Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2020;32(1):43-48
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20200008
To determine the independent risk factors associated with mortality in adult burn patients.
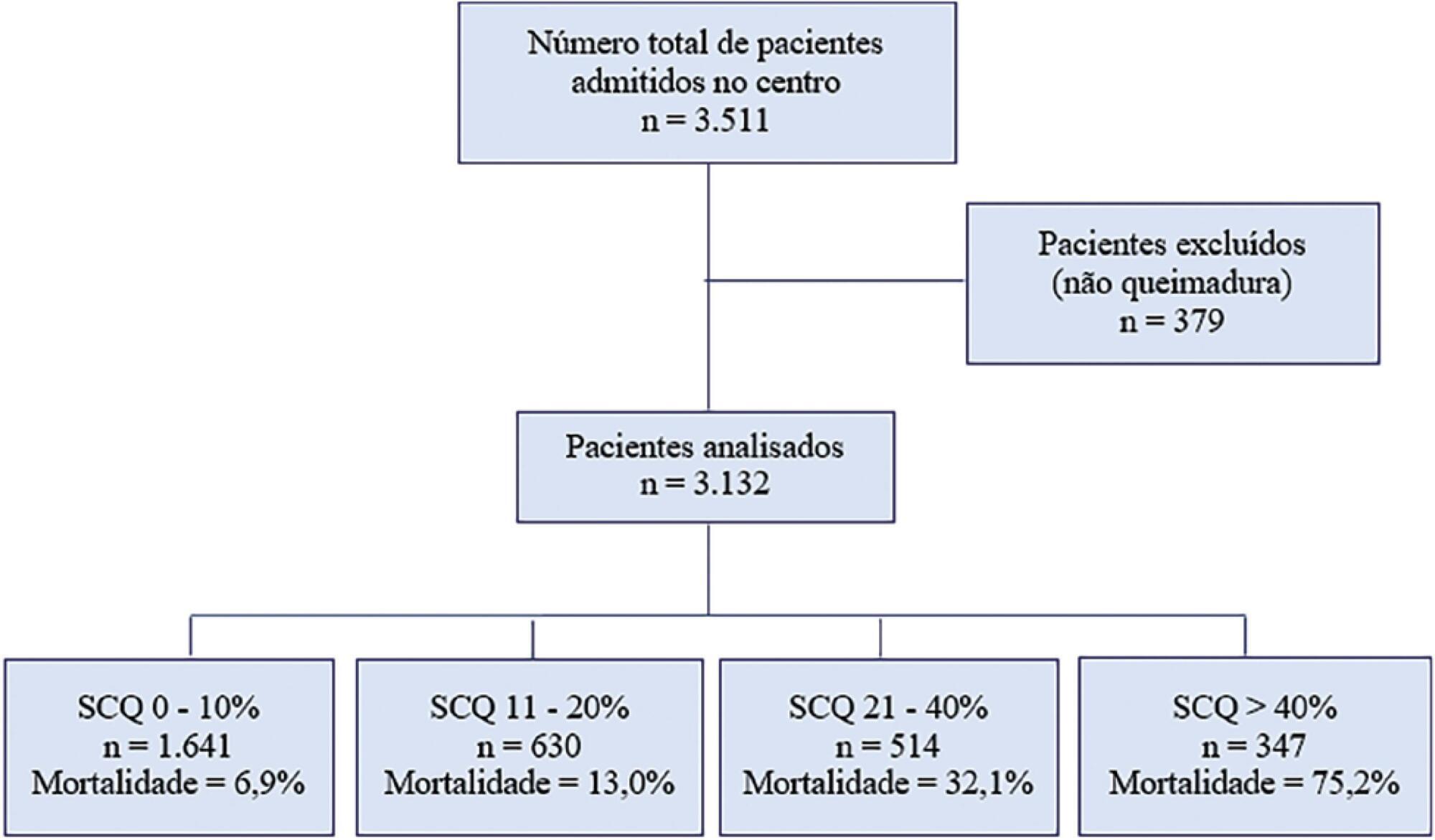
This was a retrospective, observational study performed at the Centro Nacional de Queimados do Uruguai. All patients with skin burns admitted to the unit since its opening on July 1, 1995 through December 31, 2018 were included. The demographic data, burn profiles, length of stay, mechanical ventilation duration and hospital mortality were studied. A multivariate logistic regression was used to identify the risk factors for mortality. The standardized mortality ratio was calculated by dividing the number of observed deaths by the number of expected deaths (according to the Abbreviated Burn Severity Index).
During the study period, 3,132 patients were included. The median total body surface area burned was 10% (3%-22%). The Abbreviated Burn Severity Index was 6 (4 - 7). Invasive mechanical ventilation was required in 60% of the patients for a median duration of 6 (3 - 16) days. The median length of stay in the unit was 17 (7 - 32) days. The global mortality was 19.9%. Crude mortality and standardized mortality ratio decreased from 1995 through 2018. The global standardized mortality ratio was 0.99. A need for mechanical ventilation (OR 8.80; 95%CI 5.68 - 13.62), older age (OR 1.07 per year; 95%CI 1.06 - 1.09), total body surface area burned (OR 1.05 per 1%; 95%CI 1.03 - 1.08) and extension of third-degree burns (OR 1.05 per 1%; 95%CI 1.03 - 1.07) were independent risk factors for mortality.
The need for mechanical ventilation, older age and burn extension were independent risk factors for mortality in the burned adult Uruguayan population.
Search
Search in:
Case reports (56) Child (53) Coronavirus infections (34) COVID-19 (46) Critical care (116) Critical illness (54) Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (26) Infant, newborn (27) Intensive care (72) Intensive care units (256) Intensive care units, pediatric (31) mechanical ventilation (38) Mortality (76) Physical therapy modalities (28) Prognosis (61) Respiration, artificial (119) Respiratory insufficiency (26) risk factors (34) SARS-CoV-2 (28) Sepsis (98)