Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2008;20(2):124-127
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2008000200002
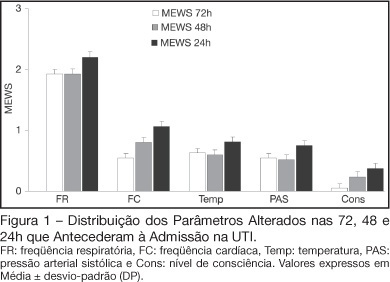
BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: Prognosis of patients in the intensive care unit (ICU) has a relation with their severity just before admission. The Modified Early Warning Score (MEWS) was used to evaluate the severe condition of patients 12, 24 and 72 hours before admission in the ICU, assess the most prevalent parameters and correlate the MEWS before ICU with the outcome (survival versus death). METHODS: Retrospective analyses of 65 patients consecutively admitted to the ICU from July to October, 2006 evaluating the physiological parameters 72 hours prior to admission. RESULTS: APACHE II mean was 22.2 ± 7.9 points, mortality was 54.6% and standardized mortality ratio means was 1.24. MEWS means were 3.7 ± 0.2; 4.0 ± 0.2 and 5.1 ± 0.2 points, calculated 72, 48 and 24 hours previous to ICU admission, respectively. An increasing percentage of patients with MEWS > 3 points within 72, 48 and 24 hours before admission - 43.8%, 59.4% and 73.4%, respectively was recorded. Among the included physiological parameters respiratory rate contributed the most to the MEWS. Highest mortality was found in patients with MEWS > 3 points already found 72 hours before admission. Patients who died presented with a significant increase in the MEWS 24 hours prior to admission to the ICU (in relation to the MEWS recorded 72 hours before) but the situation was not identified in survivors. CONCLUSIONS: MEWS closely identified the severity of patients admitted to the ICU, suggesting that it can be a reliable score, useful in the situations preceding the ICU.