Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2012;24(4):401-406
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2012000400018
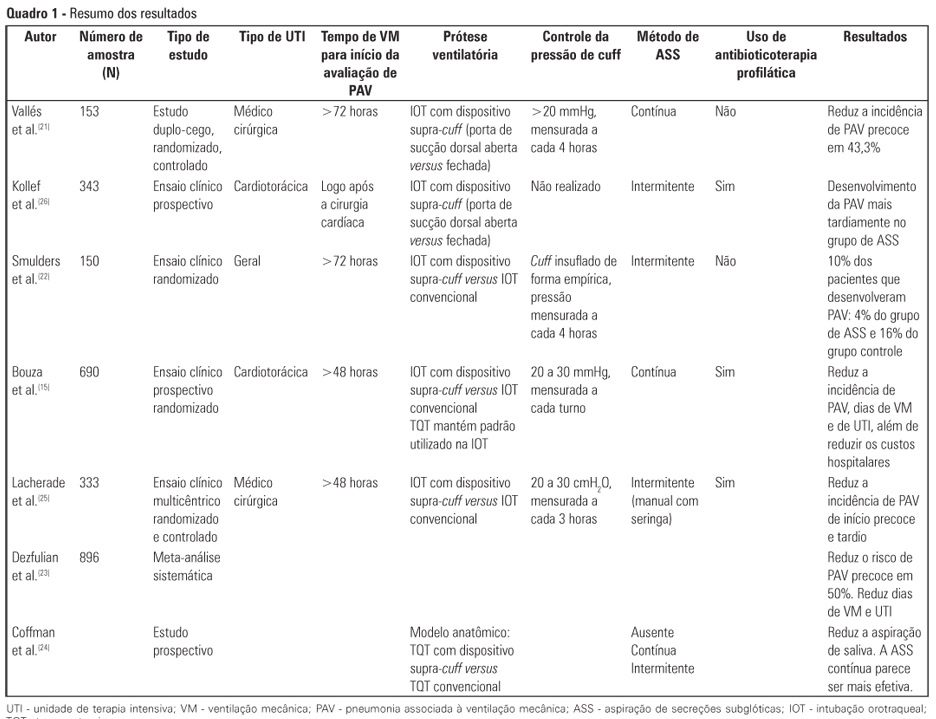
Critically ill patients are intubated or tracheostomized because, in most cases, these individuals require invasive mechanical ventilation. The cannulae that are used include the cuff, which can act as a reservoir for oropharyngeal secretions, predisposing to ventilator-associated pneumonia. Studies have revealed that the suction of subglottic secretions through the dorsal suction lumen above the endotracheal tube cuff delays the onset and reduces the incidence of ventilator-associated pneumonia. The aim of this review is to assess published studies regarding the significance of using suction with a supra-cuff device for the prevention of ventilator-associated pneumonia in critically ill patients treated with orotracheal intubation or tracheostomy. Therefore, by searching national and international databases, a literature review was undertaken of studies published between the years 1986 and 2011. Few results were found relating the suction of subglottic secretions to decreased duration of mechanical ventilation and length of stay in the intensive care unit. The suction of subglottic secretions is ineffective in decreasing mortality but is effective in reducing the incidence of early-onset ventilator-associated pneumonia and hospital costs. Techniques involving continuous suction of subglottic secretions may be particularly efficient in removing secretions; however, intermittent suction appears to be the least harmful method. In conclusion, cannulae with a supra-cuff suction device enable the aspiration of subglottic secretions, providing benefits to critically ill patients by reducing the incidence of ventilator-associated pneumonia and, consequently, hospital costs - with no large-scale adverse effects.