Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2022;34(2):255-261
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20220023-en
To test whether tissue oxygen saturation (StO2) after a venous occlusion test estimates central venous oxygen saturation (ScvO2).
Observational study in intensive care unit patients. Tissue oxygen saturation was monitored (InSpectra Tissue Spectrometer Model 650, Hutchinson Technology Inc., MN, USA) with a multiprobe (15/25mm) in the thenar position. A venous occlusion test in volunteers was applied in the upper arm to test the tolerability and pattern of StO2 changes during the venous occlusion test. A sphygmomanometer cuff was inflated to a pressure 30mmHg above diastolic pressure until StO2 reached a plateau and deflated to 0mmHg. Tissue oxygen saturation parameters were divided into resting StO2 (r-StO2) and minimal StO2 (m-StO2) at the end of the venous occlusion test. In patients, the cuff was inflated to a pressure 30mmHg above diastolic pressure for 5 min (volunteers’ time derived) or until a StO2 plateau was reached. Tissue oxygen saturation parameters were divided into r-StO2, m-StO2, and the mean time that StO2 reached ScvO2. The StO2 value at the mean time was compared to ScvO2.
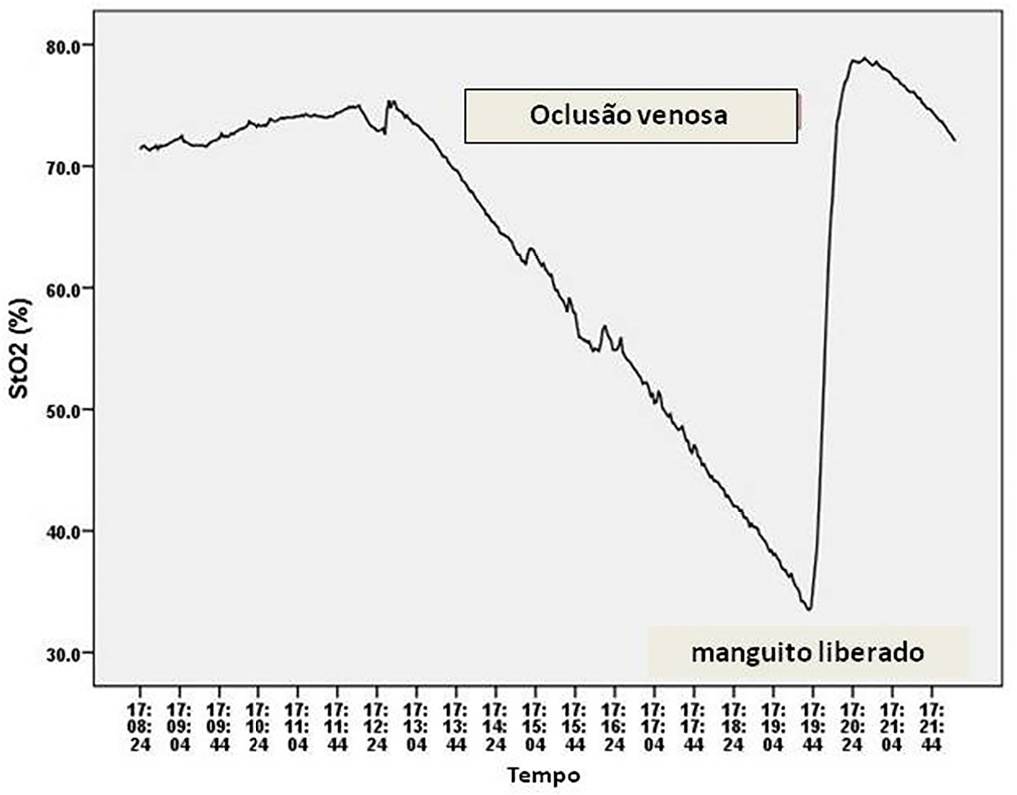
All 9 volunteers tolerated the venous occlusion test. The time for tolerability or the StO2 plateau was 7 ± 1 minutes. We studied 22 patients. The mean time for StO2 equalized ScvO2 was 100 sec and 95 sec (15/25mm probes). The StO2 value at 100 sec ([100-StO2] 15mm: 74 ± 7%; 25mm: 74 ± 6%) was then compared with ScvO2 (75 ± 6%). The StO2 value at 100 sec correlated with ScvO2 (15 mm: R2 = 0.63, 25mm: R2 = 0.67, p < 0.01) without discrepancy (Bland Altman).
Central venous oxygen saturation can be estimated from StO2 during a venous occlusion test.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2011;23(3):341-351
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2011000300013
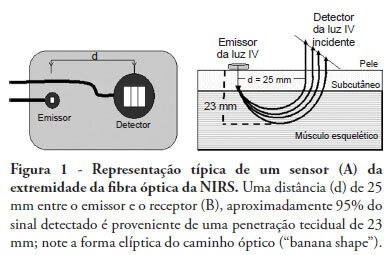
Near infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) is a non-invasive technique that allows determination of tissue oxygenation based on spectro-photometric quantitation of oxy- and deoxyhemoglobin within a tissue. This technique has gained acceptance as a tool to monitor peripheral tissue perfusion in critically ill patient. NIRS principle is based on the use of near-infrared electromagnetic waves for qualitative and quantitative assessments of molecular factors related to tissue oxygenation. Although this technique can be apllied in any tissue, it is primarily used for monitoring peripheral oxygenation in the muscle. Parameters that are determined using NIRS can be either directly calculated or can be derived from physiological interventions, such as arterial and venous occlusions methods. Information regarding muscle oxygen saturation, muscle oxygen consumption and regional blood flow can therefore be obtained. Clinical applications of NIRS include peripheral oxygenation monitoring during resuscitation of trauma and septic shock as well as the assessment of regional microcirculatory disorders. This review provides a brief discussion of NIRS basic principles and main clinical uses of this technique, with a specific focus on studies that assess the usefulness of NIRS in intensive care and emergency patients.
Search
Search in:
Case reports (56) Child (53) Coronavirus infections (34) COVID-19 (46) Critical care (116) Critical illness (54) Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (26) Infant, newborn (27) Intensive care (72) Intensive care units (256) Intensive care units, pediatric (31) mechanical ventilation (38) Mortality (76) Physical therapy modalities (28) Prognosis (61) Respiration, artificial (119) Respiratory insufficiency (26) risk factors (34) SARS-CoV-2 (28) Sepsis (98)