Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2010;22(4):358-362
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2010000400008
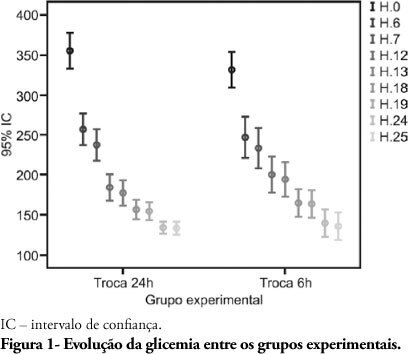
BACKGROUND: Hyperglycemia is frequent in the critically ill patient, and is a risk factor for unfavorable clinical outcomes, including mortality. During the recent years, intensive blood glucose control using intravenous insulin infusion has gained a prominent role in the critically ill patient management. There is important concern on insulin solution continued efficacy over the time, as little the literature available on this subject is poor. Lack of evidence is known to lead to inappropriate practices. This study aimed to compare the blood glucose levels between two different protocols in an intensive care unit in Porto Alegre, using the same solution concentration and two different replacement times during the first 24 hours, and additionally to assess the protocol-related hypoglycemia rate. METHODS: The medical charts of 80 patients under insulin therapy for over 24 hours during 2008 were revised; 40 patients had their insulin solution replaced every 6 hours and for 40 patients the insulin solution was replaced after 24 hours. RESULTS: The causes for admission to the intensive care unit included more frequently hypertensive (68.8%) and diabetic (45%) patients. No significant capillary blood glucose differences were seen for the every 6 or 24 hours solution replacement groups. Only 3 mild hypoglycemia cases were observed in the every 6 hours replacement group, and no hypoglycemia was seen in the 24 hours replacement group. CONCLUSION: We concluded that keeping insulin infusion, replacing the solution every 24 hours is feasible. However, longer infusion time studies are required to check for possible hypoglycemic events as insulin therapy advances.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2006;18(3):298-306
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2006000300013
BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: Nutritional state of patients affects them in their clinical evolution. Protein-caloric malnutrition contributes to the increase of morbidity and mortality in critical care. Regardless all the parameters available to assessment, there is no standard in hospital centers. In this review, we were looking for a method to nutrition assessment (NA) in critical patient that allow more adequate assessment and contribute to improvement in critical care. CONTENTS: In order to compare methods in NA in critical patient, search was performed in scientific papers aboutthis area. The keywords usedwere nutritional assessment, critical patient, critical care, hospital undernourishment and anthropometry. CONCLUSIONS: There are restrictions to different anthropometric parameters for NA when referring to critical patients. There is no consensus within authors about the best method for these patients and they no advise to choose only one parameter. We suggest for practice clinical in NA, one tool that include objective and subjective aspects in critical patients and identify those that are either undernourishments or in nutritional risks (Appendix 1).