Home
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2006;18(4):380-384
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2006000400010
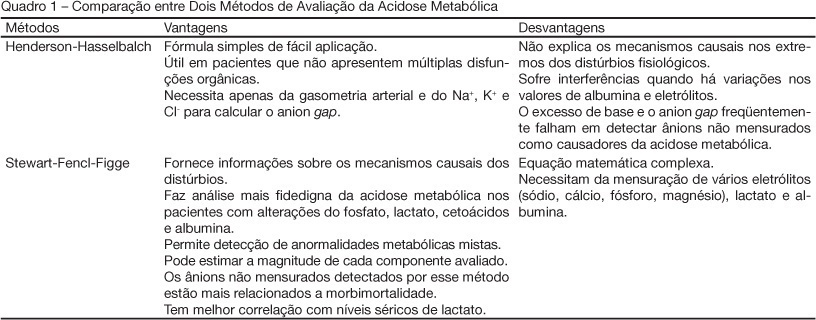
BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: To review strategies of assessment of metabolic acidosis giving emphasis to the of Stewart-Fencl-Figge method versus the traditional method of Henderson-Hasselbalch. CONTENTS: Metabolic acidosis is a common issue in critically ill patients, an important cause of myocardial contractility depression and sensible marker of impaired tissue oxygenation. Traditionally, is evaluated by the Henderson-Hasselbalch approach in which an arterial blood sample provides information about the presence and type of acid base disturbance. However, this method is not always capable to explain the causes of the metabolic acidosis and, therefore, several studies have explored mechanisms to improve its interpretation. The Stewart-Fencl-Figge method calculated through a mathematical formula, where in addition to arterial blood gas levels, serum levels of electrolytes, lactate and albumin are used, supplies trustworthy information allowing detection of mixed metabolic abnormalities and quantification of the magnitude of each component, mainly in patients with multiple organic dysfunctions. In these individuals, the presence of unmeasured anions in the plasma is an important mechanism of metabolic acidosis and its early detection fundamental to avoid deleterious effect on the organism. CONCLUSIONS: The traditional Henderson-Hasselbalch approach fails in analyzing the underlying mechanisms of metabolic acidosis and possesses many variables that intervene with its result especially in the critically ill patient. The Stewart-Fencl-Figge method offers a broader analysis of metabolic acidosis, indicating its mechanisms and guiding a better therapeutically strategy. As an alternative, the albumin-corrected and lactate-corrected anion gap seems to be as useful as the Stewart approach in identifying the unmeasured anions.


Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2006;18(4):380-384
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2006000400010
BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: To review strategies of assessment of metabolic acidosis giving emphasis to the of Stewart-Fencl-Figge method versus the traditional method of Henderson-Hasselbalch. CONTENTS: Metabolic acidosis is a common issue in critically ill patients, an important cause of myocardial contractility depression and sensible marker of impaired tissue oxygenation. Traditionally, is evaluated by the Henderson-Hasselbalch approach in which an arterial blood sample provides information about the presence and type of acid base disturbance. However, this method is not always capable to explain the causes of the metabolic acidosis and, therefore, several studies have explored mechanisms to improve its interpretation. The Stewart-Fencl-Figge method calculated through a mathematical formula, where in addition to arterial blood gas levels, serum levels of electrolytes, lactate and albumin are used, supplies trustworthy information allowing detection of mixed metabolic abnormalities and quantification of the magnitude of each component, mainly in patients with multiple organic dysfunctions. In these individuals, the presence of unmeasured anions in the plasma is an important mechanism of metabolic acidosis and its early detection fundamental to avoid deleterious effect on the organism. CONCLUSIONS: The traditional Henderson-Hasselbalch approach fails in analyzing the underlying mechanisms of metabolic acidosis and possesses many variables that intervene with its result especially in the critically ill patient. The Stewart-Fencl-Figge method offers a broader analysis of metabolic acidosis, indicating its mechanisms and guiding a better therapeutically strategy. As an alternative, the albumin-corrected and lactate-corrected anion gap seems to be as useful as the Stewart approach in identifying the unmeasured anions.


Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2007;19(4):437-443
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2007000400006
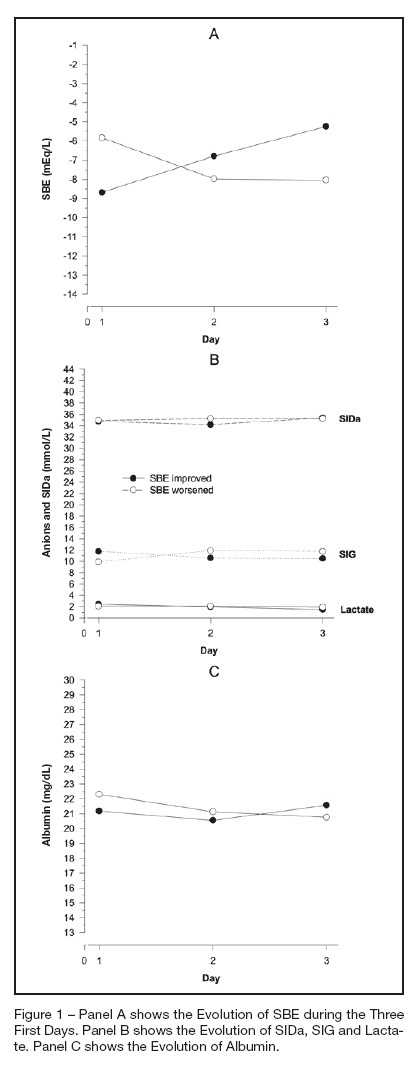
BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: The amount of metabolic acidosis measured through the standard base excess (SBE) has been shown to be an outcome marker and its improvement has been associated with better survival. We studied the mechanism of standard base excess variation in the first three days of intensive care unit (ICU) stay through the evaluation of independent variables of physico-chemical approach. METHODS: Data were retrieved from our prospective collected data base from patients with diagnosis of septic shock, daily up to the third day after the ICU admission. Single correlations between SBE and independent variables were performed as well as a mathematical multilinear model was built to disclose the SBE variation determinants. RESULTS: We have shown that in septic shock patients the standard base excess variation during the first three days of ICU stay is weakly correlated to strong ion gap (SIG), lactate, creatinin and PaCO2 when individually analyzed. Analyzing concomitantly those independent variables, we built a mathematical model with a stepwise multilinear regression composed by apparent strong ion difference (SIDa), SIG, PaCO2, albumin and diuresis that resulted in a R² coefficient of 0.866 to determine SBE variation. CONCLUSIONS: Variations of metabolic acidosis measured through the standard base excess in septic shock patients when analyzed until the third day after intensive care unit admission, is resultant of interaction of several independent determinants as PaCO2, diuresis, SIG, SIDa and albumin.


Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2007;19(4):437-443
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2007000400006
BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: The amount of metabolic acidosis measured through the standard base excess (SBE) has been shown to be an outcome marker and its improvement has been associated with better survival. We studied the mechanism of standard base excess variation in the first three days of intensive care unit (ICU) stay through the evaluation of independent variables of physico-chemical approach. METHODS: Data were retrieved from our prospective collected data base from patients with diagnosis of septic shock, daily up to the third day after the ICU admission. Single correlations between SBE and independent variables were performed as well as a mathematical multilinear model was built to disclose the SBE variation determinants. RESULTS: We have shown that in septic shock patients the standard base excess variation during the first three days of ICU stay is weakly correlated to strong ion gap (SIG), lactate, creatinin and PaCO2 when individually analyzed. Analyzing concomitantly those independent variables, we built a mathematical model with a stepwise multilinear regression composed by apparent strong ion difference (SIDa), SIG, PaCO2, albumin and diuresis that resulted in a R² coefficient of 0.866 to determine SBE variation. CONCLUSIONS: Variations of metabolic acidosis measured through the standard base excess in septic shock patients when analyzed until the third day after intensive care unit admission, is resultant of interaction of several independent determinants as PaCO2, diuresis, SIG, SIDa and albumin.


Search
Search in:
Case reports Child Coronavirus infections COVID-19 Critical care Critical illness Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation Infant, newborn Intensive care Intensive care units Intensive care units, pediatric mechanical ventilation Mortality Physical therapy modalities Prognosis Respiration, artificial Respiratory insufficiency risk factors SARS-CoV-2 Sepsis


