Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2015;27(1):5-6
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20150002
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2015;27(1):1-4
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20150001
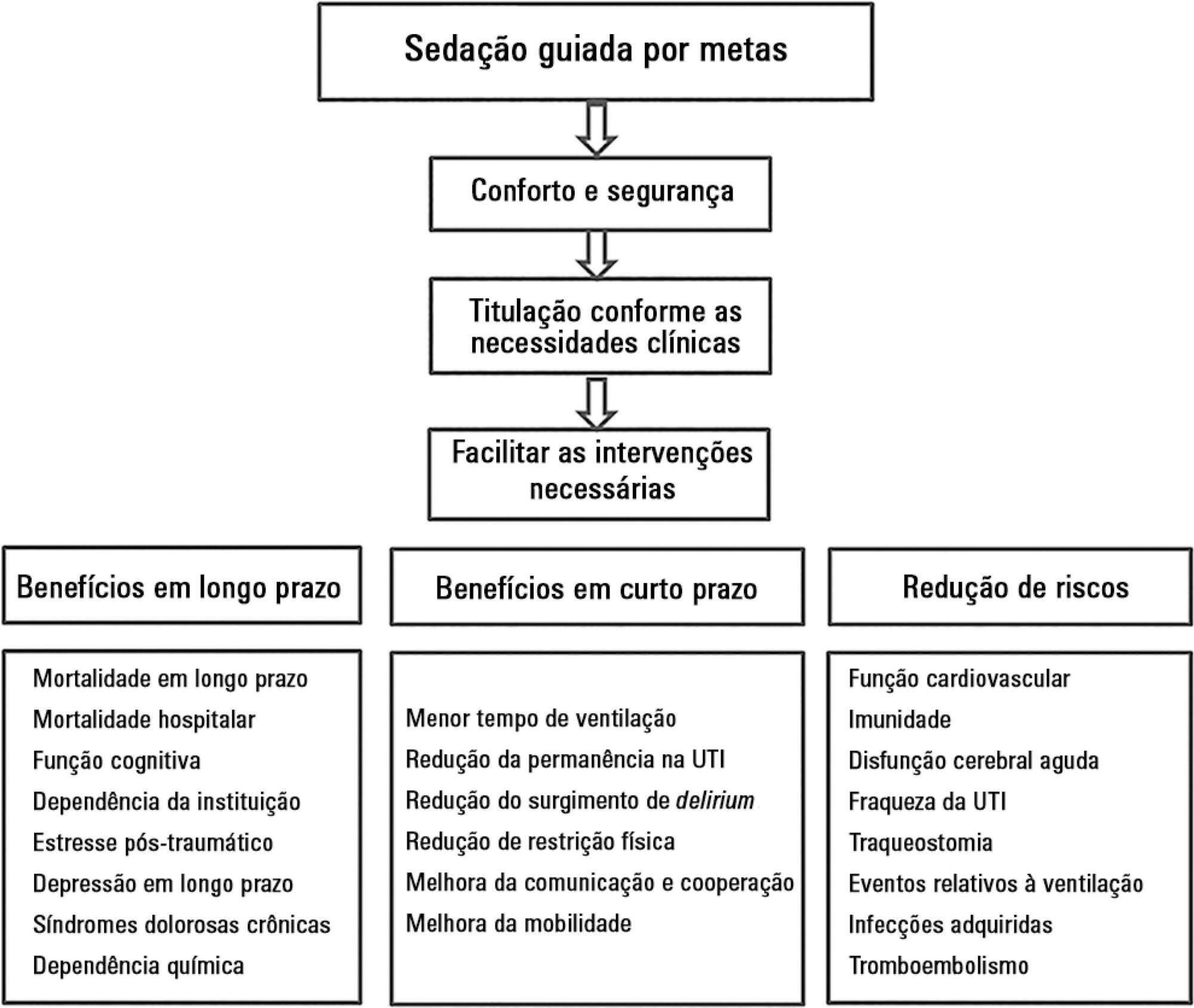
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2015;27(3):202-204
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20150041
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2015;27(2):102-104
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20150019
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2015;27(2):96-101
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20150018
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2015;27(2):92-95
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20150017
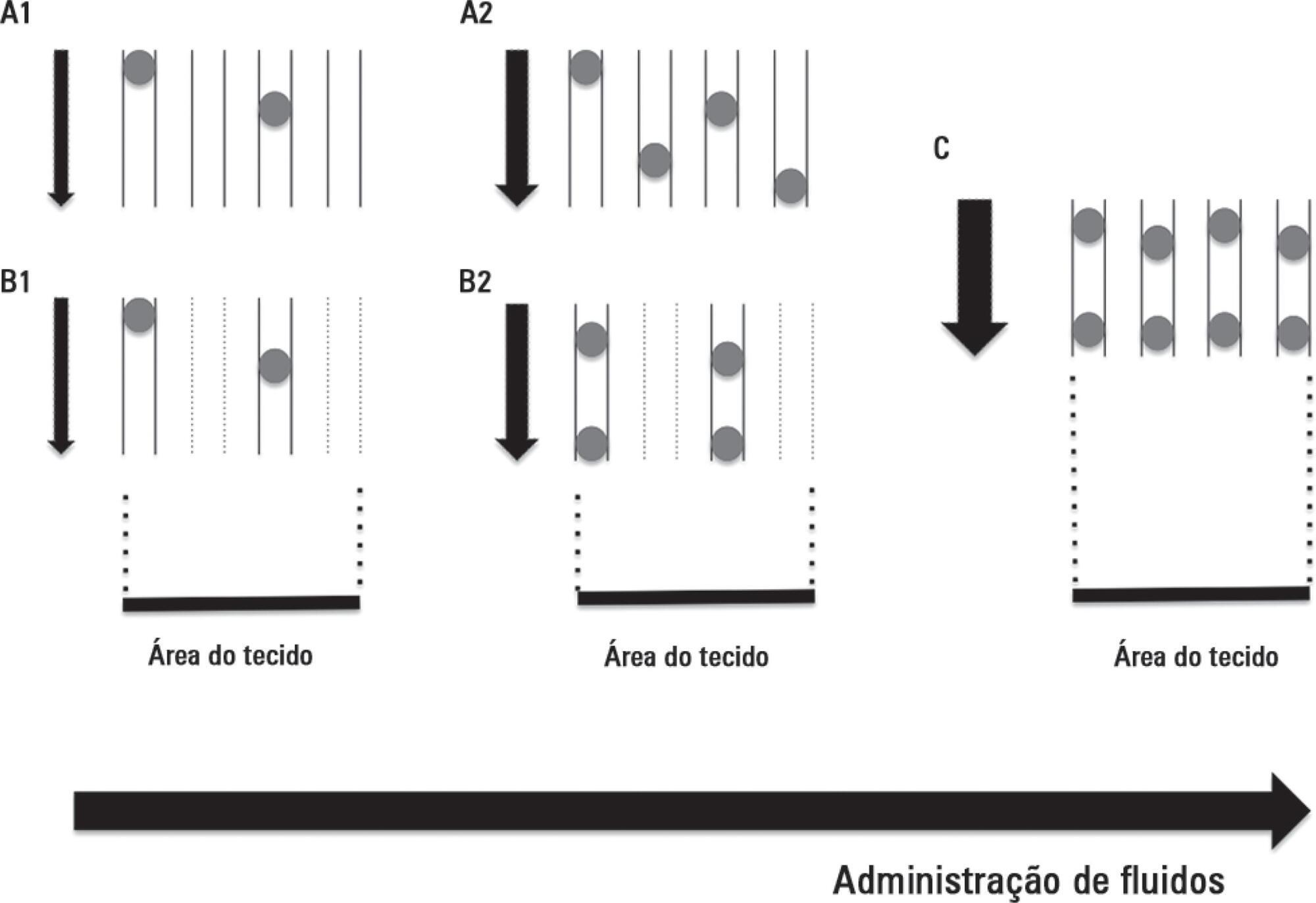
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2014;26(4):330-332
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20140049
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2014;26(4):335-338
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20140051