Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2006;18(3):256-262
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2006000300007
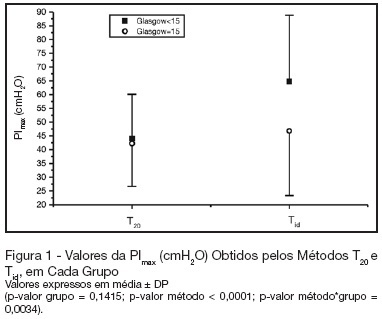
BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: There is no literature consensus about the time of airway occlusion sufficient enough to get a true PImax during weaning from mechanical ventilation (MV). So, the main objectives of the present study were to compare two methods PImax measurement and to evaluate the influence of patients' level of conscience on them. METHODS: The population was composed by 28 general ICU patients, with MV > 48h, in a weaning process, divided into two groups according to Glasgow coma scale score: with (GCS < 15) and without (GCS = 15) alterations of conscience level. The airway was occluded by using an unidirectional valve for 20s (PImaxT20), or for a maximum time of one minute if a plateau of inspiratory pressure was not observed during three consecutive inspirations (PImaxTid). RESULTS: PImaxT20 (mean ± SD, cmH2O) values were similar in both groups (44 ± 16 vs42 ± 15, p = 0.52). However, PImaxTid values, as long as the time needed to their attainment, were greater in GCS < 15 group (65 ± 24 vs 47 ± 23cmH2O and 37 ± 10 vs24 ± 8s, p = 0.04 and 0.0019, respectively). CONCLUSIONS: The method commonly used of 20s airway occlusion seems to be inadequate to get the true PImax in patients with alterations of the level of conscience. Additional studies, now in a more homogeneous group (e. g.: patients with structural brain lesion), are needed to clarify these findings.