Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2008;20(1):31-36
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2008000100005
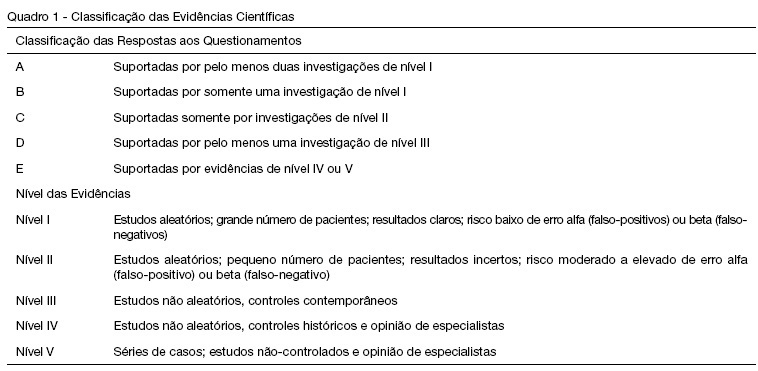
BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: Peritoneal dialysis (PD) is frequently used to replace glomerular filtration and to control acid-base, electrolyte and fluid disturbances in critically ill children with acute renal failure. However, cardiorespiratory changes can happen during this procedure. The objective of this review is to describe the PD cardio-respiratory repercutions in the pediatric patient and the evidence level of the studies that approach these repercutions. METHODS: Bibliographic revision about PD cardio-respiratory repercutions in the pediatric patient. Medline, Ovid e Lilacs databases were searched for articles from 1990 to 2007 with the following key words in Portuguese, English and Spanish: diálise peritoneal, efeitos hemodinâmicos, complicações respiratórias, complicações cardíacas, Pediatria; peritoneal dialysis, hemodynamic effects, respiratory complications, cardiac complications, Pediatric; peritoneal diálisis, efecto hemodinámico, complicaciones respiratorias, complicaciones cardiacas, Pediatria. The retrieved articles were classified according to Cook et al. 1992. RESULTS: Thirteen articles were retrieved, 8 of them were about cardiorespiratory repercussions and five approached respiratory repercussions of PD. These studies evaluated 178 critically ill patients, from newborns to adolescents. Among the respiratory repercutions during PD the most frequent ones were decrease of the pulmonary compliance and arterial oxygen partial pressure and increase of airway resistance and carbon dioxide partial pressure; after the infusion of PD fluid the studies pointed out an increased arterial oxygen partial pressure/ inspired oxygen fraction relation and diminution of the alveolar-arterial difference and oxygenation index. Increase of the mean arterial pressure, pulmonary artery pressure, right and left atrial pressure and systemic vascular resistance and, reduction of the central venous pressure were the described cardio-circulatory repercutions during PD. CONCLUSIONS: Pulmonary volumes, gas exchange and cardio-circulatory alterations are the most frequent complications during and after PD in the pediatric patient. Therefore critically ill pediatric patients with acute renal failure needing PD should be monitored during and after this procedure to avoid clinical deterioration and to educate the multi-professional team.