Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2020;32(1):108-114
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20200016
To examine the effectiveness of stratification to identify and target antioxidant therapy for animal models of lethal sepsis and in patients who develop sustained hypotension.
Rats were subjected to sepsis induced by cecal ligation and puncture. Animals were divided into two groups: those with high and low plasma levels of interleukin-6. Following stratification, N-acetylcysteine plus deferoxamine or saline was administered to animals starting 3 and 12 hours after surgery. N-Acetylcysteine plus deferoxamine or placebo was administered within 12 hours of meeting the inclusion criteria in hypotensive patients.
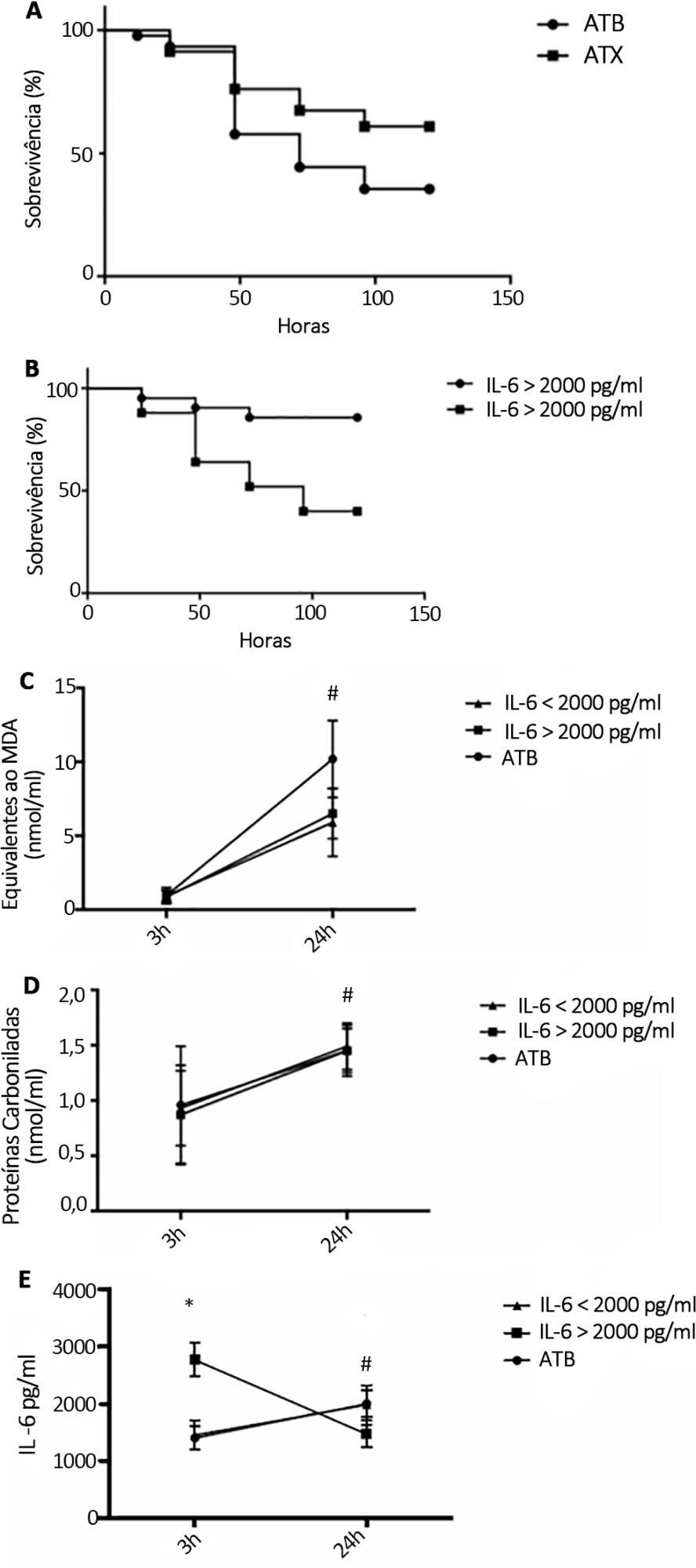
N-Acetylcysteine plus deferoxamine increased survival in the cecal ligation and puncture model when administered 3 and 12 hours after sepsis induction. When dividing animals that received antioxidants using plasma interleukin-6 levels, the protective effect was observed only in those animals with high IL-6 levels. The antioxidant effect of N-acetylcysteine + deferoxamine was similar in the two groups, but a significant decrease in plasma interleukin-6 levels was observed in the high-interleukin-6-level group. Compared with patients treated with antioxidants in the low-interleukin-6 subgroup, those in the high-interleukin-6 subgroup had a lower incidence of acute kidney injury but were not different in terms of acute kidney injury severity or intensive care unit mortality.
Targeting antioxidant therapy to a high inflammatory phenotype would select a responsive population.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2012;24(3):219-223
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2012000300003
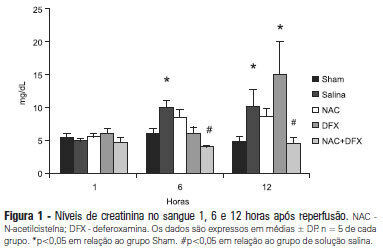
OBJECTIVE: Antioxidants are widely used in animal models to prevent renal injury after ischemia/reperfusion, but it is unknown if the benefits of antioxidants are additive. In this study, we aimed to investigate the protective effects of N-acetylcysteine plus deferoxamine in an animal model of kidney ischemia/reperfusion injury. METHODS: Bilateral kidney ischemia was mastintained for 45 minutes. N-acetylcysteine, deferoxamine or both were administered into the aorta above the renal arteries immediately prior to induction of ischemia. Five rats from each group were sacrificed 1, 6 or 12 hours after reperfusion for the determination of blood creatinine, kidney oxidative damage parameters and myeloperoxidase activity. RESULTS: The combination of N-acetylcysteine and deferoxamine, but not their isolated use, prevented the increase in creatinine after ischemia/reperfusion. This prevention was followed by a consistent decrease in myeloperoxidase activity and oxidative damage parameters both in the kidney cortex and medulla. CONCLUSION: Treatment with N-acetylcysteine and deferoxamine was superior to the isolated use of either compound in an animal model of kidney ischemia/reperfusion.