Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2015;27(3):252-259
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20150046
To describe postextubation noninvasive positive pressure ventilation use in intensive care unit clinical practice and to identify factors associated with noninvasive positive pressure ventilation failure.
This prospective cohort study included patients aged ≥ 18 years consecutively admitted to the intensive care unit who required noninvasive positive pressure ventilation within 48 hours of extubation. The primary outcome was noninvasive positive pressure ventilation failure.
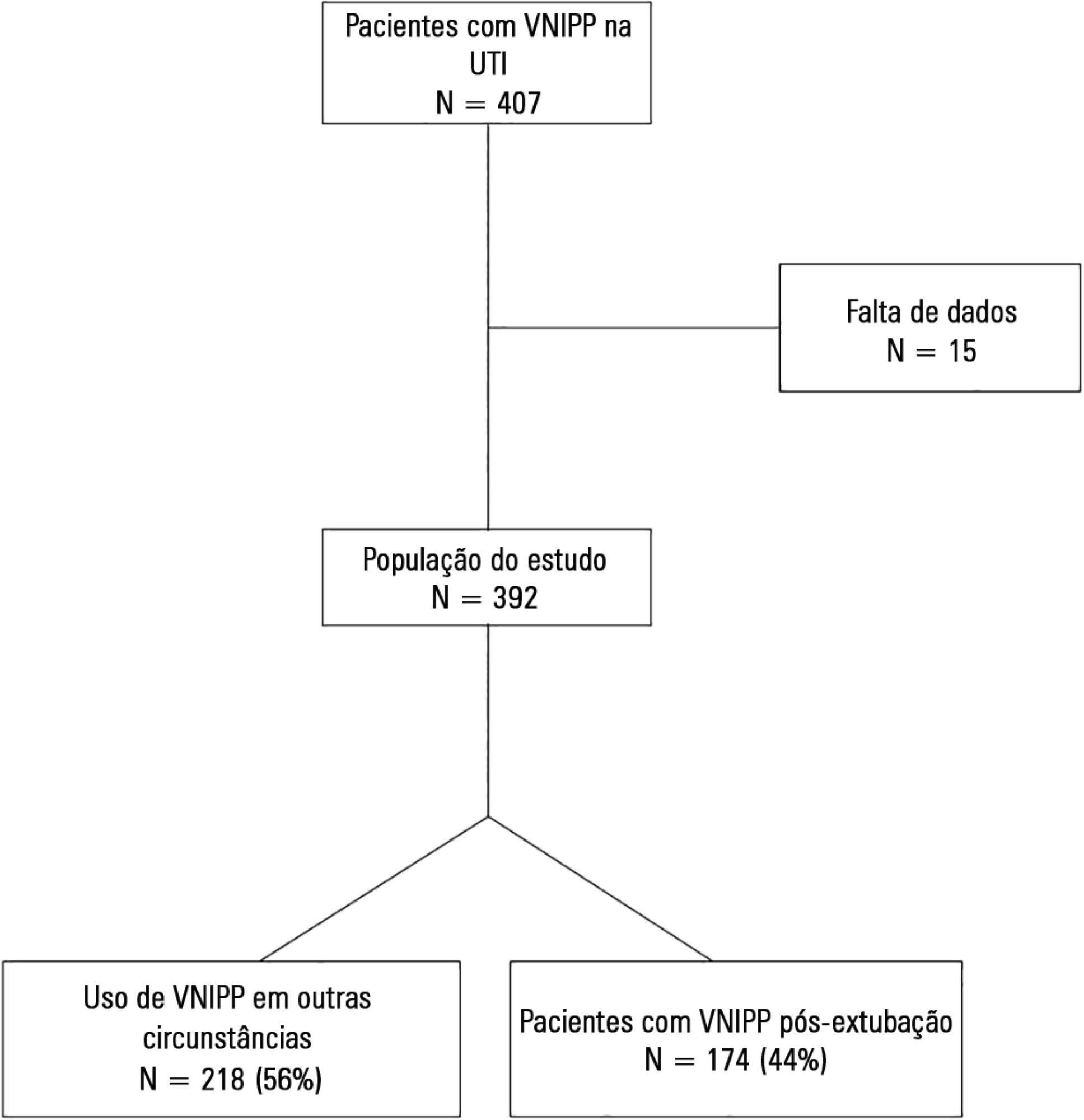
We included 174 patients in the study. The overall noninvasive positive pressure ventilation use rate was 15%. Among the patients who used noninvasive positive pressure ventilation, 44% used it after extubation. The failure rate of noninvasive positive pressure ventilation was 34%. The overall mean ± SD age was 56 ± 18 years, and 55% of participants were male. Demographics; baseline pH, PaCO2 and HCO3; and type of equipment used were similar between groups. All of the noninvasive positive pressure ventilation final parameters were higher in the noninvasive positive pressure ventilation failure group [inspiratory positive airway pressure: 15.0 versus 13.7cmH2O (p = 0.015), expiratory positive airway pressure: 10.0 versus 8.9cmH2O (p = 0.027), and FiO2: 41 versus 33% (p = 0.014)]. The mean intensive care unit length of stay was longer (24 versus 13 days), p < 0.001, and the intensive care unit mortality rate was higher (55 versus 10%), p < 0.001 in the noninvasive positive pressure ventilation failure group. After fitting, the logistic regression model allowed us to state that patients with inspiratory positive airway pressure ≥ 13.5cmH2O on the last day of noninvasive positive pressure ventilation support are three times more likely to experience noninvasive positive pressure ventilation failure compared with individuals with inspiratory positive airway pressure < 13.5 (OR = 3.02, 95%CI = 1.01 - 10.52, p value = 0.040).
The noninvasive positive pressure ventilation failure group had a longer intensive care unit length of stay and a higher mortality rate. Logistic regression analysis identified that patients with inspiratory positive airway pressure ≥ 13.5cmH2O on the last day of noninvasive positive pressure ventilation support are three times more likely to experience noninvasive positive pressure ventilation failure.