You searched for:"Cristiano Corrêa Batista"
We found (2) results for your search.Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2007;19(2):151-160
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2007000200003
BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: Currently, the reformulation of intensive care goals, often shifting from the search for a cure to offering comfort, has become more and more necessary. The intensivist is frequently confronted with the decision to suspend or not offer a specific therapy, despite its availability. The objective of this study was to estimate the developing risk of probability of death for individual ICU patients with respiratory failure, identify which life-sustaining therapies were administered, time of internment and outcome. Compare the death outcome in relation to UNICAMP II and APACHE II models, as well as verify if the life-sustaining therapies may be limited or suspended. METHODS: It is the observational, prospective cohort study of 150 patients with respiratory failure confined to the intensive care unit. Statistical analysis was carried out using Generalized Linear Models. RESULTS: Age, sex, race or morbidity did not reveal statistical significance in predicting outcome. This prediction was confirmed more accurately by means of changes in the individual prognostic index of death probability during the first seven days of ICU internment. A 10% worsening prognosis in patients who presented initial death risk of 70% to 80%, utilizing the UNICAMP II Model, showed a specificity of 97.4% - 98.6%. CONCLUSIONS: Prognostic changes in patients during the first seven days of ICU internment are of great aid, from an objective point of view, for ethical decision-making in relation to not-offering new life-sustaining therapies.
Abstract
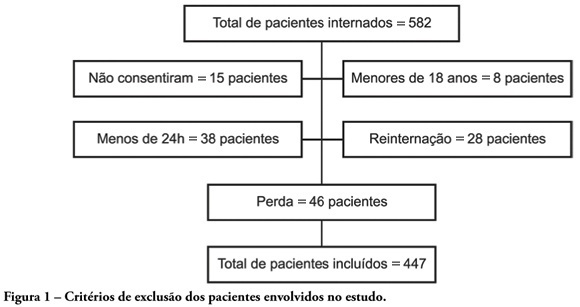
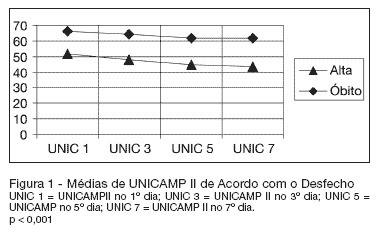
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2009;21(3):247-254
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2009000300003
OBJECTIVES: Availability of state-of-the-art technology at intensive care units has often turned into a tool aggravating suffering by prolonging the end-of-life process. Distinguishing therapeutic persistence from therapeutic obstinacy has become a great challenge for present-day medicine. The aim of this study was to assess the benefit-harm relation in the use of life-sustaining therapies by means of an evolutionary system of individual prognostic assessment. METHODS: A cohort, prospective, observational study at the intensive care unit of the São Francisco De Paula University Hospital of UCPel, Pelotas RS from March 2006 to August 31, 2007. Individual prognostic assessments were recorded by using an evolutionary system, the UNICAMP II index, associated with albumin transferrin and lymphocytes serum levels, life- sustaining therapies and the outcome. Statistical analysis was carried out by the Student's t-test, ANOVA test, Chi-square test, Fisher's exact test, Spearman's correlation test and area under the receiver-operating characteristic curve. A p value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. RESULTS: Four hundred forty seven patients were assessed during the study. Prevalence of death was significantly higher among those who received life-sustaining therapies at a later stage of the intervention, and those whose prognostic index and nutritional status worsened at an early stage of intervention. CONCLUSION: Assessment of individual evolutionary prognostic proved to be a useful method to objectively subsidize ethical decisions related to therapeutic persistence and therapeutic obstinacy.