You searched for:"Carolina Enrico"
We found (1) results for your search.-
Original Articles
Urinary strong ion difference is a major determinant of plasma chloride concentration changes in postoperative patients
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2013;25(3):197-204
Abstract
Original ArticlesUrinary strong ion difference is a major determinant of plasma chloride concentration changes in postoperative patients
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2013;25(3):197-204
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20130035
Views1See moreOBJECTIVE:
To show that alterations in the plasma chloride concentration ([Cl–]plasma) during the postoperative period are largely dependent on the urinary strong ion difference ([SID]urine=[Na+]urine+[K+]urine-[Cl-]urine) and not on differences in fluid therapy.
METHODS:
Measurements were performed at intensive care unit admission and 24 hours later in a total of 148 postoperative patients. Patients were assigned into one of three groups according to the change in [Cl–]plasma at the 24 hours time point: increased [Cl–]plasma (n=39), decreased [Cl–]plasma (n=56) or unchanged [Cl–]plasma (n=53).
RESULTS:
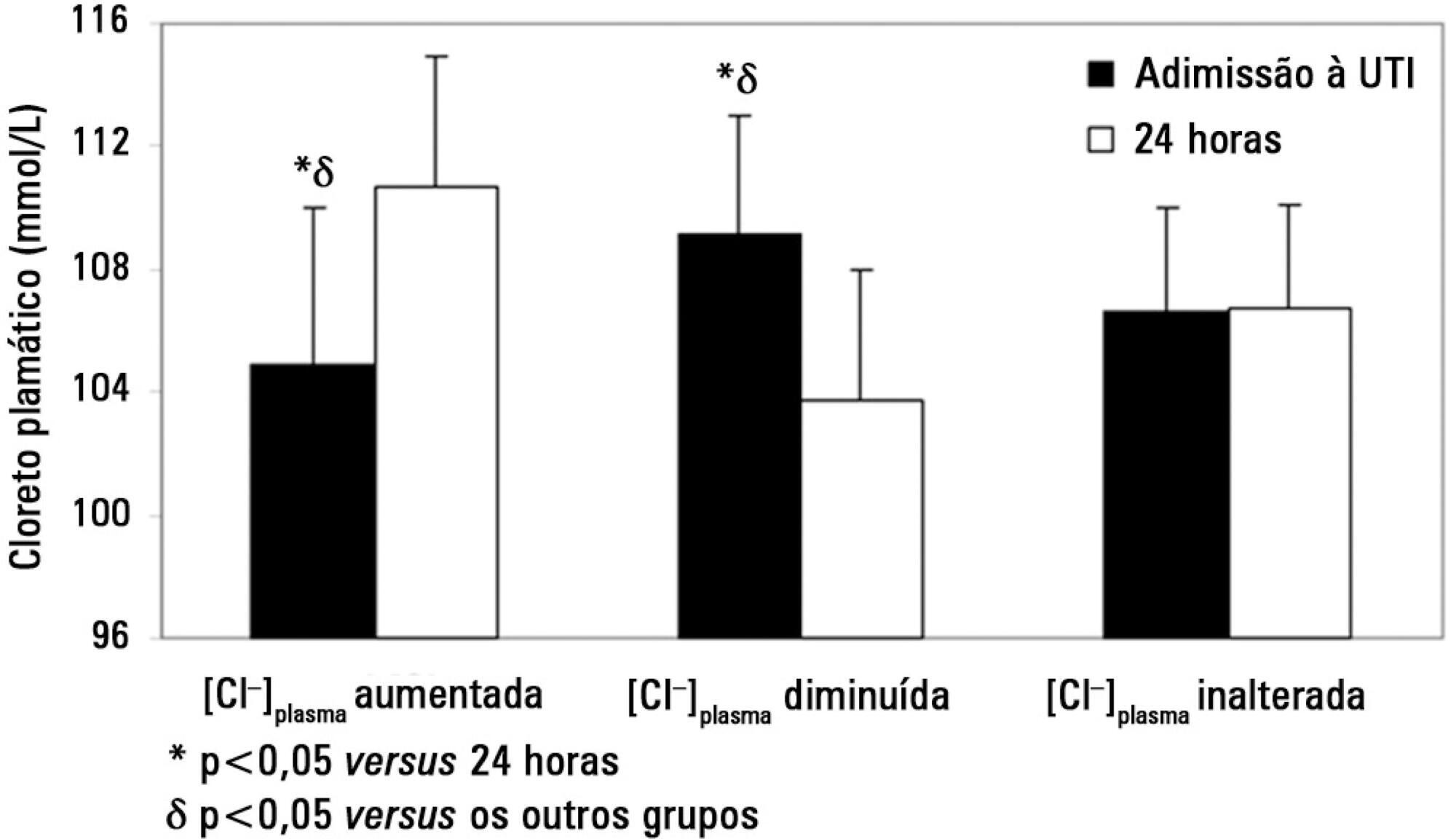
On admission, the increased [Cl–]plasma group had a lower [Cl–]plasma (105±5 versus 109±4 and 106±3mmol/L, p<0.05), a higher plasma anion gap concentration ([AG]plasma) and a higher strong ion gap concentration ([SIG]). After 24 hours, the increased [Cl–]plasma group showed a higher [Cl–]plasma (111±4 versus 104±4 and 107±3mmol/L, p<0.05) and lower [AG]plasma and [SIG]. The volume and [SID] of administered fluids were similar between groups except that the [SID]urine was higher (38±37 versus 18±22 and 23±18mmol/L, p<0.05) in the increased [Cl–]plasma group at the 24 hours time point. A multiple linear regression analysis showed that the [Cl–]plasma on admission and [SID]urine were independent predictors of the variation in [Cl–]plasma 24 hours later.
CONCLUSIONS:
Changes in [Cl–]plasma during the first postoperative day were largely related to [SID]urine and [Cl–]plasma on admission and not to the characteristics of the infused fluids. Therefore, decreasing [SID]urine could be a major mechanism for preventing the development of salineinduced hyperchloremia.
Views1

Abstract
Original ArticlesUrinary strong ion difference is a major determinant of plasma chloride concentration changes in postoperative patients
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2013;25(3):197-204
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20130035
Views1See moreOBJECTIVE:
To show that alterations in the plasma chloride concentration ([Cl–]plasma) during the postoperative period are largely dependent on the urinary strong ion difference ([SID]urine=[Na+]urine+[K+]urine-[Cl-]urine) and not on differences in fluid therapy.
METHODS:
Measurements were performed at intensive care unit admission and 24 hours later in a total of 148 postoperative patients. Patients were assigned into one of three groups according to the change in [Cl–]plasma at the 24 hours time point: increased [Cl–]plasma (n=39), decreased [Cl–]plasma (n=56) or unchanged [Cl–]plasma (n=53).
RESULTS:
On admission, the increased [Cl–]plasma group had a lower [Cl–]plasma (105±5 versus 109±4 and 106±3mmol/L, p<0.05), a higher plasma anion gap concentration ([AG]plasma) and a higher strong ion gap concentration ([SIG]). After 24 hours, the increased [Cl–]plasma group showed a higher [Cl–]plasma (111±4 versus 104±4 and 107±3mmol/L, p<0.05) and lower [AG]plasma and [SIG]. The volume and [SID] of administered fluids were similar between groups except that the [SID]urine was higher (38±37 versus 18±22 and 23±18mmol/L, p<0.05) in the increased [Cl–]plasma group at the 24 hours time point. A multiple linear regression analysis showed that the [Cl–]plasma on admission and [SID]urine were independent predictors of the variation in [Cl–]plasma 24 hours later.
CONCLUSIONS:
Changes in [Cl–]plasma during the first postoperative day were largely related to [SID]urine and [Cl–]plasma on admission and not to the characteristics of the infused fluids. Therefore, decreasing [SID]urine could be a major mechanism for preventing the development of salineinduced hyperchloremia.


Search
Search in:
KEY WORDS
Case reports Child Coronavirus infections COVID-19 Critical care Critical illness Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation Infant, newborn Intensive care Intensive care units Intensive care units, pediatric mechanical ventilation Mortality Physical therapy modalities Prognosis Respiration, artificial Respiratory insufficiency risk factors SARS-CoV-2 Sepsis


