You searched for:"Fabrício Edler Macagnan"
We found (2) results for your search.-
Review Article
Safety and potential benefits of physical therapy in adult patients on extracorporeal membrane oxygenation support: a systematic review
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2019;31(2):227-239
Abstract
Review ArticleSafety and potential benefits of physical therapy in adult patients on extracorporeal membrane oxygenation support: a systematic review
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2019;31(2):227-239
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20190017
Views0Abstract
Scientific and technological advances, coupled with the work of multidisciplinary teams in intensive care units, have increased the survival of critically ill patients. An essential life support resource used in intensive care is extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. Despite the increased number of studies involving critically ill patients, few studies to date have demonstrated the safety and benefits of physical therapy combined with extracorporeal membrane oxygenation support. This review identified the clinical outcomes of physical therapy in adult patients on extracorporeal membrane oxygenation support by searching the MEDLINE®, PEDro, Cochrane CENTRAL, LILACS, and EMBASE databases and by manually searching the references of the articles published until September 2017. The database search retrieved 1,213 studies. Of these studies, 20 were included in this review, with data on 317 subjects (58 in the control group). Twelve studies reported that there were no complications during physical therapy. Cannula fracture during ambulation (one case), thrombus in the return cannula (one case), and leg swelling (one case) were reported in two studies, and desaturation and mild vertigo were reported in two studies. In contrast, improvements in respiratory/pulmonary function, functional capacity, muscle strength (with reduced muscle mass loss), incidence of myopathy, length of hospitalization, and mortality in patients who underwent physical therapy were reported. The analysis of the available data indicates that physical therapy, including early progressive mobilization, standing, ambulation, and breathing techniques, together with extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, is feasible, relatively safe, and potentially beneficial for critically ill adult patients.
Keywords:Early ambulationExtracorporeal membrane oxygenationPhysical therapy modalitiesPhysical therapy specialtyRehabilitationSee more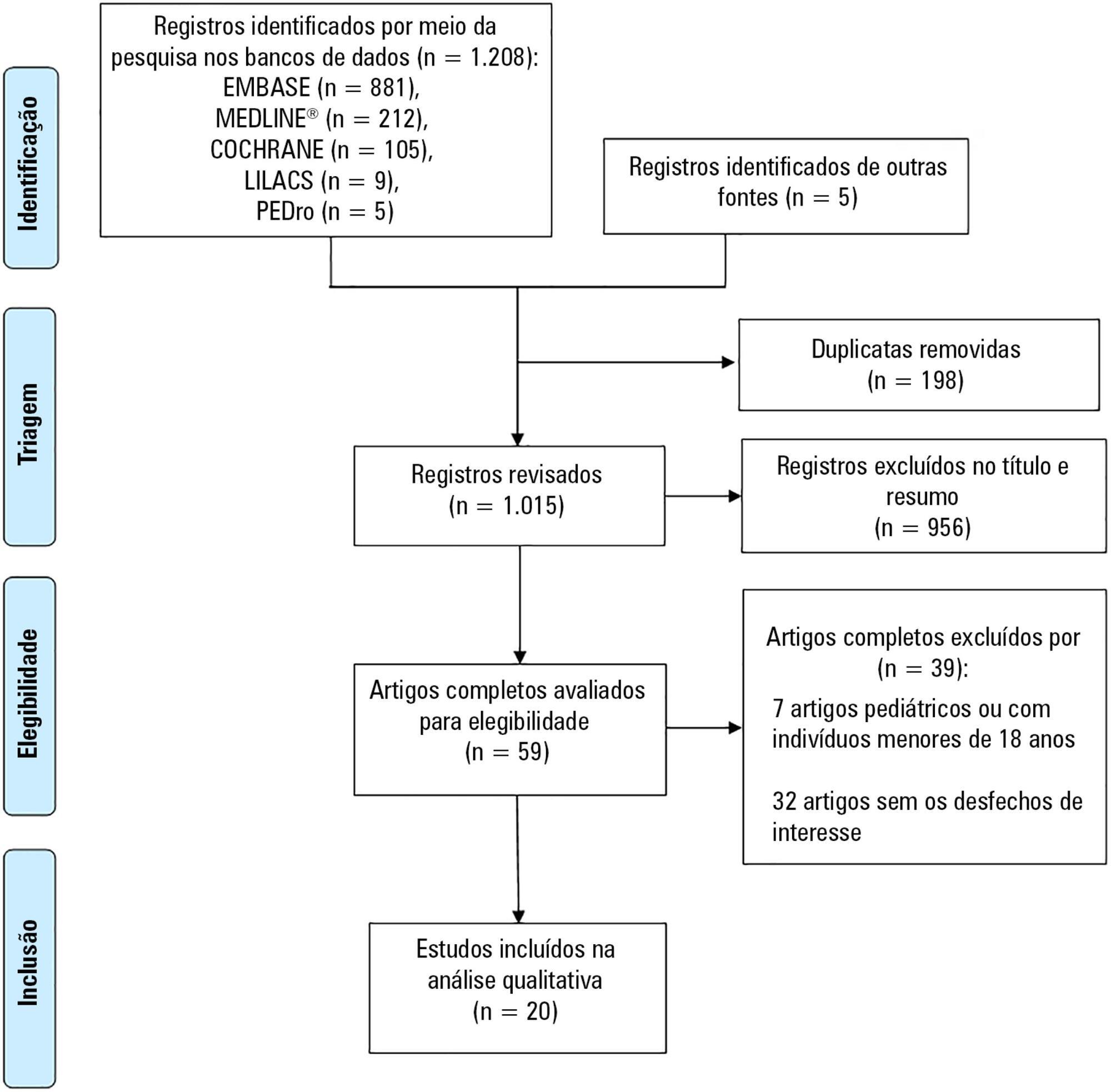
-
Review Articles
Expiratory rib cage compression in mechanically ventilated adults: systematic review with meta-analysis
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2017;29(1):96-104
Abstract
Review ArticlesExpiratory rib cage compression in mechanically ventilated adults: systematic review with meta-analysis
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2017;29(1):96-104
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20170014
Views0See moreABSTRACT
Objective:
To review the literature on the effects of expiratory rib cage compression on ventilatory mechanics, airway clearance, and oxygen and hemodynamic indices in mechanically ventilated adults.
Methods:
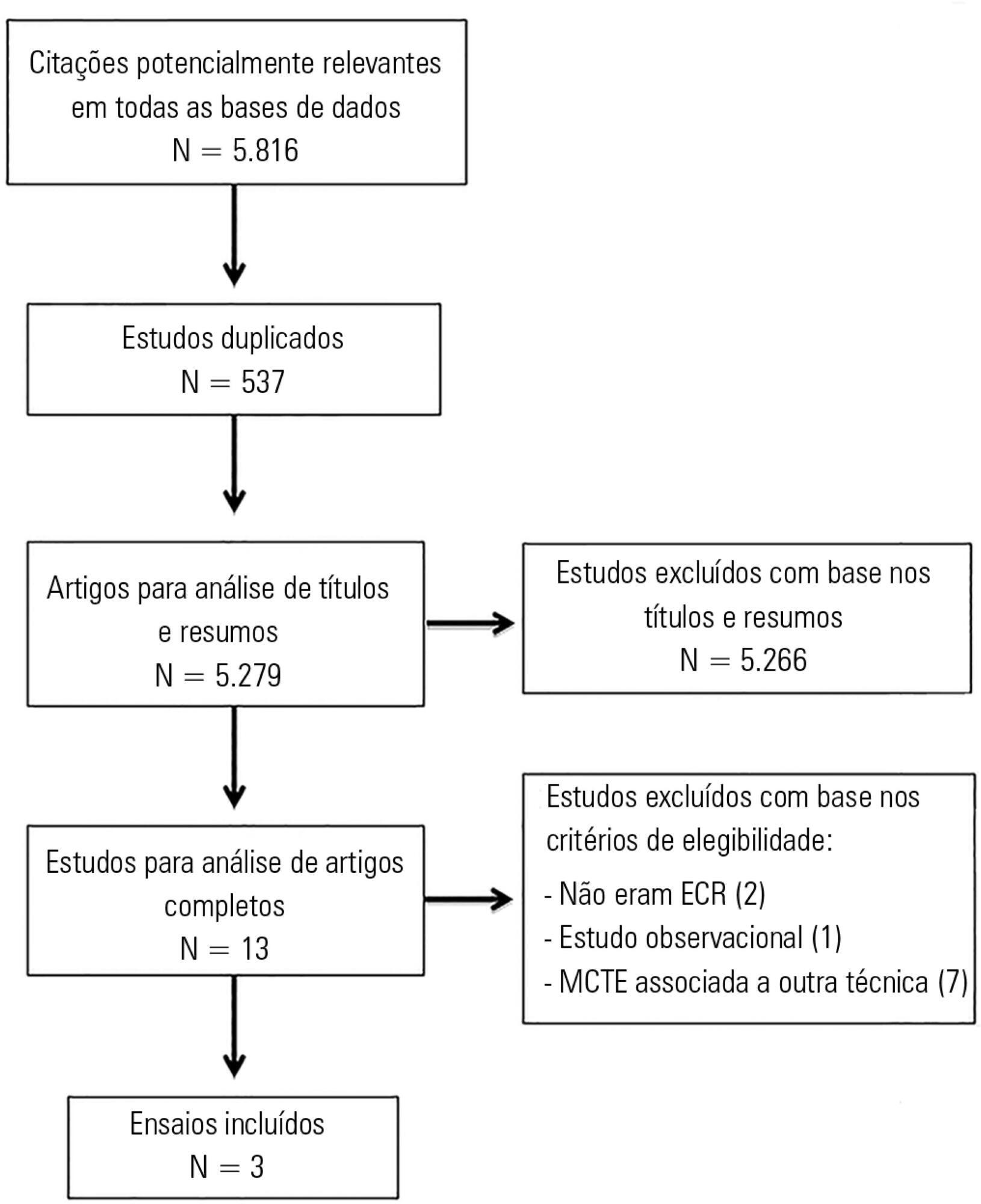
Systematic review with meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials in the databases MEDLINE (via PubMed), EMBASE, Cochrane CENTRAL, PEDro, and LILACS. Studies on adult patients hospitalized in intensive care units and under mechanical ventilation that analyzed the effects of expiratory rib cage compression with respect to a control group (without expiratory rib cage compression) and evaluated the outcomes static and dynamic compliance, sputum volume, systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, mean arterial pressure, heart rate, peripheral oxygen saturation, and ratio of arterial oxygen partial pressure to fraction of inspired oxygen were included. Experimental studies with animals and those with incomplete data were excluded.
Results:
The search strategy produced 5,816 studies, of which only three randomized crossover trials were included, totaling 93 patients. With respect to the outcome of heart rate, values were reduced in the expiratory rib cage compression group compared with the control group [-2.81 bpm (95% confidence interval [95%CI]: -4.73 to 0.89; I2: 0%)]. Regarding dynamic compliance, there was no significant difference between groups [-0.58mL/cmH2O (95%CI: -2.98 to 1.82; I2: 1%)]. Regarding the variables systolic blood pressure and diastolic blood pressure, significant differences were found after descriptive evaluation. However, there was no difference between groups regarding the variables secretion volume, static compliance, ratio of arterial oxygen partial pressure to fraction of inspired oxygen, and peripheral oxygen saturation.
Conclusion:
There is a lack of evidence to support the use of expiratory rib cage compression in routine care, given that the literature on this topic offers low methodological quality and is inconclusive.
Search
Search in:
KEY WORDS
Case reports Child Coronavirus infections COVID-19 Critical care Critical illness Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation Infant, newborn Intensive care Intensive care units Intensive care units, pediatric mechanical ventilation Mortality Physical therapy modalities Prognosis Respiration, artificial Respiratory insufficiency risk factors SARS-CoV-2 Sepsis




