You searched for:"Norberto Tiribelli"
We found (2) results for your search.-
Original Articles
Effect of PEEP on inspiratory resistance components in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome ventilated at low tidal volume
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2019;31(4):483-489
Abstract
Original ArticlesEffect of PEEP on inspiratory resistance components in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome ventilated at low tidal volume
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2019;31(4):483-489
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20190071
Views0ABSTRACT
Objective:
To describe the behavior of inspiratory resistance components when positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) increases in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome under a protective ventilation strategy.
Methods:
In volume-controlled mode, at 6mL/kg and constant flow, end-inspiratory occlusions were performed at 0, 5 10, 15 and 20cmH2O PEEP. Peak, initial and plateau pressure values were assessed, calculating the maximum, minimum and differential resistances. The results were compared by repeated measures analysis of variance (ANOVA) with post hoc Bonferroni correction, considering p < 0.05 significant.
Results:
The highest maximum resistance was observed at the lowest PEEP levels. The values for 10 and 15cmH2O PEEP significantly differed from those for 5 and 0cmH2O PEEP, whereas that for 20cmH2O PEEP only significantly differed from that for 0cmH2O PEEP (p < 0.05). The minimum resistance behaved similarly to the maximum resistance; the values for PEEP levels from 10cmH2O to 20cmH2O significantly differed from those for 0 and 5cmH2O PEEP (p < 0.05). Differential resistance showed the opposite variation to the maximum and minimum resistances. The only PEEP level that showed significant differences from 0 and 5cmH2O PEEP was 20cmH2O PEEP. Significant differences were also found between 15 and 5cmH2O PEEP (p < 0.05).
Conclusions:
During protective ventilation in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome, the maximum resistance of the respiratory system decreases with PEEP, reflecting the minimum resistance response, whereas differential resistance increases with PEEP.
Keywords:Continuous positive airway pressureRespiration, artificialRespiratory distress syndrome, adultSee more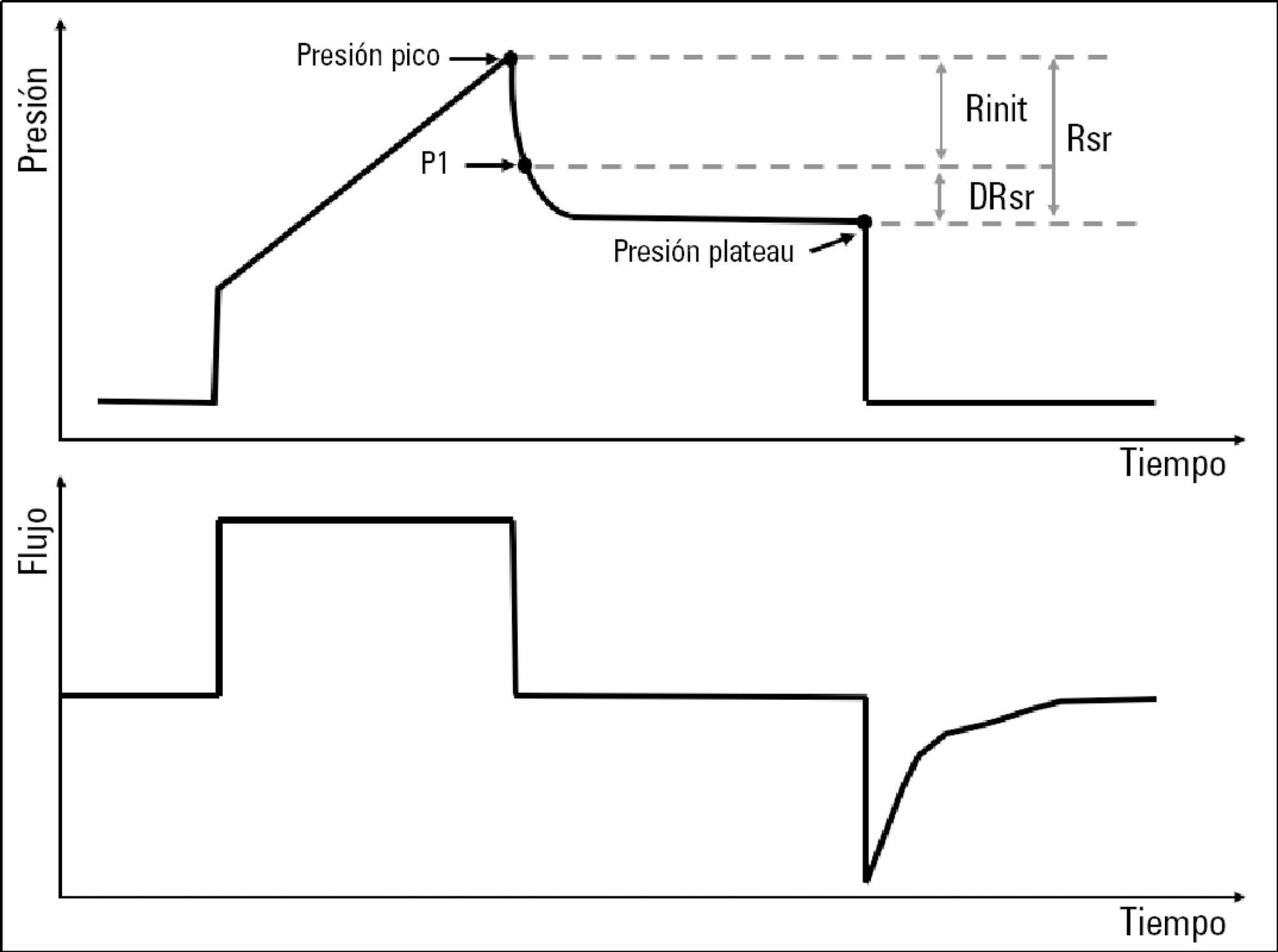
-
Review Articles
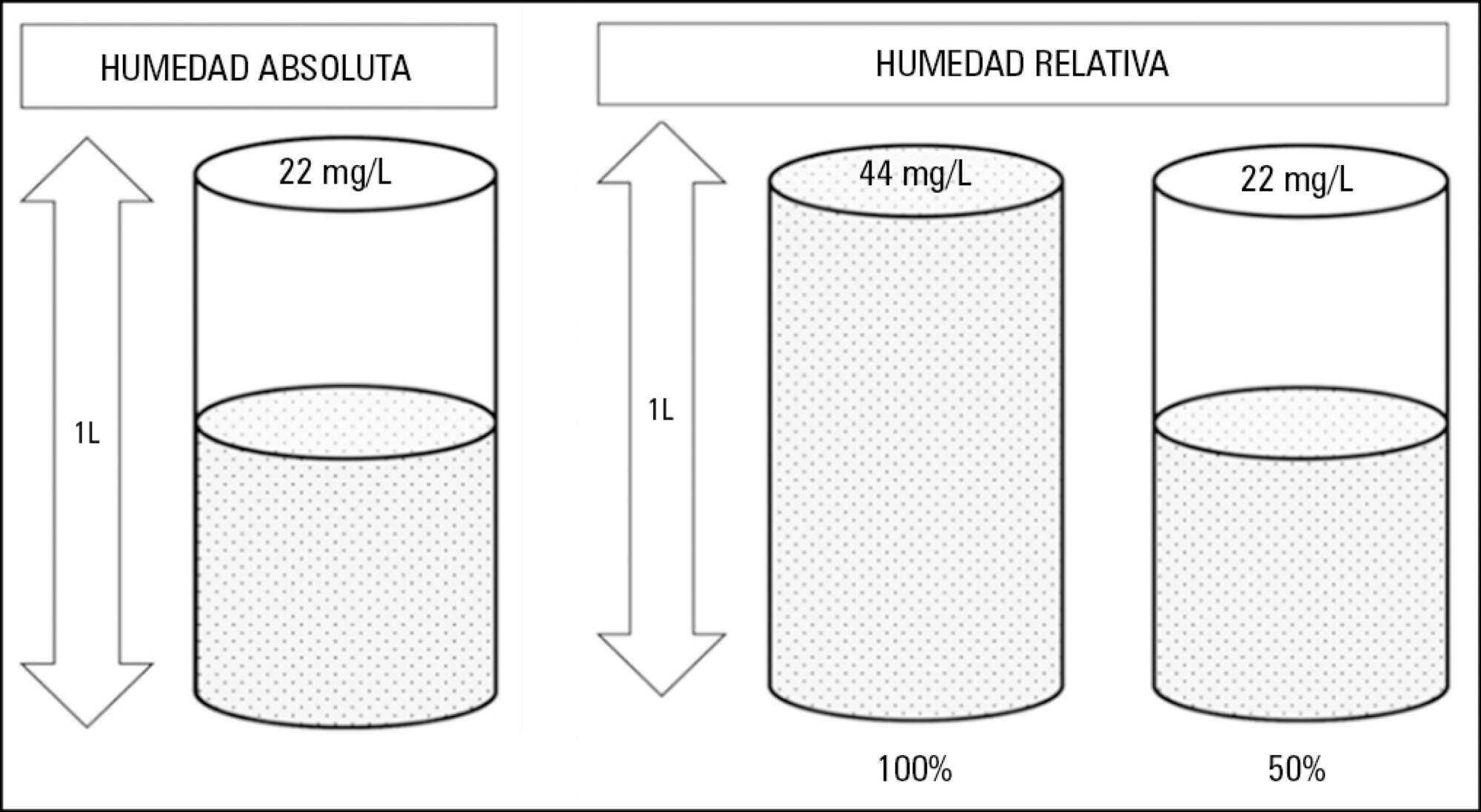
Humidification and heating of inhaled gas in patients with artificial airway. A narrative review
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2018;30(1):86-97
Abstract
Review ArticlesHumidification and heating of inhaled gas in patients with artificial airway. A narrative review
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2018;30(1):86-97
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20180015
Views2See moreABSTRACT
Instrumentation of the airways in critical patients (endotracheal tube or tracheostomy cannula) prevents them from performing their function of humidify and heating the inhaled gas. In addition, the administration of cold and dry medical gases and the high flows that patients experience during invasive and non-invasive mechanical ventilation generate an even worse condition. For this reason, a device for gas conditioning is needed, even in short-term treatments, to avoid potential damage to the structure and function of the respiratory epithelium. In the field of intensive therapy, the use of heat and moisture exchangers is common for this purpose, as is the use of active humidification systems. Acquiring knowledge about technical specifications and the advantages and disadvantages of each device is needed for proper use since the conditioning of inspired gases is a key intervention in patients with artificial airway and has become routine care. Incorrect selection or inappropriate configuration of a device can have a negative impact on clinical outcomes. The members of the Capítulo de Kinesiología Intensivista of the Sociedad Argentina de Terapia Intensiva conducted a narrative review aiming to show the available evidence regarding conditioning of inhaled gas in patients with artificial airways, going into detail on concepts related to the working principles of each one.
Search
Search in:
KEY WORDS
Case reports Child Coronavirus infections COVID-19 Critical care Critical illness Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation Infant, newborn Intensive care Intensive care units Intensive care units, pediatric mechanical ventilation Mortality Physical therapy modalities Prognosis Respiration, artificial Respiratory insufficiency risk factors SARS-CoV-2 Sepsis




