Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2006;18(2):177-185
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2006000200011
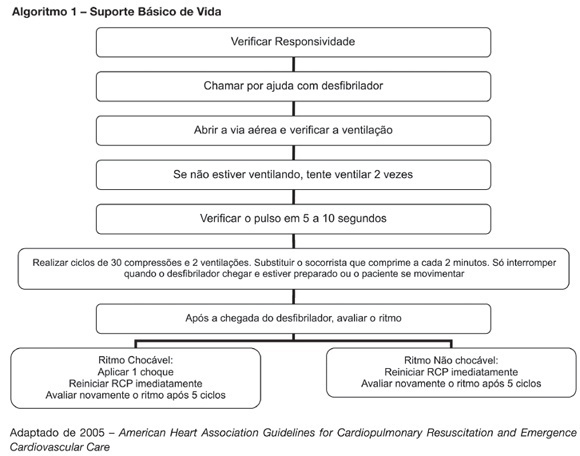
BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: New resuscitation guidelines contain significant changes intended to improve resuscitation practice and survival from cardiac arrest. This article provides an overview of the key changes on resuscitation for healthcare provider. CONTENTS: There are several new recommendations on cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR), the major are intended to provide good circulation during cardiac arrest. The most important change is the emphasis on high-quality chest compressions with minimal interruptions. The universal 30:2 ratio is recommended to simplify training, to achieve optimal compression rates and to reduce the frequency of interruptions. Only one shock is delivered when indicated, followed immediately by CPR. This shock should be of 120-200J on a biphasic wave or 360J on a monophasic wave. Rescuers should not interrupt chest compressions to check rhythm until after about 5 cycles or approximately 2 minutes of CPR. After this period, if an organized rhythm is present, the healthcare provider should check for a pulse. There are several little changes about the drugs administrated during CPR according to the rhythm. Given the lack of documented effect of drug therapy in improving long-term outcome from cardiac arrest, the sequence for CPR deemphasizes drug administration and reemphasizes basic life support. CONCLUSIONS: The update on the new resuscitation guidelines is important to improve the quality of resuscitation and achieve better survival rates from our critical care patients.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2006;18(4):374-379
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2006000400009
BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: New resuscitation guidelines contain significant changes intended to improve resuscitation practice and survival from cardiac arrest. The objective of this study was to evaluate the theoretical knowledge about cardiac arrest (CA) and cardiac and pulmonary resuscitation (CPR) among doctors after five years of the graduation. METHODS: The questionnaire survey was conducted in an Emergency Hospital in the State of Alagoas. The population was composed of doctors with five years after your graduation. The data was collected with a questionnaire with questions about the theme. The results were analyzed based on bibliographies about CA and CPR. RESULTS: Thirty-nine professionals answered the questionnaire. The CA diagnostic was correct in 76.9% and increased to 82.7 when the case report was included. Questions about sodium bicarbonate and vasopressin were correctly answered by 30.8% and 15.4% of the participants. CONCLUSIONS: The greatest difficulty reported in this study was on the CA arrest Most of the participants of the survey are not aware of the correct indications of vasopressin and sodium bicarbonate in the CPR. According to this study, a continuing medical education program on CPR for physicians with more than five years of graduations warranted.