Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2011;23(3):291-296
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2011000300006
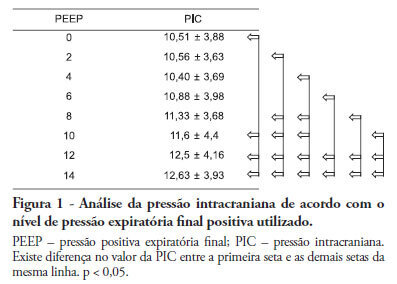
Positive intrathoracic pressure may cause hemodynamic changes, which can be transmitted to the cranial compartment, changing intracranial pressure and cerebral perfusion pressure. This can be increased when high positive end-expiratory pressure values are used. OBJECTIVE: To measure the impact of different positive end-expiratory pressure levels on intracranial pressure, cerebral perfusion pressure and mean blood pressure. METHOD: This study was conducted in a neurological intensive care unit and included 25 adult hemorrhagic stroke patients who were mechanically ventilated on airway pressure control mode. Patients were subjected to various positive end-expiratory values ranging between 0 and 14 cmH2O. The order of these values were randomized, and the variables were assessed five minutes after each new positive end-expiratory pressure level was initiated. RESULTS: Incremental positive end-expiratory pressures led to increased intracranial pressure (p < 0.001), however, no statistically significant changes were observed in mean blood pressure or cerebral perfusion pressure. CONCLUSION: In this population of patients with hemorrhagic stroke, positive end-expiratory pressure values up to 14 cmH2O did not alter cerebral perfusion pressure or mean blood pressure. Increased intracranial pressures were noted, although these elevations were not clinically significant