You searched for:"Rachel Duarte Moritz"
We found (12) results for your search.Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2008;20(4):422-428
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2008000400016
The objective of this review was to evaluate current knowledge regarding terminal illness and palliative care in the intensive care unit, to identify the major challenges involved and propose a research agenda on these issues The Brazilian Critical Care Association organized a specific forum on terminally ill patients, to which were invited experienced and skilled professionals on critical care. These professionals were divided in three groups: communication in the intensive care unit, the decision making process when faced with a terminally ill patient and palliative actions and care in the intensive care unit. Data and bibliographic references were stored in a restricted website. During a twelve hour meeting and following a modified Delphi methodology, the groups prepared the final document. Consensual definition regarding terminality was reached. Good communication was considered the cornerstone to define the best treatment for a terminally ill patient. Accordingly some communication barriers were described that should be avoided as well as some approaches that should be pursued. Criteria for palliative care and palliative action in the intensive care unit were defined. Acceptance of death as a natural event as well as respect for the patient's autonomy and the nonmaleficence principles were stressed. A recommendation was made to withdraw the futile treatment that prolongs the dying process and to elected analgesia and measures that alleviate suffering in terminally ill patients. To deliver palliative care to terminally ill patients and their relatives some principles and guides should be followed, respecting individual necessities and beliefs. The intensive care unit staff involved with the treatment of terminally ill patients is subject to stress and tension. Availability of a continuous education program on palliative care is desirable.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2007;19(4):485-489
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2007000400014
BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: The suffering with the death and the prolonged time of patient's admission in a intensive care unit (ICU) are factors that leads to necessity the best communication with the personal that works in ICU, patients and their family, and its justify this work, whose objective is discuss this subject. CONTENTS: The professional experience of the author was used in this issue and the articles written during the last five years about death, communication and ICU were reviewed by means of MedLine, Up to Date, Google and Brazilian Journal of Intensive Therapy. CONCLUSIONS: It was concluded that the physician, the patient together with her/his family, and the multiprofessional staff of the ICU is one of the main factors that interferes with the process of satisfying both the patient and the ones who work on such unities. For adequate information, the physician must be conscious about therapeutic limits, and must learn how to treat the patient during the process of dying. In this way, the physician will be apt to talk about death. The ideal situation would be that the professional, responsible to give the news, should be experience, from the technical point of view as well as ethical, and should be the same person, as always as possible, when necessary. The patient mostly little be able to influence in her/his process of dying, but if communication is possible, it be simple, honest and humane. The patient's family members have the right of being together with the one who they love, and of being steadily informed about the real situation. All the members in the process must know the truth and the chosen therapeutic orientation to be taken. Communication should be done in a quiet and prived place.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2007;19(1):60-66
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2007000100008
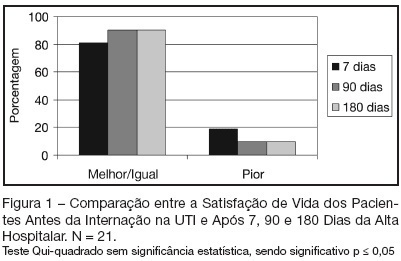
BACKGROUND AND OBJETIVES: To evaluate the quality and satisfaction of life (QSL) of patients before admission in ICU, and after hospital discharge. To verify the influence of the patient's demographic/clinic/therapeutic factors in the QSL. METHODS: Prospective cohort study with quali-quantitative approach. All patients admitted in ICU/HU/UFSC from April-July 2005, who's stayed more than 24 hours were included. Initially, the data of QSL before ICU admission, patient's demographics/clinics/therapeutics features were recorded. Afterwards, by telephone, 7, 90 and 180 days after hospital discharge, the patients answered the questionnaires about QSL. In the sequence, all patients were subdivided into 2 main groups: unchanged or better, and worse QSL. Data were analyzed using t Student and Chi-square tests (p-value < 0.05). RESULTS: Sixty eight patients were enrolled into the study. Completed questionnaires were obtained from 21 of them. A comparison of 7, 90 and 180 days after hospital discharge showed that QSL of patients was unchanged or better at 90 and 180 days. The majority of patients expressed more satisfaction in that moment. Unchanged or better QSL was associated with advanced age. However, there were no statistical significant differences in sex, schooling, APACHE II score, length of stay, mechanical ventilation and used drugs. Sixty percent returned to their previous work. CONCLUSIONS: There was a tendency for patients who felt themselves satisfied after hospital discharge to have their QSL improved as time went bye. Better QSL was associated with advanced age. Even when patients reported worse QSL they returned to their previous work.