Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2016;28(1):55-61
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20160003
To analyze the characteristics of children with acute viral bronchiolitis subjected to mechanical ventilation for three consecutive years and to correlate their progression with mechanical ventilation parameters and fluid balance.
Longitudinal study of a series of infants (< one year old) subjected to mechanical ventilation for acute viral bronchitis from January 2012 to September 2014 in the pediatric intensive care unit. The children's clinical records were reviewed, and their anthropometric data, mechanical ventilation parameters, fluid balance, clinical progression, and major complications were recorded.
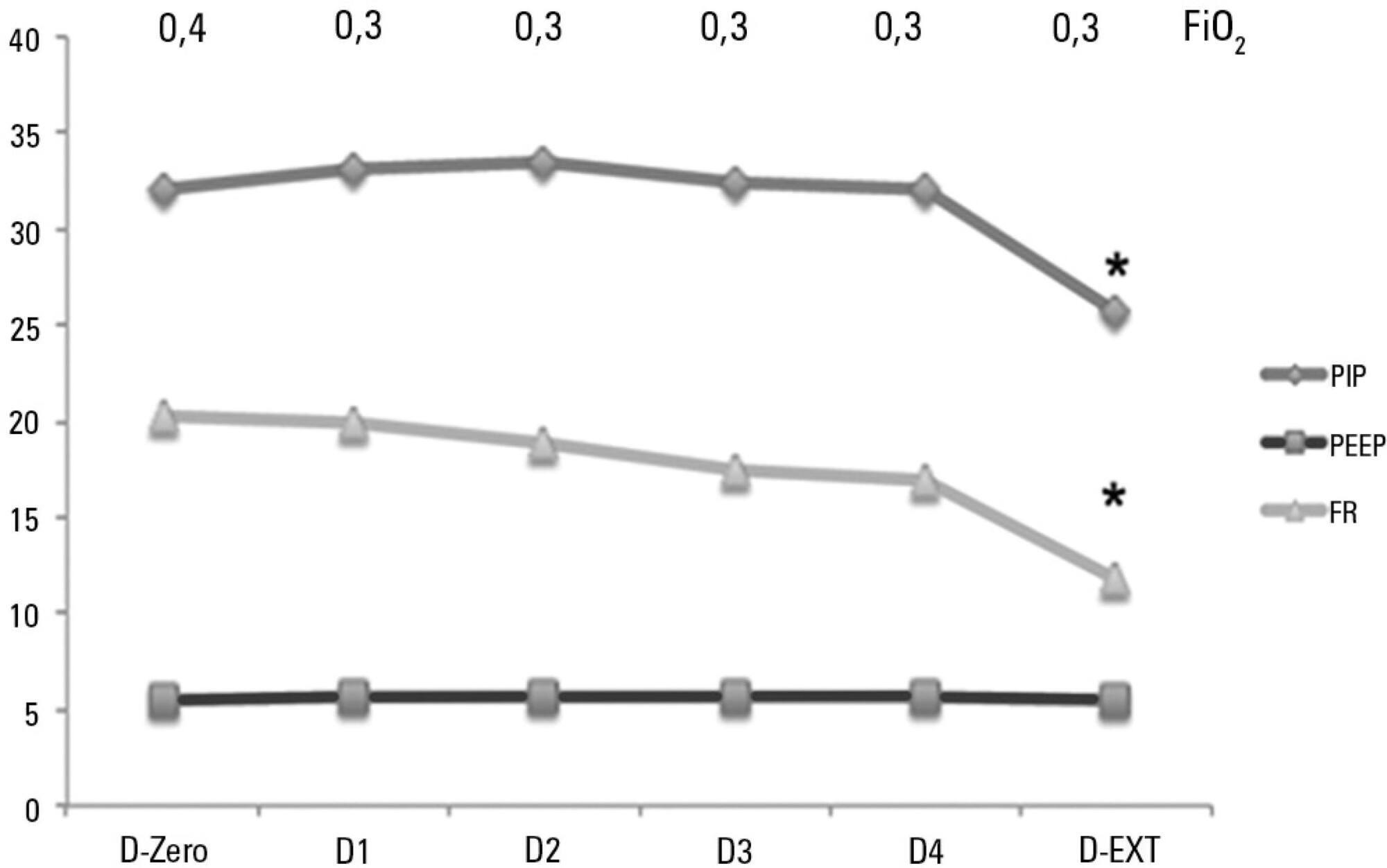
Sixty-six infants (3.0 ± 2.0 months old and with an average weight of 4.7 ± 1.4kg) were included, of whom 62% were boys; a virus was identified in 86%. The average duration of mechanical ventilation was 6.5 ± 2.9 days, and the average length of stay in the pediatric intensive care unit was 9.1 ± 3.5 days; the mortality rate was 1.5% (1/66). The peak inspiratory pressure remained at 30cmH2O during the first four days of mechanical ventilation and then decreased before extubation (25 cmH2O; p < 0.05). Pneumothorax occurred in 10% of the sample and extubation failure in 9%, which was due to upper airway obstruction in half of the cases. The cumulative fluid balance on mechanical ventilation day four was 402 ± 254mL, which corresponds to an increase of 9.0 ± 5.9% in body weight. Thirty-seven patients (56%) exhibited a weight gain of 10% or more, which was not significantly associated with the ventilation parameters on mechanical ventilation day four, extubation failure, duration of mechanical ventilation or length of stay in the pediatric intensive care unit.
The rate of mechanical ventilation for acute viral bronchiolitis remains constant, being associated with low mortality, few adverse effects, and positive cumulative fluid balance during the first days. Better fluid control might reduce the duration of mechanical ventilation.
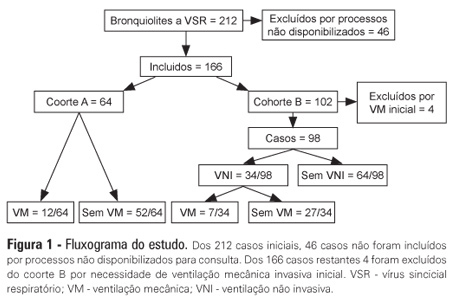
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2012;24(4):375-380
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2012000400014
OBJECTIVES: The present study focused on respiratory syncytial virus bronchiolitis with respiratory failure. The aim of the study was to determine whether noninvasive ventilation reduces the need for endotracheal intubation or slows the clinical progression of acute respiratory syncytial virus bronchiolitis by reducing the incidence of infectious complications. METHODS: The present study was a retrospective cohort study. Cohort A was comprised of children who were admitted to the pediatric intensive and special care unit from 2003-2005 before starting noninvasive ventilation; cohort B was comprised of children who were admitted to the pediatric intensive and special care unit from 2006-2008 after starting noninvasive ventilation. With the exception of noninvasive ventilation, the therapeutic support was the same for the two groups. All children who were diagnosed with respiratory syncytial virus bronchiolitis and respiratory failure between November 2003 and March 2008 were included in the cohort. Demographic, clinical and blood gas variables were analyzed. RESULTS: A total of 162 children were included; 75% of the subjects were less than 3 months old. Group A included 64 children, and group B included 98 children. In group B, 34 of the children required noninvasive ventilation. The distributions of the variables age, preterm birth, congenital heart disease, cerebral palsy and chronic lung disease were similar between the two groups. On admission, the data for blood gas analysis and the number of apneas were not significantly different between the groups. In group B, fewer children required invasive ventilation (group A: 12/64 versus group B: 7/98; p=0.02), and there was a reduction in the number of cases of bacterial pneumonia (group A: 19/64 versus group B: 12/98; p=0.008). There was no record of mortality in either of the groups. CONCLUSION: By comparing children with the same disease both before and after noninvasive ventilation was used for ventilation support, we verified a reduction in infectious complications and cases requiring intubation.