You searched for:"Mariana Barbosa Monteiro"
We found (1) results for your search.-
Original Articles
Reclassifying the spectrum of septic patients using lactate: severe sepsis, cryptic shock, vasoplegic shock and dysoxic shock
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2013;25(4):270-278
Abstract
Original ArticlesReclassifying the spectrum of septic patients using lactate: severe sepsis, cryptic shock, vasoplegic shock and dysoxic shock
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2013;25(4):270-278
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20130047
Views1See moreObjective:
The current definition of severe sepsis and septic shock includes a heterogeneous profile of patients. Although the prognostic value of hyperlactatemia is well established, hyperlactatemia is observed in patients with and without shock. The present study aimed to compare the prognosis of septic patients by stratifying them according to two factors: hyperlactatemia and persistent hypotension.
Methods:
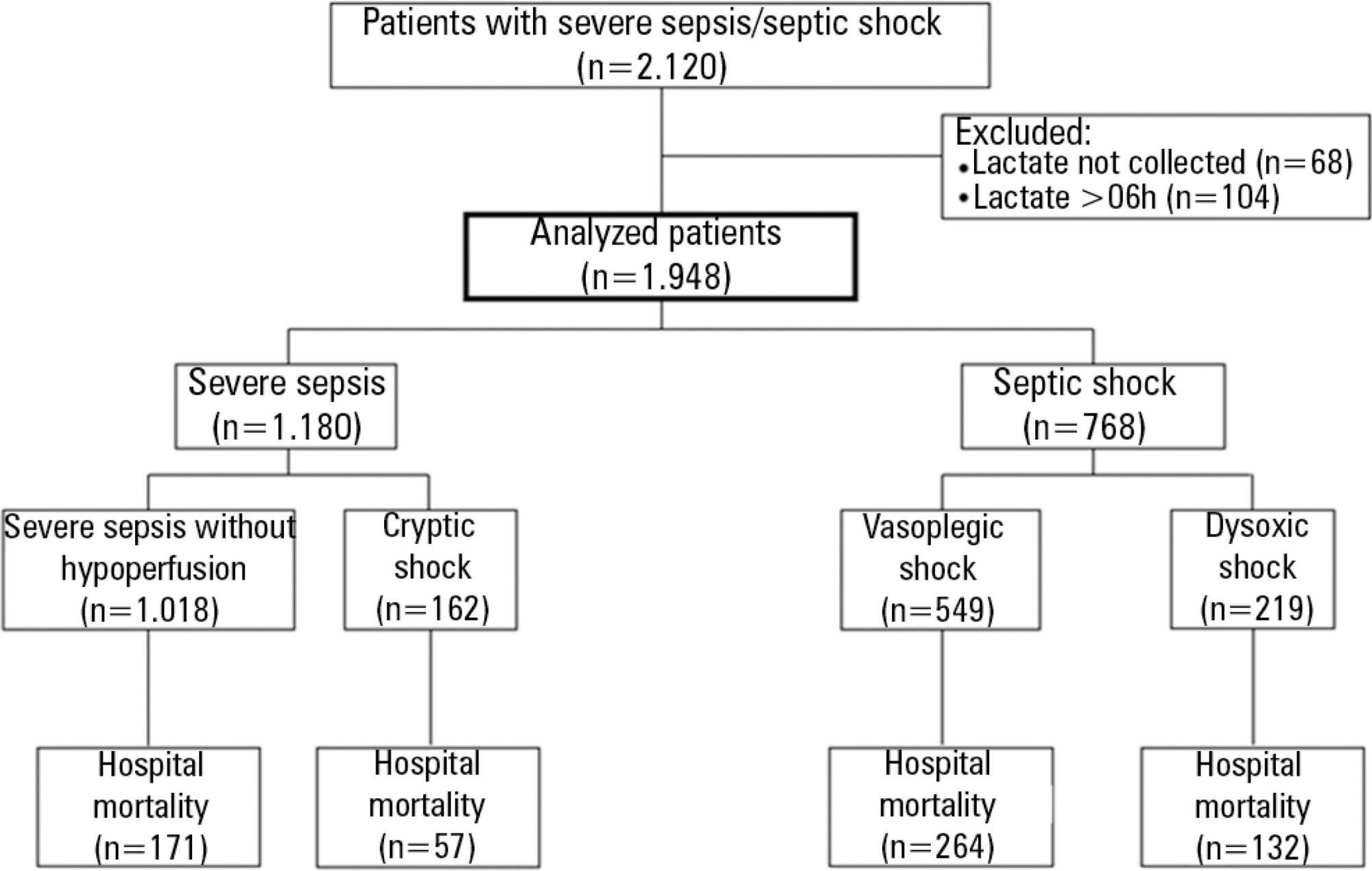
The present study is a secondary analysis of an observational study conducted in ten hospitals in Brazil (Rede Amil – SP). Septic patients with initial lactate measurements in the first 6 hours of diagnosis were included and divided into 4 groups according to hyperlactatemia (lactate >4mmol/L) and persistent hypotension: (1) severe sepsis (without both criteria); (2) cryptic shock (hyperlactatemia without persistent hypotension); (3) vasoplegic shock (persistent hypotension without hyperlactatemia); and (4) dysoxic shock (both criteria).
Results:
In total, 1,948 patients were analyzed, and the sepsis group represented 52% of the patients, followed by 28% with vasoplegic shock, 12% with dysoxic shock and 8% with cryptic shock. Survival at 28 days differed among the groups (p<0.001). Survival was highest among the severe sepsis group (69%, p<0.001 versus others), similar in the cryptic and vasoplegic shock groups (53%, p=0.39), and lowest in the dysoxic shock group (38%, p<0.001 versus others). In the adjusted analysis, the survival at 28 days remained different among the groups (p<0.001) and the dysoxic shock group exhibited the highest hazard ratio (HR=2.99, 95%CI 2.21-4.05).
Conclusion:
The definition of sepsis includes four different profiles if we consider the presence of hyperlactatemia. Further studies are needed to better characterize septic patients, to understand the etiology and to design adequate targeted treatments.
Search
Search in:
KEY WORDS
Case reports Child Coronavirus infections COVID-19 Critical care Critical illness Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation Infant, newborn Intensive care Intensive care units Intensive care units, pediatric mechanical ventilation Mortality Physical therapy modalities Prognosis Respiration, artificial Respiratory insufficiency risk factors SARS-CoV-2 Sepsis




