Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2012;24(1):79-85
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2012000100012
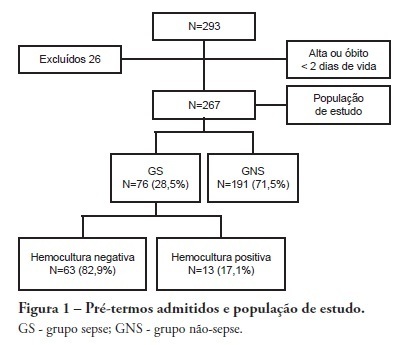
OBJECTIVE: To evaluate the prevalence factors and etiologies associated with late neonatal sepsis in preterm neonates in a neonatal intensive care unit. METHODS: This was a cross-sectional study of secondary data pertaining to preterm neonates admitted to the neonatal intensive care unit between 2008 and 2010 and was gathered from medical charts. The outcome variable, late neonatal sepsis, was characterized using the Brazilian national health surveillance agency criteria. Pearson's Chi-squared test, Fisher's exact test and the linear trend Chi-squared test were used to assess the qualitative variables for linear trends. The statistical significance level was set at p < 0.05. Bivariate and multivariate analyses of the independent and dependent variables were conducted to obtain a measure of the effect and prevalence ratios, considering a p-value of less than 0.20 to indicate statistical significance. RESULTS: This study included 267 preterm neonates. Of the participants, 28.5% were characterized as having late-onset sepsis. Positive blood cultures were recorded for 17.1% of the neonates. Death occurred in 8.2% of the total cases, and of these deaths, 68.2% occurred within the sepsis group. Three deaths were associated with positive blood cultures, all of which grew Gram-negative bacteria. The bivariate analysis demonstrated that as the gestational age and birth weight decreased, the prevalence of late-onset sepsis trended upward. Ten or more days on mechanical ventilation was associated with late-onset neonatal sepsis in 80.8% of cases. Peripherally inserted central catheters left in place for 11 or more days were associated with late-onset neonatal sepsis in 76.2% of cases. The multivariate analysis demonstrated that a peripherally inserted catheter left in place for less than 11 days was associated with late-onset neonatal sepsis. Gram-negative bacteria, including Klebsiella pneumoniae and Escherichia coli, were the most frequent causative agents. CONCLUSIONS: Late sepsis remains a concern because of its prevalence in intensive care units and because it increases the number of invasive procedures that preterm children usually undergo in these units. The authors emphasize the expanding role of Gram-negative bacteria in late-onset neonatal sepsis and the need for more efficient methods to identify confirmed sepsis.