Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2014;26(2):137-142
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20140020
Early weaning from mechanical ventilation is one of the primary goals in managing critically ill patients. There are various techniques and measurement parameters for such weaning. The objective of this study was to describe the practices of ventilatory weaning in adult intensive care units in the city of Cali.
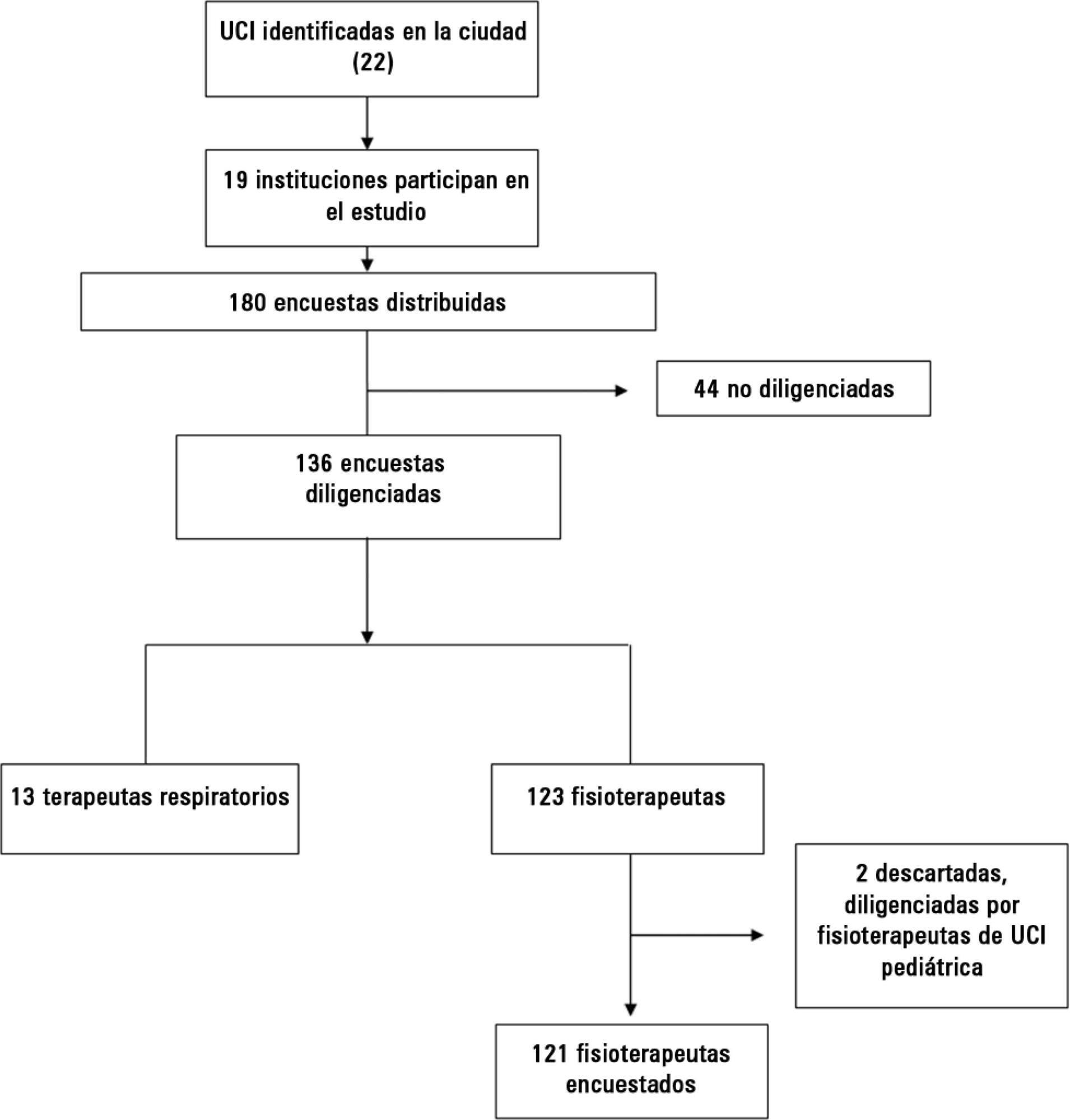
A survey of 32 questions (some multiple choice) evaluating weaning practices was distributed to physiotherapists and respiratory therapists working in intensive care units, to be answered anonymously.
The most common strategy for the parameter set was the combination of continuous positive airway pressure with pressure support (78%), with a large variability in pressure levels, the most common range being 6 to 8cmH2O. The most common weaning parameters were as follows: tidal volume (92.6%), respiratory rate (93.3%) and oxygen saturation (90.4%). The most common waiting time for registration of the parameters was >15 minutes (40%). The measurements were preferably obtained from the ventilator display.
The methods and measurement parameters of ventilatory weaning vary greatly. The most commonly used method was continuous positive airway pressure with more pressure support and the most commonly used weaning parameters were the measured tidal volume and respiratory rate.