to tracheal aspiration alone [0.7g (0.1 - 2.5g) versus 0.2g (0.0 - 0.6g), p value = 0.006].
Compared to tracheal aspiration alone, the combination of hyperinflation with mechanical ventilator + vibrocompression techniques was most efficient for increasing the amount of aspirated secretions.
Search
Search in:
Case reports (56) Child (53) Coronavirus infections (34) COVID-19 (46) Critical care (116) Critical illness (54) Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (26) Infant, newborn (27) Intensive care (72) Intensive care units (256) Intensive care units, pediatric (31) mechanical ventilation (38) Mortality (76) Physical therapy modalities (28) Prognosis (61) Respiration, artificial (119) Respiratory insufficiency (26) risk factors (34) SARS-CoV-2 (28) Sepsis (98)